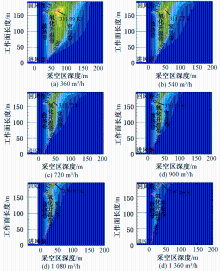
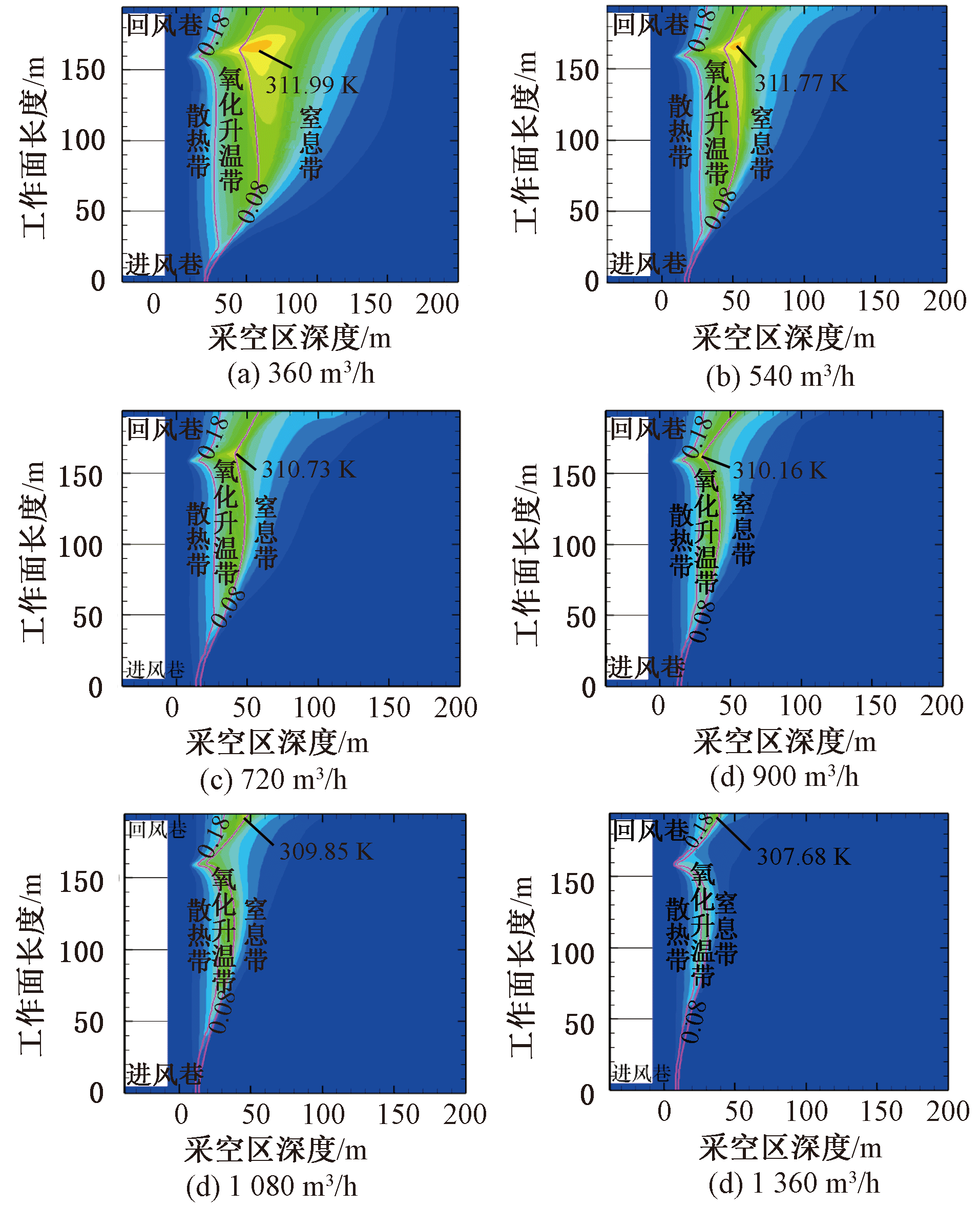
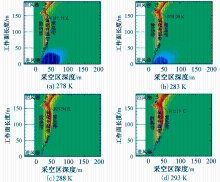
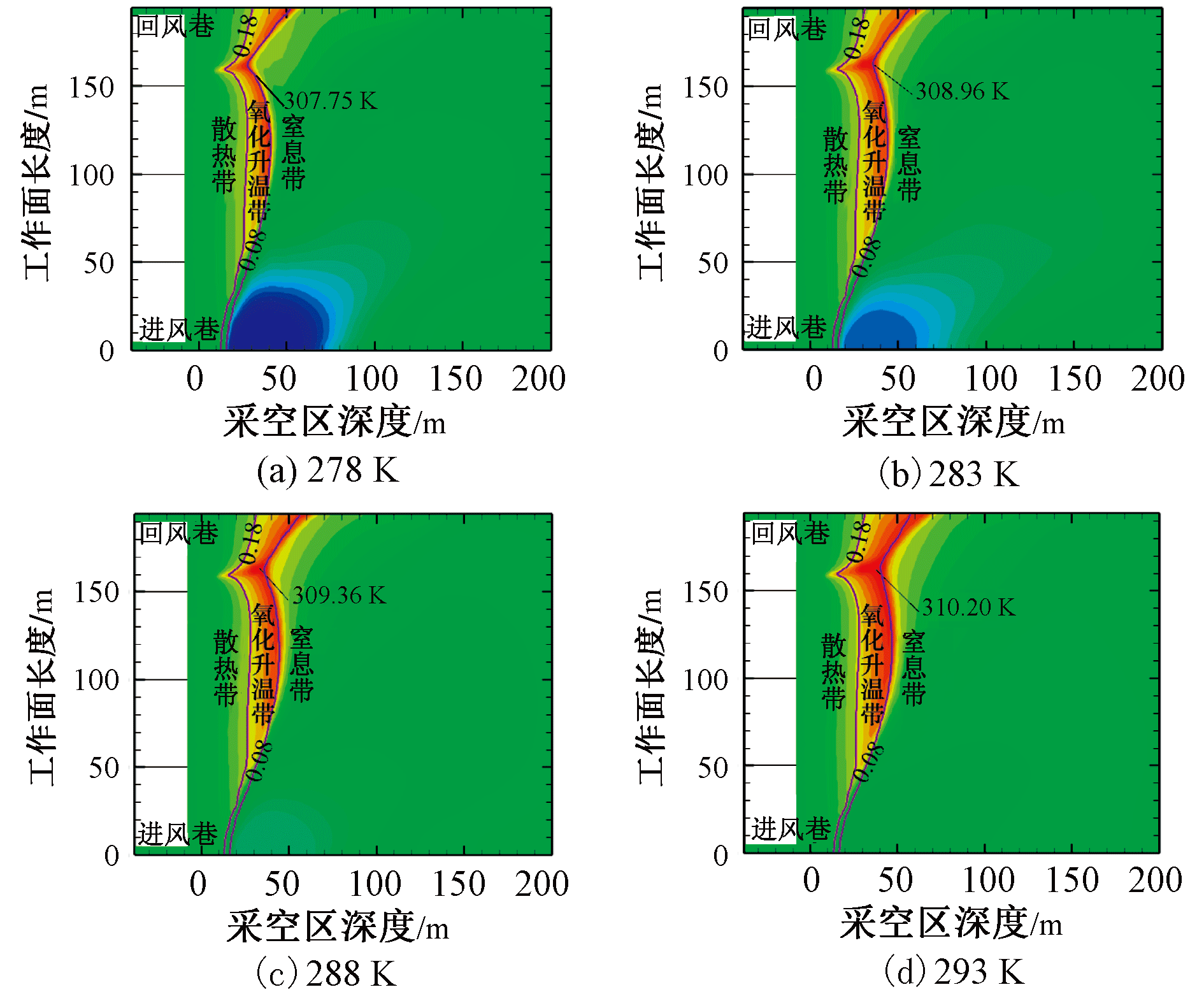
| [1] |
王志坚. 矿山救护指挥员[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 2007:5-8.
|
| [2] |
王继仁, 邓存宝. 煤微观结构与组分量质差异自燃理论[J]. 煤炭学报, 2007, 32(12):1291-1 296.
|
|
WANG Jiren, DENG Cunbao. The spontaneous combustion theory of coal microcosmic structure and component differences in quantity and quality[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2007, 32(12):1291-1 296.
|
| [3] |
王继仁. 煤自燃量子化学理论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007:69-81.
|
| [4] |
徐精彩, 薛韩玲, 文虎, 等. 煤氧复合热效应的影响因素分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2001, 11(2):34-39.
|
|
XU Jingcai, XUE Hanling, WEN Hu, et al. Analysis on influential factors of thermal effect in coal oxidation[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2001, 11(2): 34-39.
|
| [5] |
刘剑, 王继仁, 孙宝铮. 煤的活化能理论研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 1999, 24(3):94-98.
|
|
LIU Jian, WANG Jiren, SUN Baozheng. A study on the theory of activation energy of coal[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 1999, 24(3):94-98.
|
| [6] |
王德明, 辛海会, 戚绪尧, 等. 煤自燃中的各种基元反应及相互关系:煤氧化动力学理论及应用[J]. 煤炭学报, 2014, 39(8):1 667-1 674.
|
|
WANG Deming, XIN Haihui, QI Xuyao, et al. Mechanism and relationships of elementary reactions in spontaneous combustion of coal:the coal oxidation kinetics theory and application[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(8):1 667-1 674.
|
| [7] |
朱令起, 刘聪, 王福生. 煤自燃过程中自由基变化规律特性研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2016, 44(10):44-47.
|
|
ZHU Lingqi, LIU Cong, WANG Fusheng. Study on variation law and features of free radicals in coal spontaneous combustion process[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2016, 44(10):44-47.
|
| [8] |
JONES J C, HENDERSON K P, LITTLEFAIR J, et al. Kinetic parameters of oxidation of coals by heat-release measurement and their relevance to self-heating tests[J]. Fuel, 1998, 77(1/2):19-22.
doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(97)00155-5
|
| [9] |
BEAMISH B B, ARISOY A. Effect of mineral matter on coal self-heating rate[J]. Fuel, 2008, 87(1):125-130.
doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2007.03.049
|
| [10] |
SCHMIDT L, ELDER J, DAVIS J. Atmospheric oxidation of coal at moderate temperatures. effect of oxidation on the carbonizing properties of representative coking coals[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2003, 32(4):548-555.
doi: 10.1021/ie00015a018
|
| [11] |
KAM A Y, HIXSON A N, PERLMUTTER D D. The oxidation of bituminous coal-I development of a mathematical model[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1976, 31(9):815-819.
doi: 10.1016/0009-2509(76)80055-3
|
| [12] |
ITAY M, HILL C R, GLASSER D. A study of the low temperature oxidation of coal[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 1989, 21(2):81-97.
doi: 10.1016/0378-3820(89)90063-5
|
| [13] |
邓军, 文虎, 徐精彩. 煤自然发火预测理论及技术[M]. 西安: 陕西科学技术出版社, 2001:11.
|
| [14] |
吴玉国, 邬剑明, 张东坡, 等. 综放工作面连续注氮下采空区气体分布及“三带”变化规律[J]. 煤炭学报, 2011, 36(5):964-967.
|
|
WU Yuguo, WU Jianming, ZHANG Dongpo, et al. Distribution law of gas and change rule of ″three zones″ in the goaf of fully mechanized top-coal caving working face under the continuous nitrogen injection[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36(5):964-967.
|
| [15] |
REN T X, EDWARDS J S. Three-dimensional computational fluid dynamics modelling of methane flow through permeable strata around a longwall face[J]. Mining Technology: IMM Transaction Section A, 2000, 109(1): 41-48.
|
| [16] |
李宗翔, 单龙彪, 张文君. 采空区开区注氮防灭火的数值模拟研究[J]. 湖南科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2004, 19(3):5-9.
|
|
LI Zongxiang, SHAN Longbiao, ZHANG Wenjun. Numerical simulation study of nitrogen injection porocess for prevention and extinguishment in goaf[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Science and Technology:Natural Science Edition, 2004, 19(3):5-9.
|
| [17] |
崔传发. 采空区瓦斯抽采钻孔参数及注氮防灭火研究[J]. 工矿自动化, 2020, 46(3):12-20.
|
|
CUI Chuanfa. Research on gas drainage drilling parameters and nitrogen injection for fire prevention in goaf[J]. Industry and Mine Automation, 2020, 46(3):12-20.
|