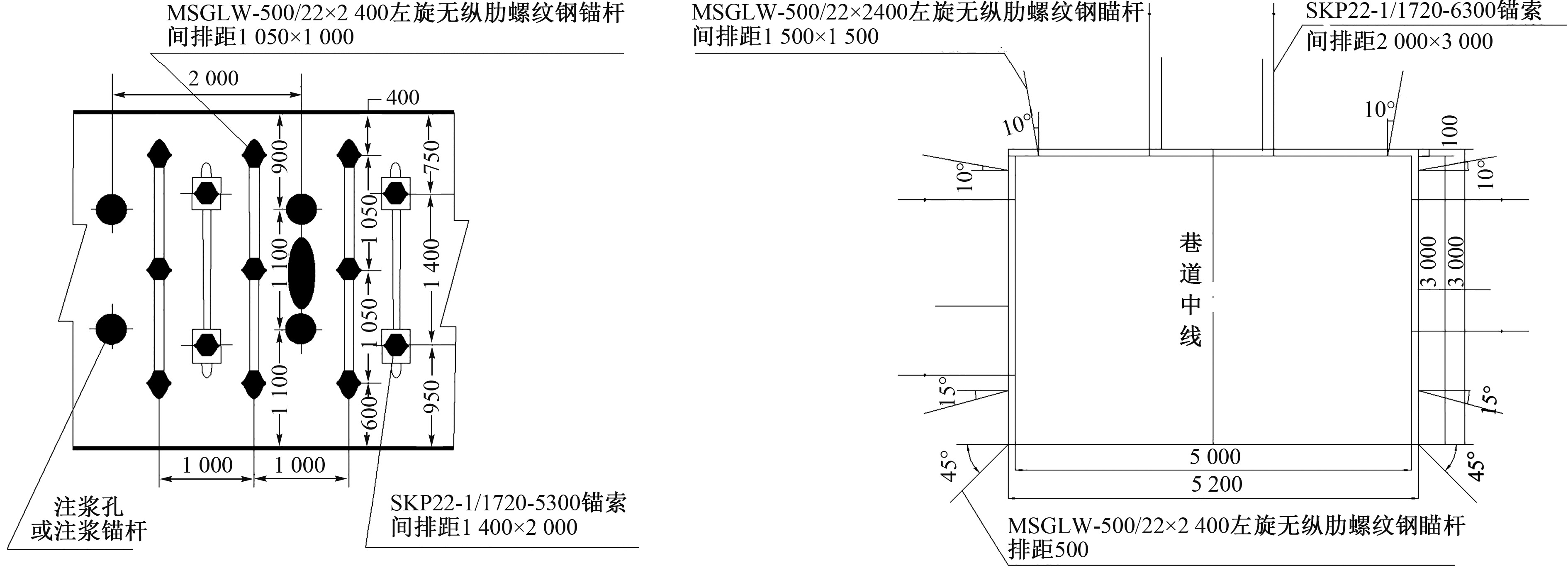
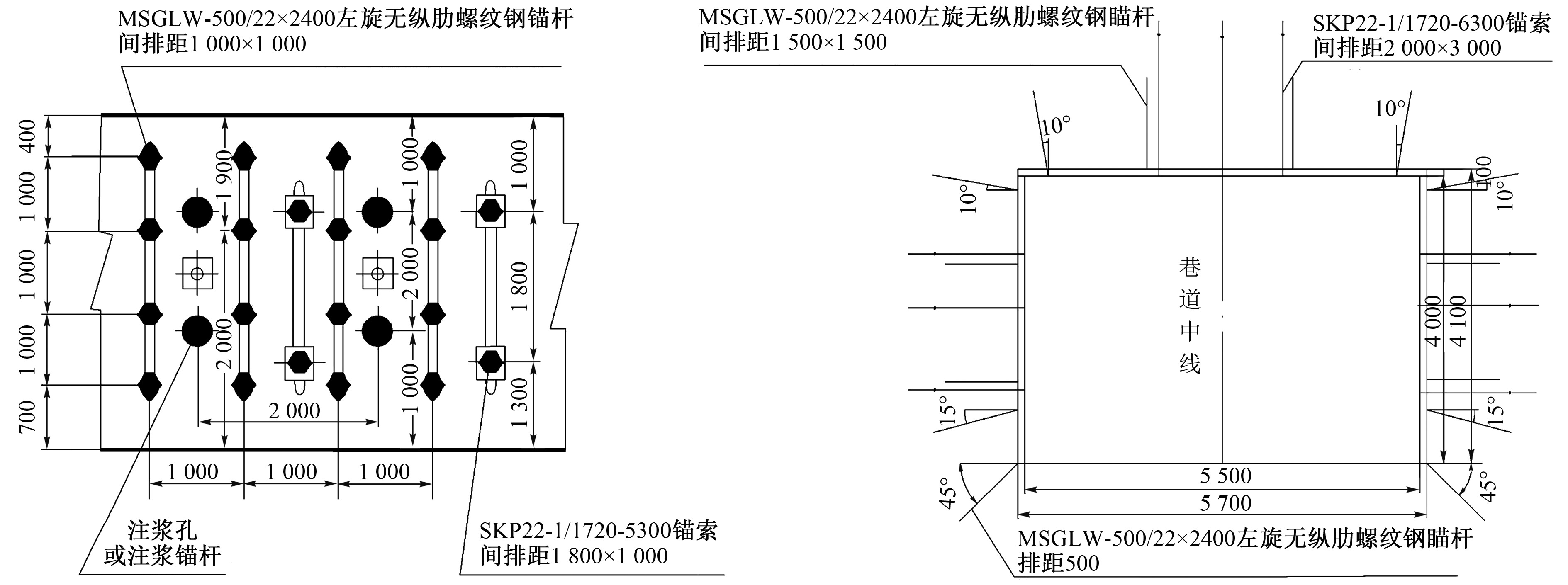
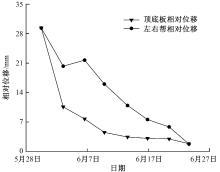
| [1] |
余熠, 石研然, 朱鹏飞, 等. 采空区治理用尾矿砂注浆材料的制备及性能研究[J]. 混凝土与水泥制品, 2024(2):97-99,103.
|
|
YU Yi, SHI Yanran, ZHU Pengfei, et al. Preparation and performance study of tailings sand grouting material for mining goaf treatment[J]. China Concrete and Cement Products, 2024(2):97-99,103.
|
| [2] |
杜金龙, 潘树仁, 刘长友, 等. 面向绿色矿山的注浆关键技术与工程示范[J]. 矿业科学学报, 2023, 8(3):293-307.
|
|
DU Jinlong, PAN Shuren, LIU Changyou, et al. Key grouting technology and engineering demonstration for green mines[J]. Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2023, 8(3):293-307.
|
| [3] |
李坤元, 刘佳亮. 磨料水射流多维参数对混凝土致裂性能影响特征[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(10):110-116.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.10.017
|
|
LI Kunyuan, LIU Jialiang. Effects of multi-dimensional parameters of abrasive water jet on cracking concrete[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(10):110-116.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.10.017
|
| [4] |
李建华, 孙立民. 新时代下可持续发展的绿色矿山开采技术分析[J]. 世界有色金属, 2024(21):124-126.
|
|
LI Jianhua, SUN Limin. Analysis of green mining technology for sustainable development in the new era[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2024(21):124-126.
|
| [5] |
杨绍斌, 董伟, 周晓谦, 等. 矿用聚氨酯注浆材料阻燃及加固性能研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2012, 22(8):48-53.
|
|
YANG Shaobin, DONG Wei, ZHOU Xiaoqian, et al. Study on flame retarding and reinforcement properties of mine polyurethane grouting materia[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2012, 22(8):48-53.
|
| [6] |
汪伟, 崔欣超, 祁云, 等. 基于SSA-RF的采空区煤自燃温度回归分析模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(9):136-141.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.09.0846
|
|
WANG Wei, CUI Xinchao, QI Yun, et al. Regression analysis model of coal spontaneous combustion temperature in goaf based on SSA-RF[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(9):136-141.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.09.0846
|
| [7] |
王泽. 煤矸石基混凝土在巷道底板硬化中的工业性试验研究[J]. 山东煤炭科技, 2023, 41(2):194-196.
|
|
WANG Ze. Industrial test study on coal gangue based concrete in roadway floor hardening[J]. Shandong Coal Technology, 2023, 41(2):194-196.
|
| [8] |
王永涛, 谢中辉, 余江, 等. 沿空巷道围岩变形破坏特征及控制技术研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2025, 42(1):161-171.
|
|
WANG Yongtao, XIE Zhonghui, YU Jiang, et al. Research on deformation and failure characteristics of surroundincrock in roadway along goaf and control techniques[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2025, 42(1):161-171.
|
| [9] |
刘洪涛, 周光东, 韩子俊, 等. 多因素影响下巷道围岩稳定性分析及优化设计研究[J]. 矿业科学学报, 2024, 9(4):504-518.
|
|
LU Hongtao, ZHOU Guangdong, HAN Zijun, et al. Stability analysis and optimization design of roadway surroundingrock under multiple factors[J]. Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2024, 9(4):504-518.
|
| [10] |
熊祖强, 刘旭锋, 王成, 等. 资源整合矿井复采面垮落废巷注浆加固技术研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2016, 26(11):104-109.
|
|
XIONG Zugiang, LIU Xufeng, WANG Cheng, et al. Research on technology for grouting reinforcement of caving waste roadways at repeated mining face in resource integrated mine[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2016, 26(11):104-109.
|
| [11] |
王新丰, 何毅, 陆明远, 等. 开挖卸荷扰动深部巷道围岩变形破坏特征研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(8):83-90.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.08.012
|
|
WANG Xinfeng, HE Yi, LU Mingyuan, et al. Study on deformation and failure characteristics of deep roadwaysurrounding rock under excavation unloading disturbance[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(8):83-90.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.08.012
|
| [12] |
王方田, 江振鹏, 刘超, 等. 深井综采面动压区沿空留巷围岩变形机理及锚索强化支护技术[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2024, 41(6):1 103-1 115.
|
|
WANG Fangtian, JIANG Zhenpeng, LIU Chao, et al. Surrounding rock movement mechanism and cable reinforcement support technology for gob-side entry retaining in the dynamic pressure area of deep fully-mechanized mining face[J]. Journal of Mining Safety Engineering, 2024, 41(6):1 103-1 115.
|
| [13] |
杨江峰, 许良全, 李子建, 等. 深部高应力软岩巷道围岩失稳机理及控制技术研究[J]. 能源与环保, 2024, 46(10):280-286.
|
|
YANG Jiangfeng, XU Liangquan, LI Zijian, et al. Research on destabilisation mechanism and control technology of surrounding rock in deep high stress soft rock roadway[J]. Energy and Environmental Protection, 2024, 46(10):280-286.
|
| [14] |
祁云, 白晨浩, 代连朋, 等. 改进双向长短期记忆神经网络的瓦斯涌出量预测[J]. 安全与环境报, 2024, 24(12):4 630-4 637.
|
|
QI Yun, BAI Chenhao, DAI Lianpeng, et al. Enhanced Bi-directional Long Short Term Memory neural network for gas emission forecasting[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2024, 24(12):4 630-4 637.
|
| [15] |
王健, 田刚, 贾哲, 等. 深部巷道围岩变形规律及支护参数优化模拟研究[J]. 煤炭技术, 2025, 44(2):45-51.
|
|
WANG Jian, TIAN Gang, JIA Zhe, et al. Simulation study on deformation law of surrounding rock in deep tunnels and optimization of support parameters[J]. Coal Technology, 2025, 44(2):45-51.
|
| [16] |
李培涛, 刘泉声, 朱元广, 等. 煤矿深部巷道大变形分步联合控制研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2025, 46(2):591-612.
|
|
LI Peitao, LIU Quansheng, ZHU Yuanguang, et al. Combined support method for large deformation of deep coal mine tunnel[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2025, 46(2):591-612.
|
| [17] |
陈梁, 孟庆彬, 戚振豪, 等. 深部厚煤层采动巷道失稳特征及锚网索注梯级支护技术[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2024, 41(3):533-548.
|
|
CHEN Liang, MENG Qingbin, QI Zhenhao, et al. Instability features of mining roadway in deep-thick coal seam and progressive bolt-mesh-cable-grouting support technology[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2024, 41(3):533-548.
|
| [18] |
李文政. 近距离煤层群孤岛工作面复用巷道围岩控制技术研究[J]. 能源与节能, 2025(4): 164-166.
|
|
LI Wenzheng. Research on the surrounding rock control technology of reused tunnels in close-proximity coal seam isolated workfaces[J]. Energy and Energy Conservation, 2025(4): 164-166.
|
| [19] |
王荣芳. 煤矿深部开采巷道围岩协同支护技术研究[J]. 内蒙古煤炭经济, 2025(5): 10-12.
|
|
WANG Rongfang. Research on collaborative support technology for surrounding rock in deep mining tunnels of coal mines[J]. Inner Mongolia Coal Economy, 2025(5): 10-12.
|
| [20] |
ZHANG Jinpeng, LIU Limin, LI Qinghai, et al. Development of cement-based self-stress composite grouting material for reinforcing rock mass and engineering application[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 201:314-327.
|
| [21] |
SUN Lei, GRASSELLI G, LIU Quansheng, et al. Coupled hydro-mechanical analysis for grout penetration in fractured rocks using the finite-discrete element method[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2019, 124: DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.104138.
|
| [22] |
LEI Zhihong, ZHANG Yulong, CUI Qiliang, et al. The injection-production performance of an enhanced geothermal system considering fracture network complexity and thermo-hydro-mechanical coupling in numerical simulations[J]. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13(1): DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-41745-7.
|
| [23] |
GULER E, SECILEN G G. Jet grouting technique and strength properties of jet grout columns[J]. Journal of Physics Conference Series, 2021, 1928(1): DOI: 10.1088/1742-6596/1928/1/012006.
|
| [24] |
LIU Hanlong, ZHOU Hang, KONG Gangqiang, et al. High pressure jet-grouting column installation effect in soft soil: Theoretical model and field application[J]. Computers & Geotechnics, 2017, 88:74-94.
|
| [25] |
LIU Xuewei, HU Cheng, LIU Quansheng, et al. Grout penetration process simulation and grouting parameters analysis in fractured rock mass using numerical manifold method[J]. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 2021, 123:93-106.
|
| [26] |
王成, 丁子文, 熊祖强, 等. 大断面动压回采巷道围岩变形规律及其控制技术[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(5):135-140.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.05.023
|
|
WANG Cheng, DING Ziwen, XIONG Zuqiang, et al. Deformation mechanism of large cross-section entry surrounding crock under dynamic stress and control technology[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(5):135-140.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.05.023
|
| [27] |
高林, 王家臣, 孔德中, 等. 动压影响半煤岩上山变形机制及修复技术[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(3):67-73.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.03.011
|
|
GAO Lin, WANG Jiachen, KONG Dezhong, et al. Deformation mechanism and repairing technology for coal-rock uphill roadway under influence of dynamic pressure[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(3):67-73.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.03.011
|