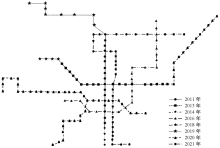
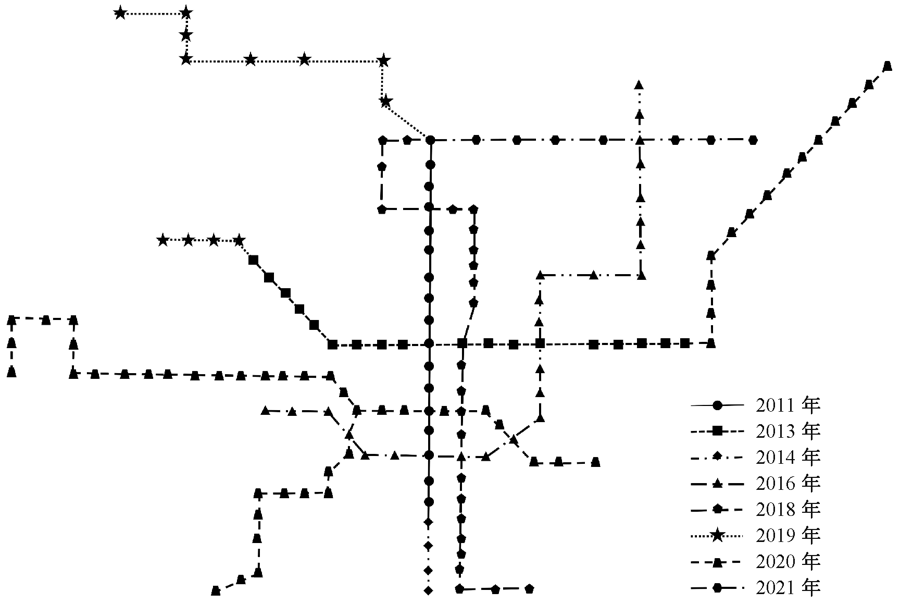
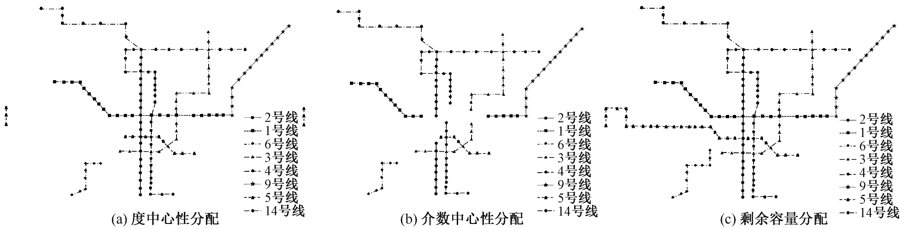
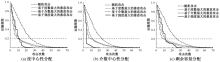
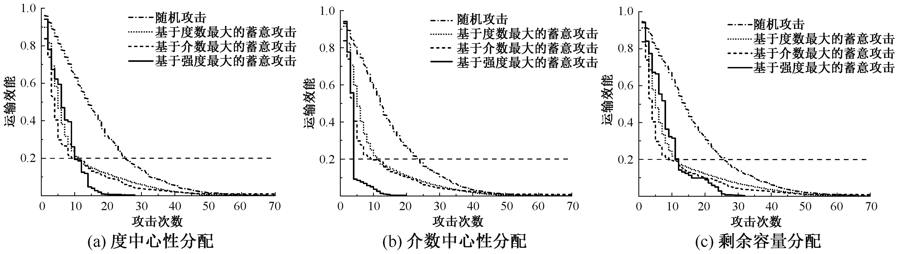
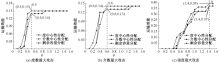
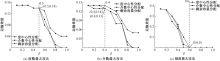
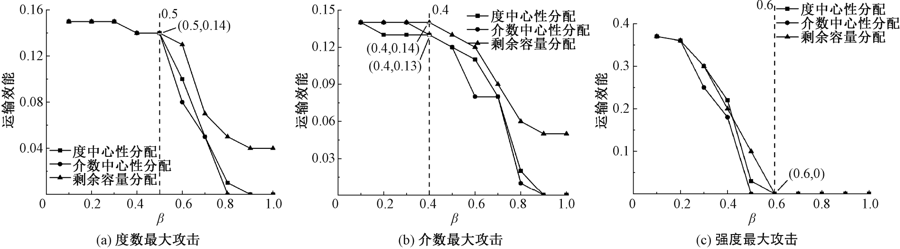
| [1] |
DERRIBLE S, KENNEDY C. Network analysis of world subway systems using update graph theory[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2009, 2112:17-25.
doi: 10.3141/2112-03
|
| [2] |
陈峰, 胡映月, 李小红, 等. 城市轨道交通有权网络相继故障可靠性研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2016, 16(2):139-145.
|
|
CHEN Feng, HU Yingyue, LI Xiaohong, et al. Cascading failures in weighted network of urban rail transit[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2016, 16(2):139-145.
|
| [3] |
杜斐, 黄宏伟, 张东明, 等. 上海轨道交通网络的复杂网络特性及鲁棒性研究[J]. 武汉大学学报:工学版, 2016, 49(5):701-707.
|
|
DU Fei, HUANG Hongwei, ZHANG Dongming, et al. Analysis of characteristics of complex network and robustness in Shanghai metro network[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2016, 49(5):701-707.
|
| [4] |
SHI Jiangang, WEN Shiping, ZHAO Xianbo, et al. Sustainable development of urban rail transit networks:a vulnerability perspective[J]. Sustainability, 2019, 11(5):1-24.
doi: 10.3390/su11010001
|
| [5] |
SUN Daniel (Jian), ZHAO Yuhan, LU Qingchang. Vulnerability analysis of urban rail transit networks:a case study of Shanghai, China[J]. Sustainability, 2015, 7:6919-6936.
doi: 10.3390/su7066919
|
| [6] |
叶青. 基于复杂网络理论的轨道交通网络脆弱性分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2012, 22(2):122-126.
|
|
YE Qing. Vulnerability analysis of rail transit based on complex network theory[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2012, 22(2):122-126.
|
| [7] |
DU Zhouyang, TANG Jinjun, QI Yong, et al. Identifying critical nodes in metro network considering topological potential:a case study in Shenzhen city—China[J]. Physica A, 2020, 539:1-13.
|
| [8] |
路庆昌, 崔欣, 徐标, 等. 公交接驳场景下轨道交通网络脆弱性研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(8):141-146.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.08.020
|
|
LU Qingchang, CUI Xin, XU Biao, et al. Vulnerability research of rail transit network under bus connection scenarios[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(8):141-146.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.08.020
|
| [9] |
韩纪彬, 郭进利, 张新波. 上海市轨道交通网络可靠性研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2012, 22(12):103-108.
|
|
HAN Jibin, GUO Jinli, ZHANG Xinbo. Reliability analysis of Shanghai rail transit network[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2012, 22(12):103-108.
|
| [10] |
ZHANG Jianhua, WANG Ziqi, WANG Shuliang, et al. Vulnerability assessments of urban rail transit networks based on redundant recovery[J]. Sustainability, 2020, 12(14):1-13.
doi: 10.3390/su12010001
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.66.065102
|
| [12] |
袁若岑, 王丽琼, 温志伟. 基于攻击策略的城市轨道交通网络脆弱性研究[J]. 城市轨道交通研究, 2015, 18(8):57-61.
|
|
YUAN Ruocen, WANG Liqiong, WEN Zhiwei. On the vulnerability of urban rail transit network based on different attack strategies[J]. Urban Mass Transit, 2015, 18(8):57-61.
|
| [13] |
王彬, 戴剑勇, 邓先红. 城市复杂地铁网络级联失效抗毁性分析[J]. 南华大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 33(6):91-96.
|
|
WANG Bin, DAI Jianyong, DENG Xianhong. Failure analysis of urban complex metro network cascading failure[J]. Journal of University of South China:Science and Technology, 2019, 33(6):91-96.
|
| [14] |
MOTTER A E, LAI Y. Cascade-based attacks on complex networks[J]. Physical Review E, 2002, 66(6):1-4.
|
| [15] |
MORENO Y, PASTOR-SATORRAS R, VÁZQUEZ A, et al. Critical load and congestion instabilities in scale free networks[J]. Europhysics Letters, 2003, 62(2):292-298.
doi: 10.1209/epl/i2003-00140-7
|
| [16] |
WEI Duqu, LUO Xiaoshu, ZHANG Bo. Analysis of cascading failure in complex power networks under the load local preferential redistribution rule[J]. Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2012, 391(8):2771-2777.
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2011.12.030
|
| [17] |
PENG Xingzhao, YAO Hong, DU Jun, et al. Invulnerability of scale-free network against critical node failures based on a renewed cascading failure model[J]. Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2015, 421:69-77.
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2014.11.024
|
| [18] |
CHEN Hong, ZHANG Jun, DU Wenbo, et al. Cascading failures with local load redistribution in interdependent Watts-Strogatz networks[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics C, 2016, 27(11):1-10.
|
| [19] |
朱天曈, 丁坚勇, 郑旭. 基于改进TOPSIS法和德尔菲—熵权法综合权重法的电网规划方案综合决策方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2018, 46(12):91-99.
|
|
ZHU Tiantong, DING Jianyong, ZHENG Xu. A comprehensive decision-making method for power network planning schemes based on the combination of the improved TOPSIS method with Delphi-entropy weight method[J]. Power Systems Protection and Control, 2018, 46(12):91-99.
|