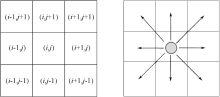
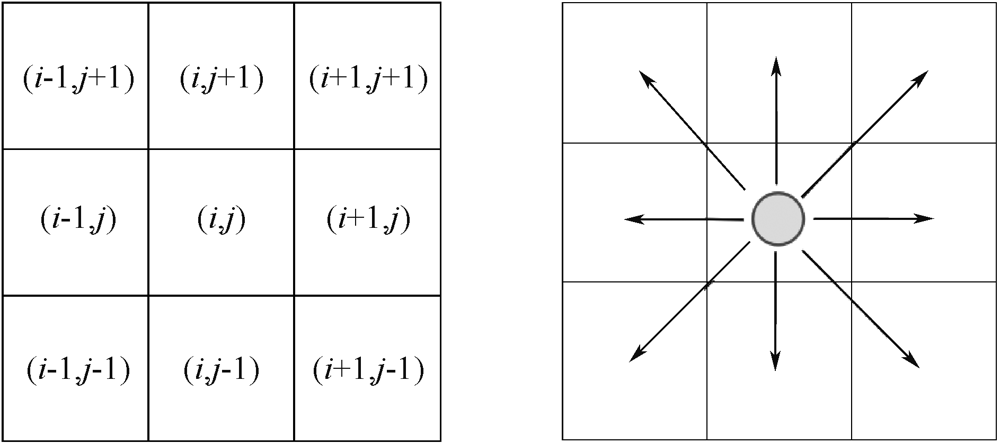
| [1] |
王惠汕. 上海外滩踩踏事件媒体报道的新闻伦理分析[J]. 新闻研究导刊, 2018, 9(17): 74, 173.
|
| [2] |
许岩, 永贵. 建筑物内人员疏散模型和行为特征[M]. 北京: 中国经济出版社, 2017:3-21.
|
| [3] |
HENDERSON L. On the fluid mechanics of human crowd motion[J]. Transportation Research, 1974, 8(6): 509-515.
doi: 10.1016/0041-1647(74)90027-6
|
| [4] |
HELBING D, MOLNAR P. Social force model for pedestrian dynamics[J]. Physical Review E, 1995, 51(5): 4282-4286.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.51.4282
|
| [5] |
BLUE V, ADLER J. Cellular automata microsimulation of bidirectional pedestrian flows[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 1999, 1678(1): 135-141.
doi: 10.3141/1678-17
|
| [6] |
REYNOLDS C. Flocks, herds and schools: a distributed behavioral model[C]. Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, 1987, 21(4): 25-34.
|
| [7] |
周美琦, 杨晓霞, 张纪会, 等. 基于改进元胞自动机模型的地铁车厢乘客疏散模拟[J]. 复杂系统与复杂性科学, 2021, 18(3): 35-44.
|
|
ZHOU Meiqi, YANG Xiaoxia, ZHANG Jihui, et al. Simulation of passenger evacuation in the metro carriage based on an improved cellular automata model[J]. Complex Systems and Complexity Science, 2021, 18(3): 35-44.
|
| [8] |
宋英华, 涂文豪, 霍非舟, 等. 考虑跨越障碍物行为的元胞自动机模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(4): 74-79.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.04.012
|
|
SONG Yinghua, TU Wenhao, HUO Feizhou, et al. Cellular automation model of pedestrian evacuation considering obstacle crossing behaviors[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(4): 74-79.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.04.012
|
| [9] |
宋英华, 张宇, 霍非舟, 等. 考虑避让行为的人员疏散元胞自动机模型研究[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2020, 32(6): 975-981.
doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.20-0195
|
|
SONG Yinghua, ZHANG Yu, HUO Feizhou, et al. Study on evacuation cellular automaton model considering avoidance behavior[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2020, 32(6): 975-981.
doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.20-0195
|
| [10] |
高国平, 管昌生. 考虑帮助行为的人员疏散元胞自动机模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(1): 56-61.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.01.010
|
|
GAO Guoping, GUAN Changsheng. A helping behavior-considering cellular automaton model for evacuation from a building[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(1): 56-61.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.01.010
|
| [11] |
李昌华, 何海彤, 李智杰, 等. 烟雾场景下的人员疏散仿真研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(4): 86-92.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.04.014
|
|
LI Changhua, HE Haitong, LI Zhijie, et al. Simulation of personnel evacuation in smoke scenario[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(4): 86-92.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.04.014
|
| [12] |
GUAN Junbiao, WANG Kaihua, CHEN Fangyue. A cellular automaton model for evacuation flow using game theory[J]. Physica A Statistical Mechanics & Its Applications, 2016, 461:655-661.
|
| [13] |
刘根旺, 周颖, 张磊, 等. 基于博弈论的人员疏散演化研究[J], 计算机工程与应用. 2020, 56(8): 49-54.
|
|
LIU Genwang, ZHOU Ying, ZHANG Lei, et al. Research on pedestrian evacuation evolution based on game theory[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications. 2020, 56(8): 49-54.
|
| [14] |
TIAN Huanhuan, WEI Yanfang, DONG Liyun, et al. Resolution of conflicts in cellular automaton evacuation model with the game-theory[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2018, 503: 991-1006.
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2018.08.140
|
| [15] |
HELBING D, FARKAS I, VICSEK T. Simulating dynamic features of escape panic[J]. Nature, 2000, 407(6803):487-490.
doi: 10.1038/35035023
|
| [16] |
陈长坤, 童蕴贺. 基于元胞自动机恐慌状态下人群疏散模型研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2019, 15(6):12-17.
|
|
CHEN Changkun, TONG Yunhe. Study on crowd evacuation model under panic state based on cellular automata[J]. Journal of Safety and Technology, 2019, 15(6):12-17.
|
| [17] |
游磊, 罗熙越, 刘旭, 等. 基于元胞自动机和SIS传染算法的恐慌状态下行人疏散模型[J]. 成都大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 31(1):51-54.
|
|
YOU Lei, LUO Xiyue, LIU Xu, et al. A panic evacuation model for pedestrians based on cellular automata and SIS infection algorithm[J]. Journal of Chengdu University:Natural Science Edition, 2020, 31(1):51-54.
|
| [18] |
CHENG Yuan, ZHENG Xiaoping. Effect of uncertainty on cooperative behaviors during an emergency evacuation[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science & Numerical Simulation, 2019, 66:216-225.
|
| [19] |
李阳, 陈建忠, 张倩, 等. 考虑环境熟悉度的人员疏散模型研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2016, 26(4):168-174.
|
|
LI Yang, CHEN Jianzhong, ZHANG Qian, et al. Study of pedestrian evacuation model considering familiarity with environment[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2016, 26(4):168-174.
|
| [20] |
李俊梅, 胡成, 李炎锋, 等. 不同类型疏散通道人群密度对行走速度的影响研究[J]. 建筑科学, 2014, 30(8):122-129.
|
|
LI Junmei, HU Cheng, LI Yanfeng, et al. Influence of crow density on the movement speed on different egress paths[J]. Building Science, 2014, 30(8):122-129.
|