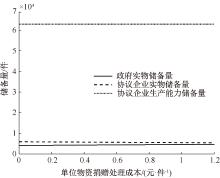
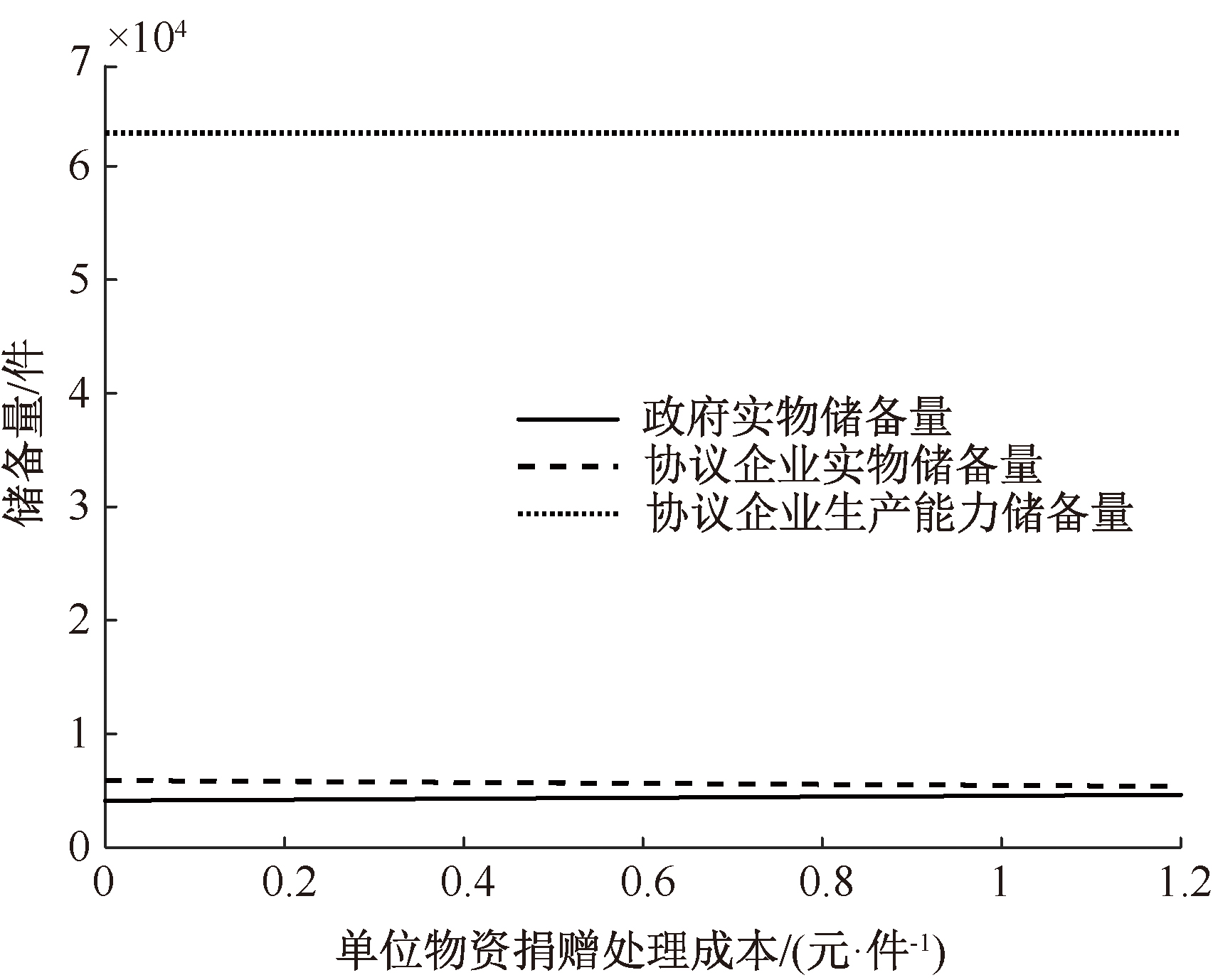
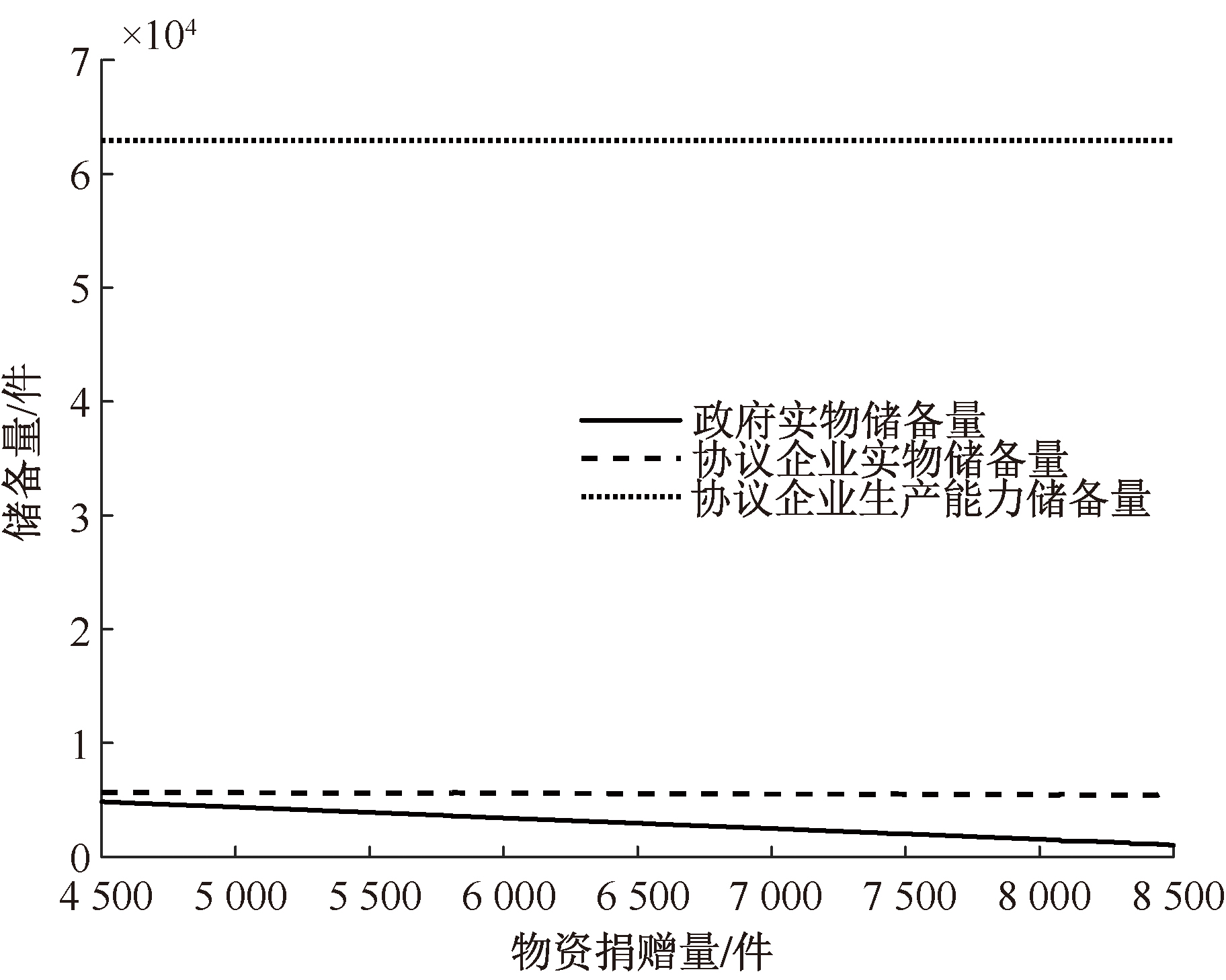
| [1] |
杨曼, 刘德海, 李德龙. 政企实物-生产能力应急物资储备与采购定价的微分博弈模型[J]. 管理评论, 2023, 35(9): 274-286.
|
|
YANG Man, LIU Dehai, LI Delong. A differential game model of government and enterprises material-production capacity emergency supplies reserve and procurement pricing[J]. Management Review, 2023, 35(9): 274-286.
|
| [2] |
扈衷权, 田军, 冯耕中, 等. 协议企业代储模式下应急物资储备策略及采购定价研究[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2020, 40(3): 605-616.
doi: 10.12011/1000-6788-2018-2550-12
|
|
HU Zhongquan, TIAN Jun, FENG Gengzhong, et al. Research on emergency supplies reserve strategy and procurement pricing under agreement enterprise reserve[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2020, 40(3): 605-616.
|
| [3] |
巩玲君, 姜星宇, 郭柯廷. 数量柔性契约下的政企三方联合储备决策研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(10): 221-228.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.10.0310
|
|
GONG Lingjun, JIANG Xingyu, GUO Keting. Research on joint reverse decision-making of government and enterprise under quantity flexibility contract[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(10): 221-228.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.10.0310
|
| [4] |
王伟, 宋月, 陈志松, 等. 防汛物资应急储备管理博弈决策模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(5): 191-198.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.05.2184
|
|
WANG Wei, SONG Yue, CHEN Zhisong, et al. Game decision model of emergency reserve management of flood control materials[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(5): 191-198.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.05.2184
|
| [5] |
CHEN Xu, HAO Gang, LI Ling. Channel coordination with a loss-averse retailer and option contracts[J]. International Journal of Production Economics, 2014, 150: 52-57.
|
| [6] |
DEVANGAN L, AMIT R K, MEHTA P, et al. Individually rational buyback contracts with inventory level dependent demand[J]. International Journal of Production Economics, 2013, 142(2): 381-387.
|
| [7] |
SHARMA A, DWIVEDI G, SINGH A. Game-theoretic analysis of a two-echelon supply chain with option contract under fairness concerns[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2019, 137: DOI: 10.1016/j.cie.2019.106096.
|
| [8] |
刘阳, 田军, 冯耕中, 等. 期权契约机制下应急物资储备模型研究[J]. 中国管理科学, 2022, 30(12): 338-351.
|
|
LIU Yang, TIAN Jun, FENG Gengzhong, et al. The model of pre-positioning relief supplies under option contracts[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2022, 30(12): 338-351.
|
| [9] |
HU Zhongquan, TIAN Jun, FENG Gengzhong. A relief supplies purchasing model based on a put option contract[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2019, 127: 253-262.
|
| [10] |
李晟, 丰景春, 吴凯丽, 等. 政企联合储备应急物资的合作策略研究[J]. 中国管理科学, 2024, 32(11): 222-232.
|
|
LI Sheng, FENG Jingchun, WU Kaili, et al. Study on cooperative strategy of government-enterprise joint reserve of emergency supplies[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2024, 32(11): 222-232.
|
| [11] |
姜旭, 秦子楚, 辛少凡. 基于代储模式政企应急物资多级储备决策[J]. 系统工程, 2024, 42(1): 87-99.
|
|
JIANG Xu, QIN Zichu, XIN Shaofan. Multi-stage reserve decision of government and enterprise emergency supplies based on agent storage mode[J]. Systems Engineering, 2024, 42(1): 87-99.
|
| [12] |
陈敬贤, 梁樑. 多产品救援物资的储备决策:一个扩展的Newsvendor模型[J]. 中国管理科学, 2018, 26(6): 143-152.
|
|
CHEN Jingxian, LIANG Liang. Pre-positioning decisions of stockpiling multiple relief materials: an extended Newsvendor approach[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2018, 26(6): 143-152.
|
| [13] |
PATRA D T P, JHA J K. Bidirectional option contract for prepositioning of relief supplies under demand uncertainty[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2022, 163: DOI: 10.1016/j.cie.2021.107861.
|
| [14] |
胡婉婷, 丁晶晶, 梁樑. 基于期权代储协议的应急物资政企联合储备模型研究[J]. 中国管理科学, 2024, 32(9): 101-112.
|
|
HU Wanting, DING Jingjing, LIANG Liang. Emergency supplies procurement pricing strategy under quantity flexible contract[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2024, 32(9): 101-112.
|
| [15] |
刘阳, 田军, 冯耕中, 等. 基于期权契约的政企联合储备应急物资模型与利润分配机制研究[J]. 中国管理科学, 2020, 28(8):162-171.
|
|
LIU Yang, TIAN Jun, FENG Gengzhong, et al. The model of joint relief supplies pre-positioning by the government two suppliers based on option contracts and suppliers'profits allocation mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2020, 28(8):162-171.
|