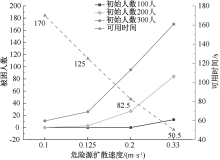
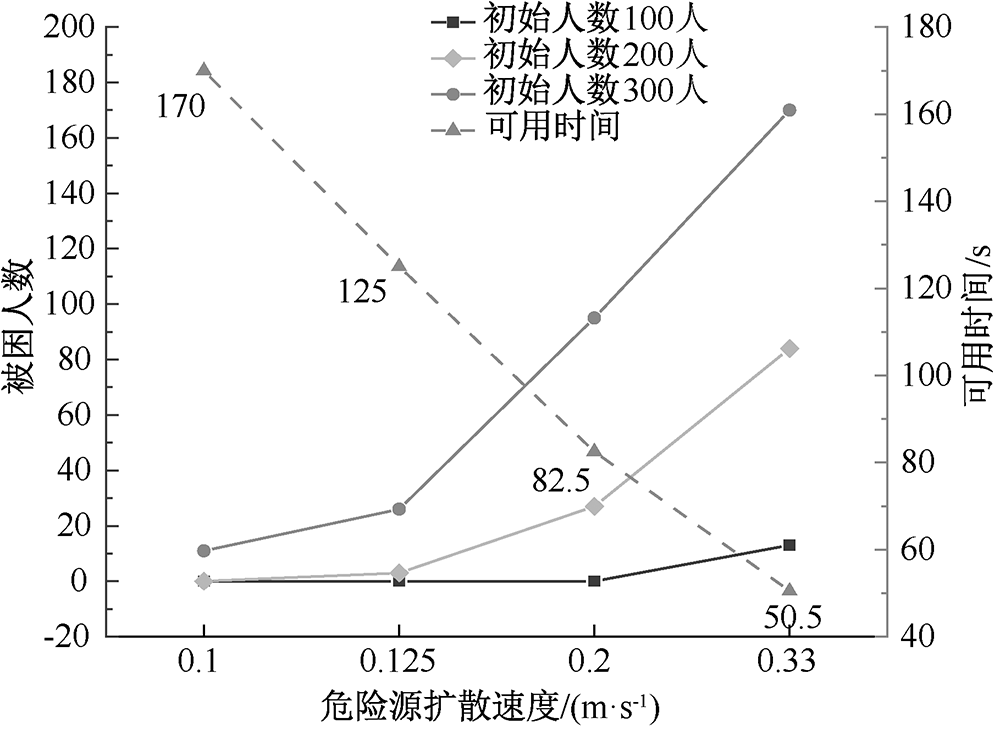
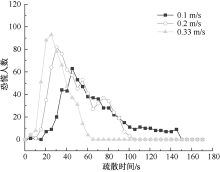
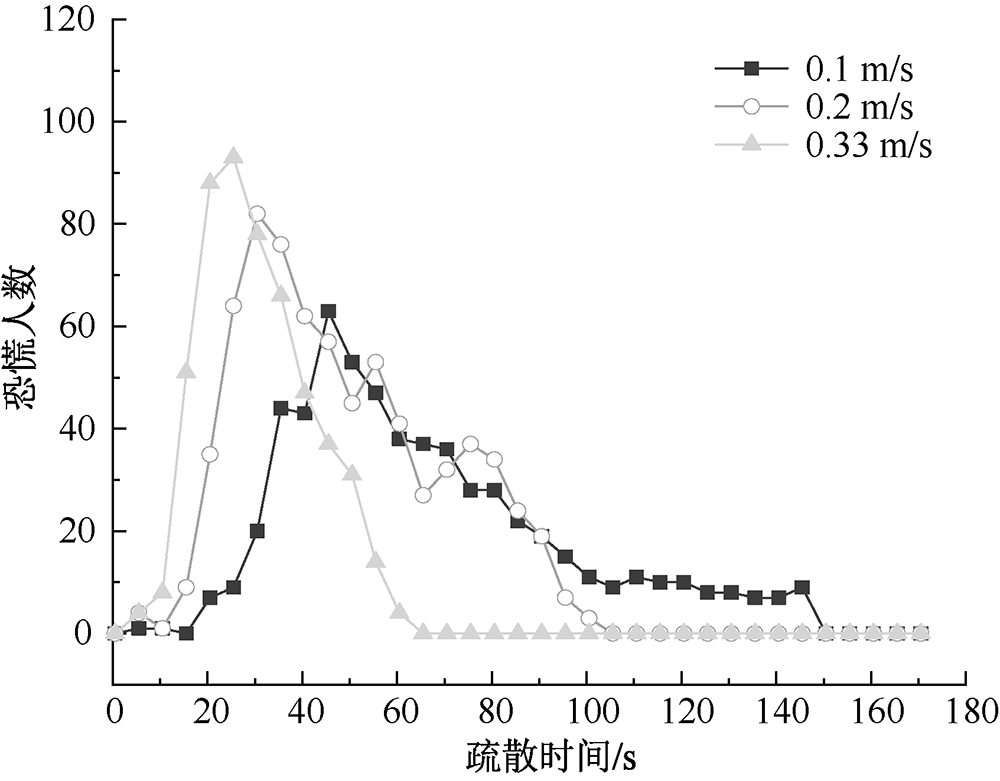
| [1] |
人民网. 洛杉矶机场误把噪音当枪声一人穿佐罗服装被拘[EB/OL]. (2016-08-29). http://world.people.com.cn/n1/2016/0829/c1002-28674588.html.
|
| [2] |
PAULSEN R L. Human behavior and fires: an introduction[J]. Fire Technology, 1984, 20(2):15-27.
doi: 10.1007/BF02384147
|
| [3] |
何梦男, 付瑜玲, 陈诚, 等. 基于元胞自动机的应急疏散最短路径优化算法[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(4): 51-57.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.04.009
|
|
HE Mengnan, FU Yuling, CHEN Cheng, et al. Optimization algorithm for shortest path of emergency evacuation based on cellular automata[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29 (4): 51-57.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.04.009
|
| [4] |
HELBING D, MUKERJI P. Crowd disasters as systemic failures: analysis of the love parade disaster[J]. Epj Data Science, 2012, 1(1):1-40.
doi: 10.1140/epjds1
|
| [5] |
HELBING D, FARKAS I, VICSEK T. Simulating dynamical features of escape panic[J]. Nature, 2000, 407(6803):487-490.
doi: 10.1038/35035023
|
| [6] |
DODDS P S, WATTS D J. Universal behavior in a generalized model of contagion[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2004, 92(21): DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevlett.92.18701.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevlett.92.18701
|
| [7] |
陈长坤, 童蕴贺. 基于元胞自动机恐慌状态下人群疏散模型研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2019, 15(6): 12-17.
|
|
CHEN Changkun, TONG Yunhe. Research on crowd evacuation model based on cellular automata in panic state[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2019, 15 (6): 12-17.
|
| [8] |
ZHENG Linjiang, PENG Xiaoli, WANG Linglin, et al. Simulation of pedestrian evacuation considering emergency spread and pedestrian panic[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2019, 522: 167-181.
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2019.01.128
|
| [9] |
GROSS J J. Antecedent- and response-focused emotion regulation: divergent consequences for experience, expression, and physiology[J]. Journal of Personality & Social Psychology, 1998, 74(1): 224-237.
|
| [10] |
VERBEKE W. Individual differences in emotional contagion of salespersons: its effect on performance and burnout[J]. Psychology & Marketing, 1997, 14(6): 617-636.
doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6793(199709)14:6【-逻*辑*与-】#x00026;lt;617::AID-MAR6【-逻*辑*与-】#x00026;gt;3.0.CO;2-A
|
| [11] |
殷雁君, 唐卫清, 李蔚清. 基于情绪感染的虚拟个体情绪模型[J]. 计算机仿真, 2013, 30(8): 216-220.
|
|
YIN Yanjun, TANG Weiqing, LI Weiqing. Virtual individual emotion model based on emotion infection[J]. Computer Simulation, 2013, 30 (8): 216-220.
|
| [12] |
KHOLSHEVNIKOV V V, SHIELDS T J, BOYCE K E, et al. Recent developments in pedestrian flow theory and research in Russia[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2008, 43(2): 108-118.
doi: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2007.05.005
|
| [13] |
ITO Y. Representation of functions by superpositions of a step or sigmoid function and their applications to neural network theory[J]. Neural Networks, 1991, 4(3): 385-394.
doi: 10.1016/0893-6080(91)90075-G
|
| [14] |
冯娇娇, 王静虹, 李佳, 等. 火灾事故下人群承受热辐射阈值差异分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(10):134-140.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.10.019
|
|
FENG Jiaojiao, WANG Jinghong, LI Jia, et al. Difference in thermal radiation threshold of people under fire accidents[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(10):134-140.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.10.019
|
| [15] |
BOSSE T, DUELL R, MEMON Z A, et al. A multi-agent model for mutual absorption of emotions[C]. European Conference on Modeling and Simulation, 2009:212-218.
|
| [16] |
罗长坤. 基于情绪感染的人员疏散实验及仿真模型研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳大学, 2021.
|
|
LUO Changkun. Research on evacuation experiment and simulation model based on emotional infection[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University, 2021.
|