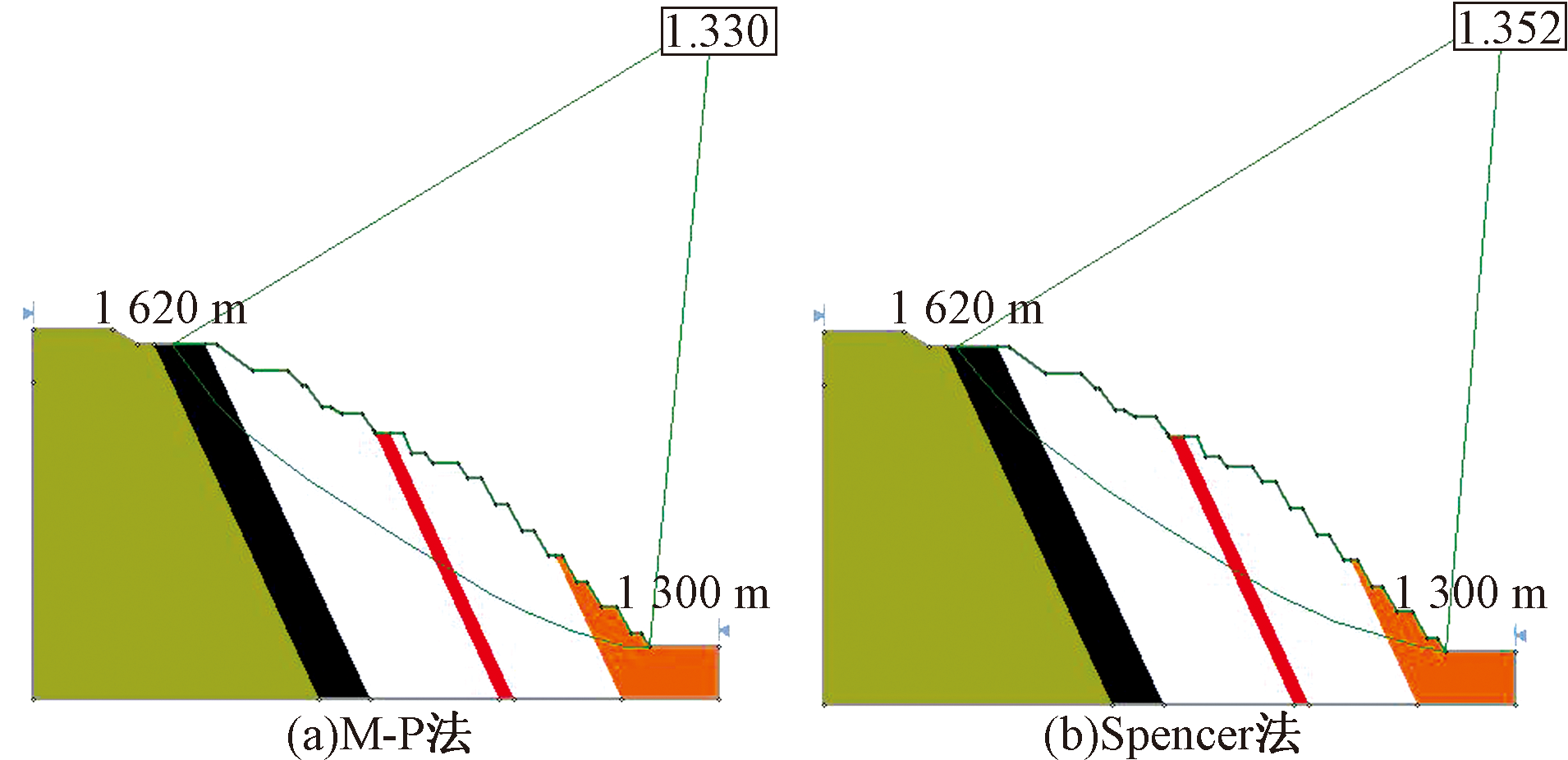
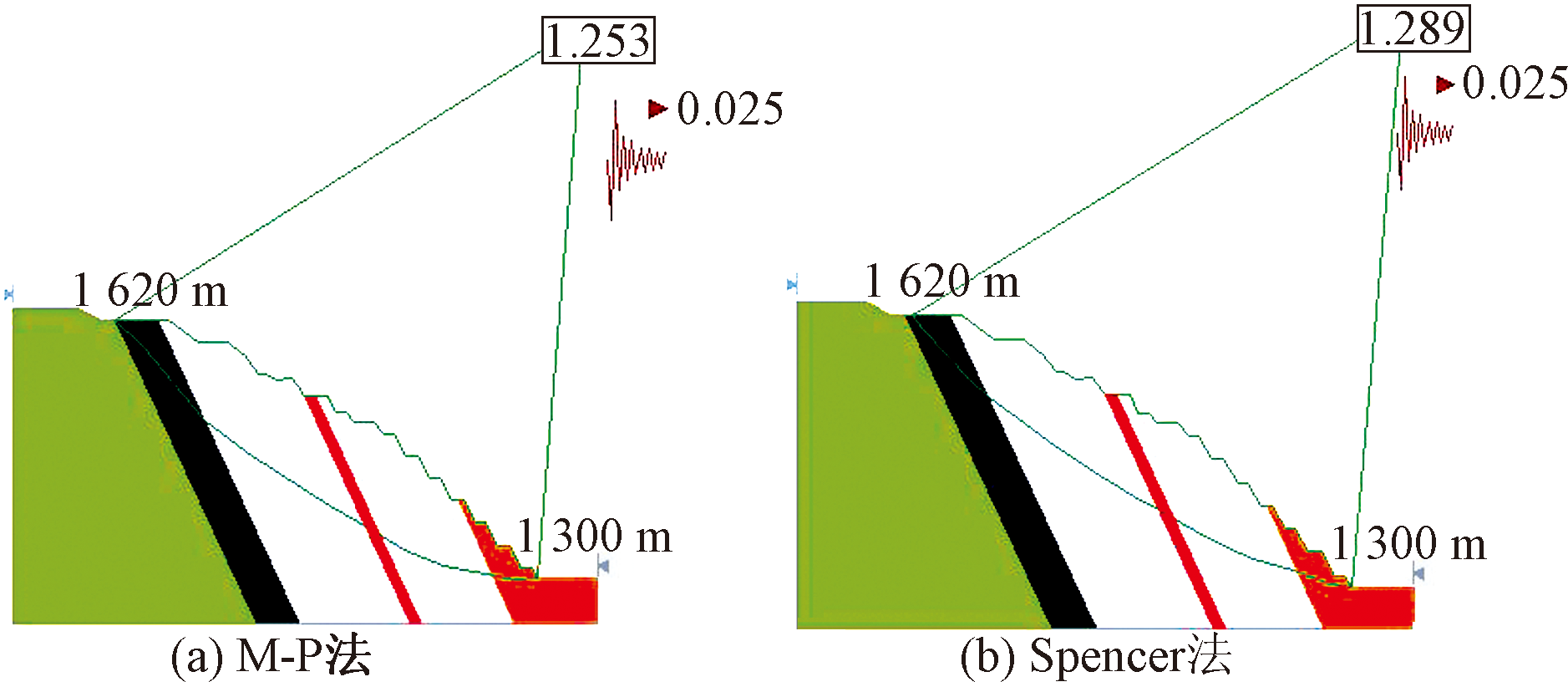
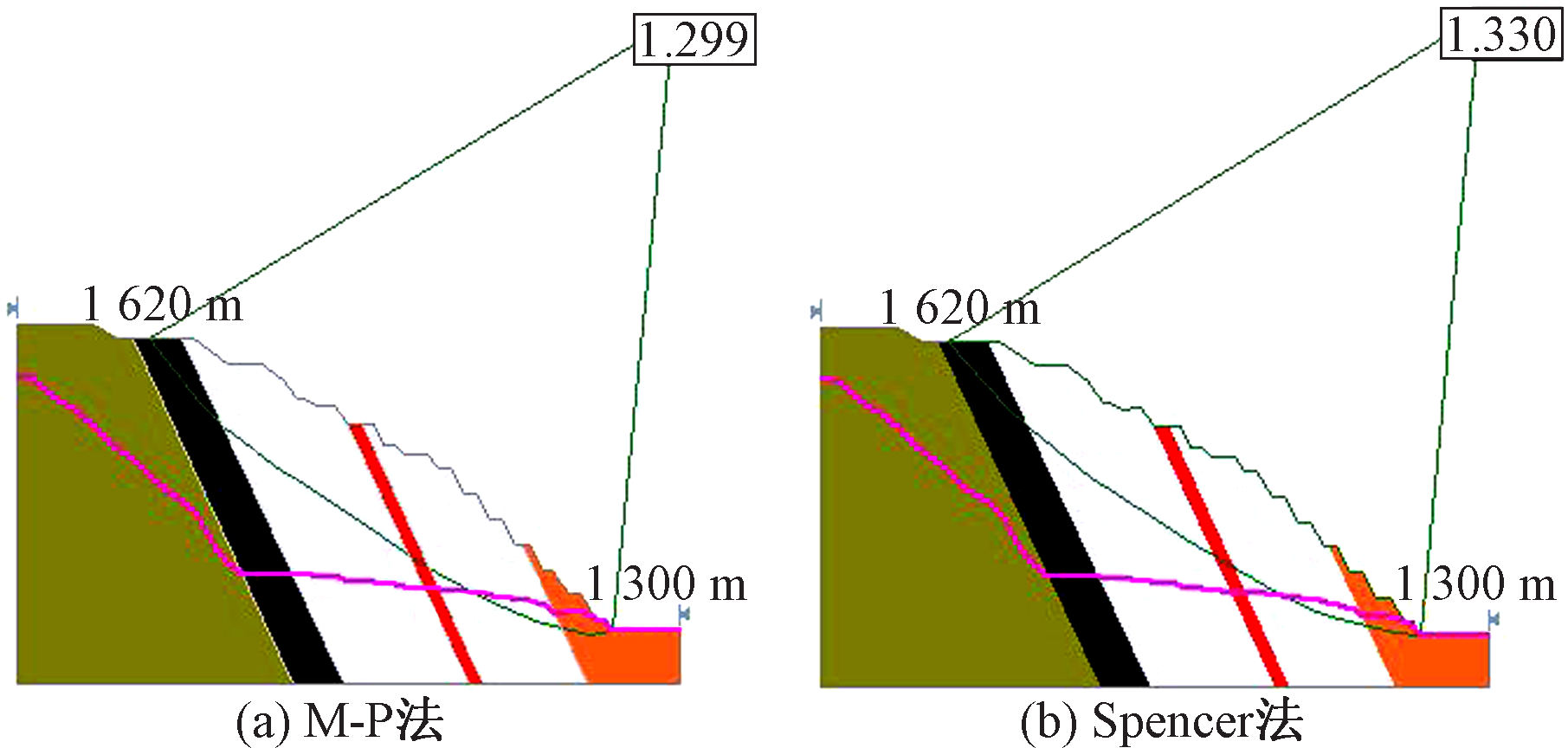
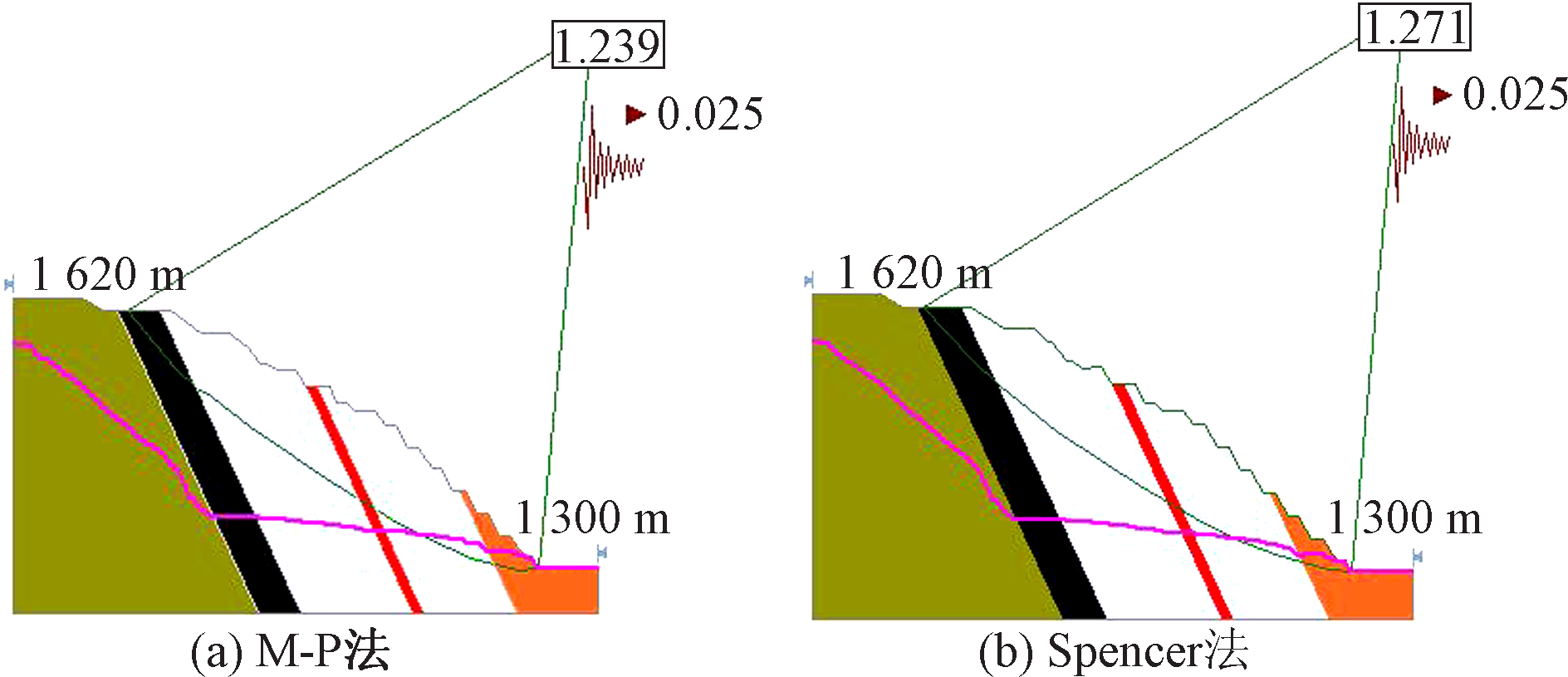
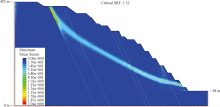
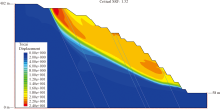
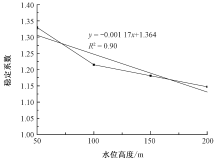
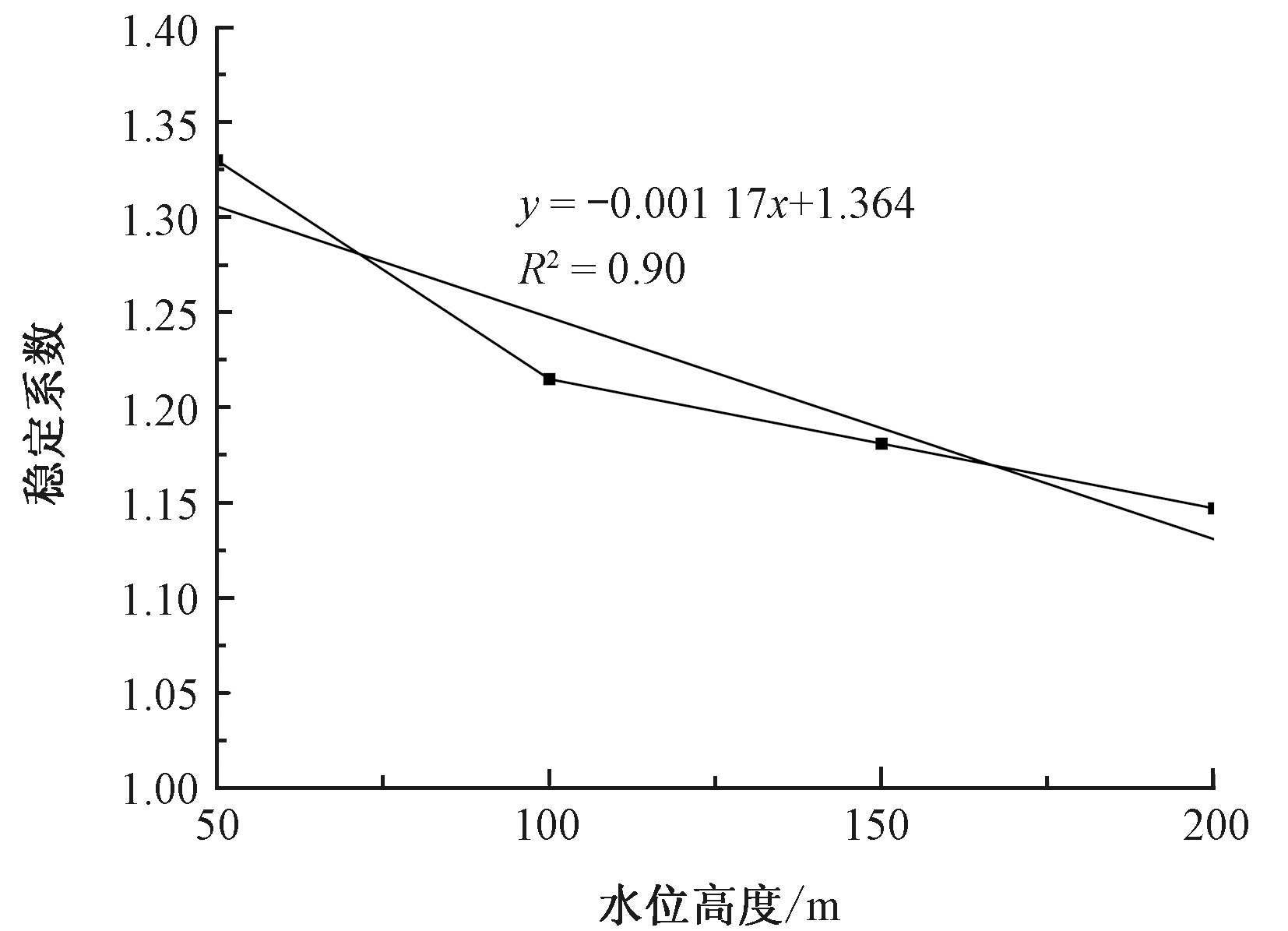
| [1] |
杨晓伟, 王妍, 刘欣, 等. 我国露天煤矿发展现状及展望[J]. 中国煤炭, 2023, 49(6):126-133.
|
|
YANG Xiaowei, WANG Yan, LIU Xin, et al. Present situation and prospect of the development of open-pit coal mine in China[J]. China Coal, 2023, 49(6):126-133.
|
| [2] |
朱晓玺, 杨曦, 张洪栋. 不同工况下露天边坡稳定性分析与监测[J]. 科技创新与应用, 2025, 15(18):88-91.
|
|
ZHU Xiaoxi, YANG Xi, ZHANG Hongdong. Analysis and monitoring of open-pit slope stability under different working conditions[J]. Technology Innovation and Application, 2025, 15(18):88-91.
|
| [3] |
宋晓东, 胡利峰, 苏亚超, 等. 露天铜钴矿采场边坡稳定性评价与数值模拟研究[J]. 矿业研究与开发, 2025, 45(8):96-106.
|
|
SONG Xiaodong, HU Lifeng, SU Yachao, et al. Study on slope stability evaluation and numerical simulation of an open-pit copper-cobalt mine[J]. Mining Research and Development, 2025, 45(8):96-106.
|
| [4] |
王发刚, 邹平, 王忠康, 等. 基于GA-BP神经网络边坡稳定性预测的方法及应用[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2024, 20(6):161-167.
|
|
WANG Fagang, ZOU Ping, WANG Zhongkang, et al. Method and application of slope stability prediction based on GA-BP neural network[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2024, 20(6):161-167.
|
| [5] |
尹永明, 朱强, 张小军, 等. 广东某建筑砂岩矿露天采场设计边坡稳定性分析[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2023, 19(增1):104-109.
|
|
YIN Yongming, ZHU Qiang, ZHANG Xiaojun, et al. Stability analysis on designed slope of a construction sandstone mine open pit in Guangdong[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2023, 19(S1):104-109.
|
| [6] |
詹浩东, 纪玮, 于燕, 等. 基于MIDAS对某露天石灰石矿山边坡稳定性研究分析[J]. 水泥工程, 2025, 38(4):65-69.
|
|
ZHAN Haodong, JI Wei, YU Yan, et al. Research and analysis on slope stability of an open-pit limestone mine based on MIDAS[J]. Cement Engineering, 2025, 38(4):65-69.
|
| [7] |
杨正良, 叶勤富, 赵庆才. 基于三维数值模拟的铜曼露天采场边坡稳定性分析[J]. 世界有色金属, 2025(10):108-110.
|
|
YANG Zhengliang, YE Qinfu, ZHAO Qingcai. Stability analysis of the open-pit slope at tongman based on three-dimensional numerical simulation[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2025(10):108-110.
|
| [8] |
GB 51016—2014,非煤露天矿边坡工程技术规范[S].
|
|
GB 51016-2014,Technical code for non-coal open-pit mine slope engineering[S].
|
| [9] |
张长锁, 刘建博. 露天矿扩界工程露天坑及排土场边坡协同稳定性分析[J]. 矿冶, 2024, 33(1):116-123.
|
|
ZHANG Changsuo, LIU Jianbo. Collaborative stability analysis of open-pit and waste dump slope in open-pit expansion project[J]. Mining and Metallurgy, 2024, 33(1):116-123.
|
| [10] |
刘威. 基于修正莫尔库伦准则的砂岩能量演化数值分析[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳建筑大学, 2022.
|
|
LIU Wei. Numerical analysis of energy evolution in sandstone based on the modified Mohr-Coulomb criterion[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Jianzhu University, 2022.
|