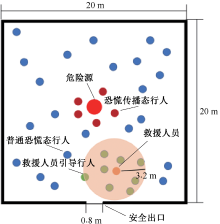
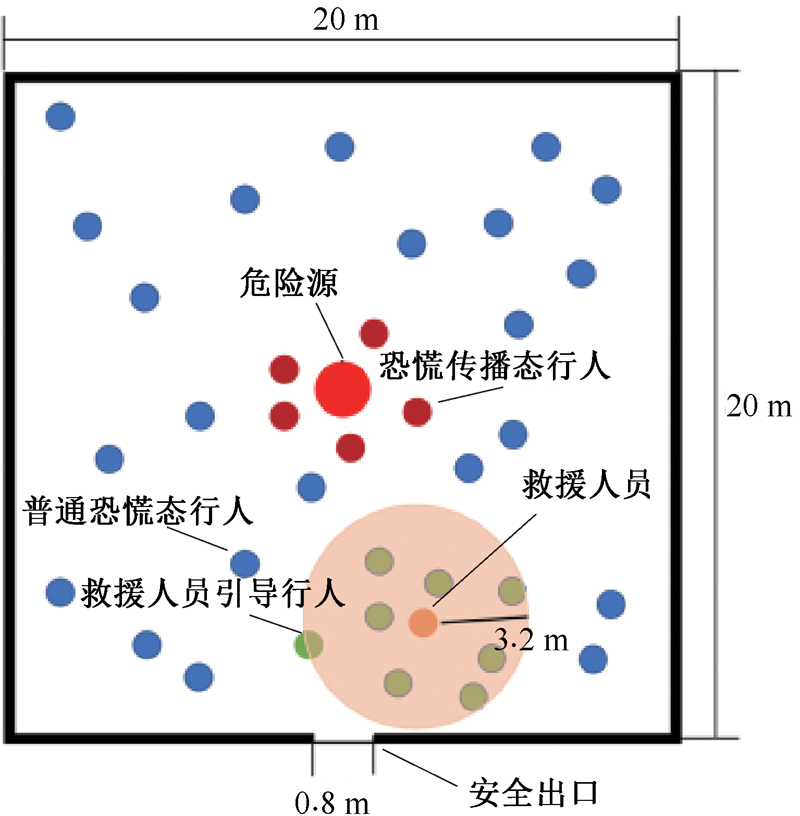
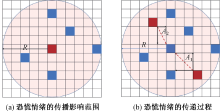
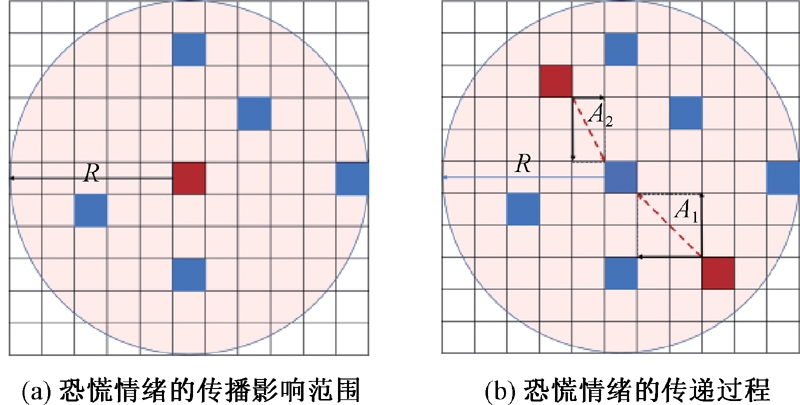
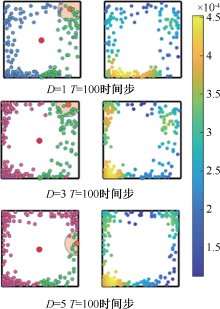
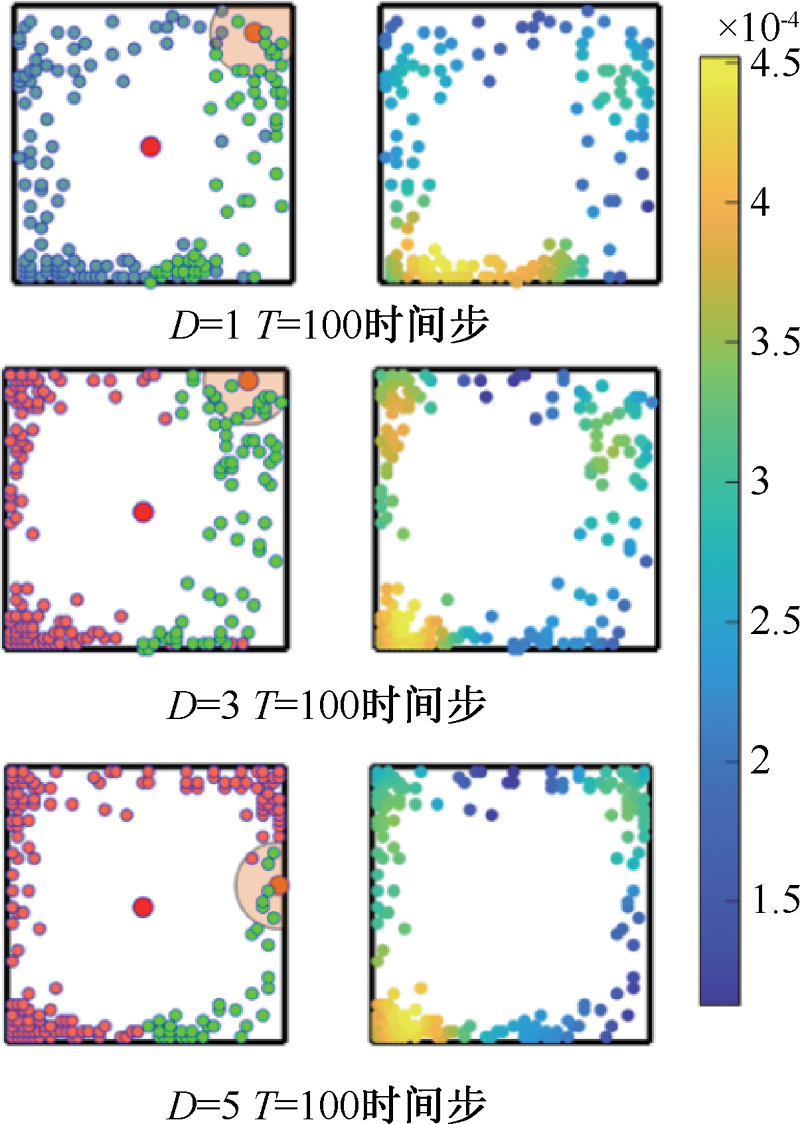
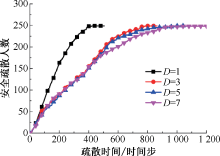
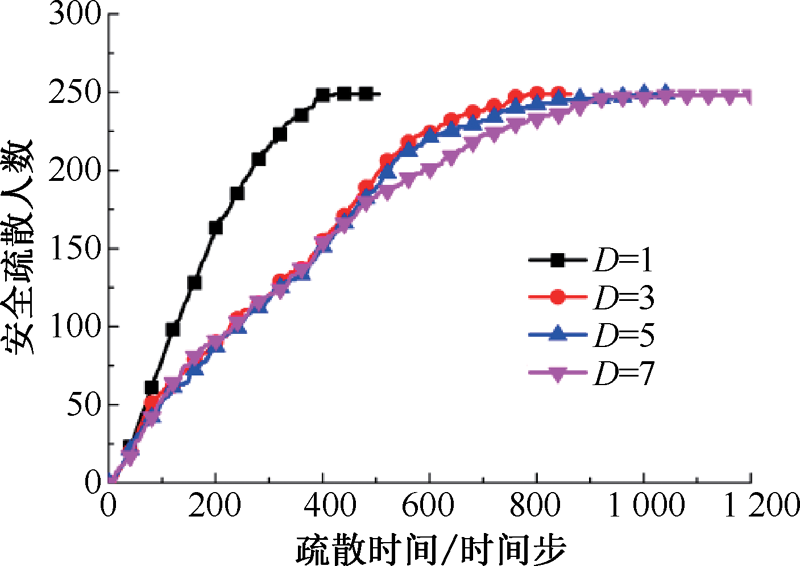
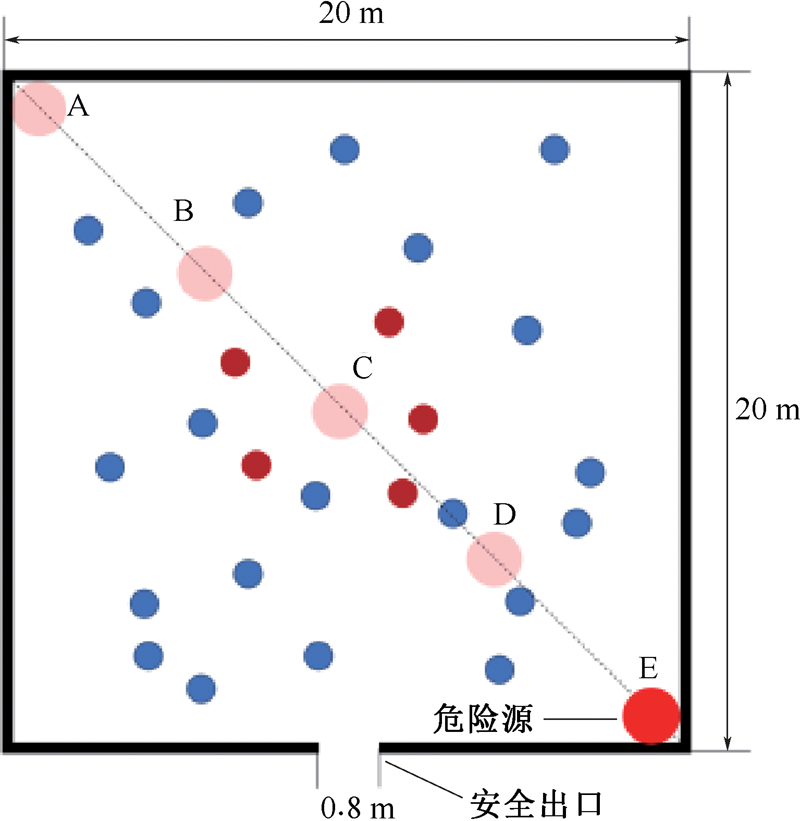
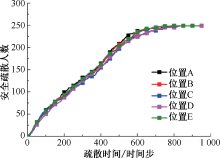
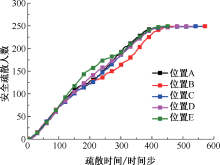
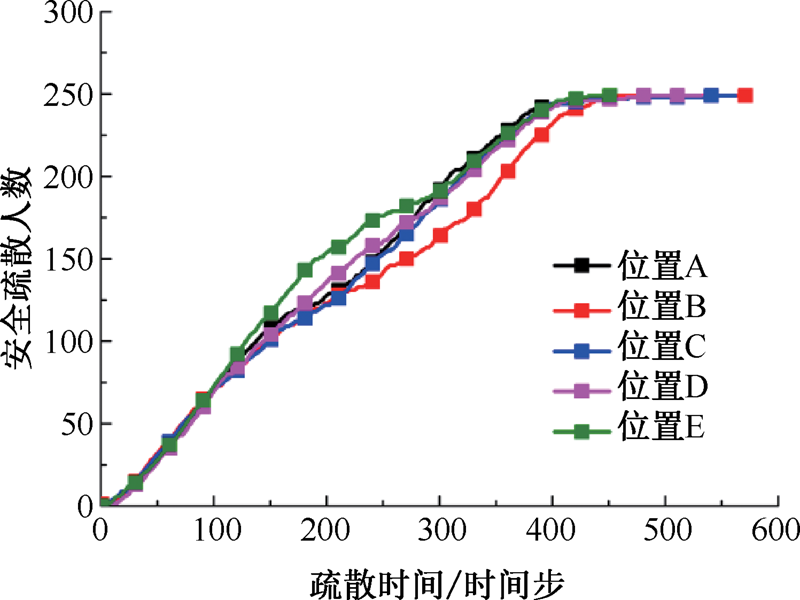
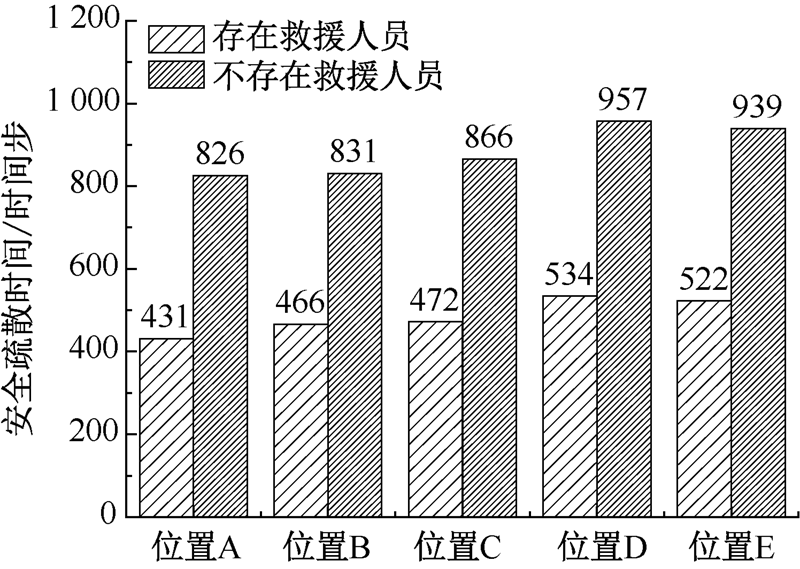
| [1] |
李昌华, 何海彤, 李智杰, 等. 烟雾场景下的人员疏散仿真研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(4):86-92.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.04.014
|
|
LI Changhua, HE Haitong, LI Zhijie, et al. Simulation of personnel evacuation in smoke scenario[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(4):86-92.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.04.014
|
| [2] |
HELBING D, FARKAS I, VICSEK T. Simulating dynamical features of escape panic[J]. Nature, 2000, 407: 487-490.
doi: 10.1038/35035023
|
| [3] |
FU Libi, SONG Weiguo, LYU Wei, et al. Simulation of emotional contagion using modified SIR model: a cellular automaton approach[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2014, 405: 380-391.
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2014.03.043
|
| [4] |
LI Fang, CHEN Shaokuan, WANG Xiudan, et al. Pedestrian evacuation modeling and simulation on metro platforms considering panic impacts[J]. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 2014, 138:314-322.
doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.07.209
|
| [5] |
LÖHNER R. On the modeling of pedestrian motion[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2010, 34(2): 366-382.
doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2009.04.017
|
| [6] |
YANG Xiaoxia, DONG Hairong, WANG Qianling, et al. Guided crowd dynamics via modified social force model[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2014, 411: 63-73.
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2014.05.068
|
| [7] |
CHEN Changkun, SUN Huakai, LEI Peng, et al. An extended model for crowd evacuation considering pedestrian panic in artificial attack[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2021, 571: DOI: 10.1016/j.physa.2021.125833.
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2021.125833
|
| [8] |
FANG Weifeng, YANG Lizhong, FAN Weicheng. Simulation of bi-direction pedestrian movement using a cellular automata model[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2003, 321(3/4): 633-640.
doi: 10.1016/S0378-4371(02)01732-6
|
| [9] |
YU W J, CHEN R, DONG L Y, et al. Centrifugal force model for pedestrian dynamics[J]. Physical Review E, 2005, 72(2): DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.72.026112.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.72.026112
|
| [10] |
SHI Dongmei, WANG Binghong. Evacuation of pedestrians from a single room by using snowdrift game theories[J]. Physical Review E, 2013, 87(2):DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.87.022802.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.87.022802
|
| [11] |
JIN T, YAMADA T. Irritating Effects of fire smoke on visibility[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 1985, 5(1): 79-90.
doi: 10.3210/fst.5.79
|
| [12] |
FRIDOLF K, RONCHI E, NILSSON D, et al. Movement speed and exit choice in smoke filled rail tunnels[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2013, 59: 8-21.
doi: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2013.03.007
|
| [13] |
COWAN N J, LEE J, FULL R J. Task-level control of rapid wall following in the american cockroach[J]. Journal of Experimental Biology, 2006, 209 (9): 1617-1629.
doi: 10.1242/jeb.02166
|
| [14] |
XUE Shuqi, JIANG Rui, WONG S C, et al. Wall-following behaviour during evacuation under limited visibility: experiment and modelling[J]. Transportmetrica A: Transport Science, 2020, 16(3): 626-653.
doi: 10.1080/23249935.2020.1722281
|
| [15] |
GUO Renyong, HUANG Haijun, WONG S C. Route choice in pedestrian evacuation under conditions of good and zero visibility: experimental and simulation results[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2012, 46 (6): 669-686.
doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2012.01.002
|
| [16] |
ANDO Y, YUTA S. Following a wall by an autonomous mobile robot with a sonar ring[C]. Proceedings of 1995 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automaton, 1995: 2599-2606.
|