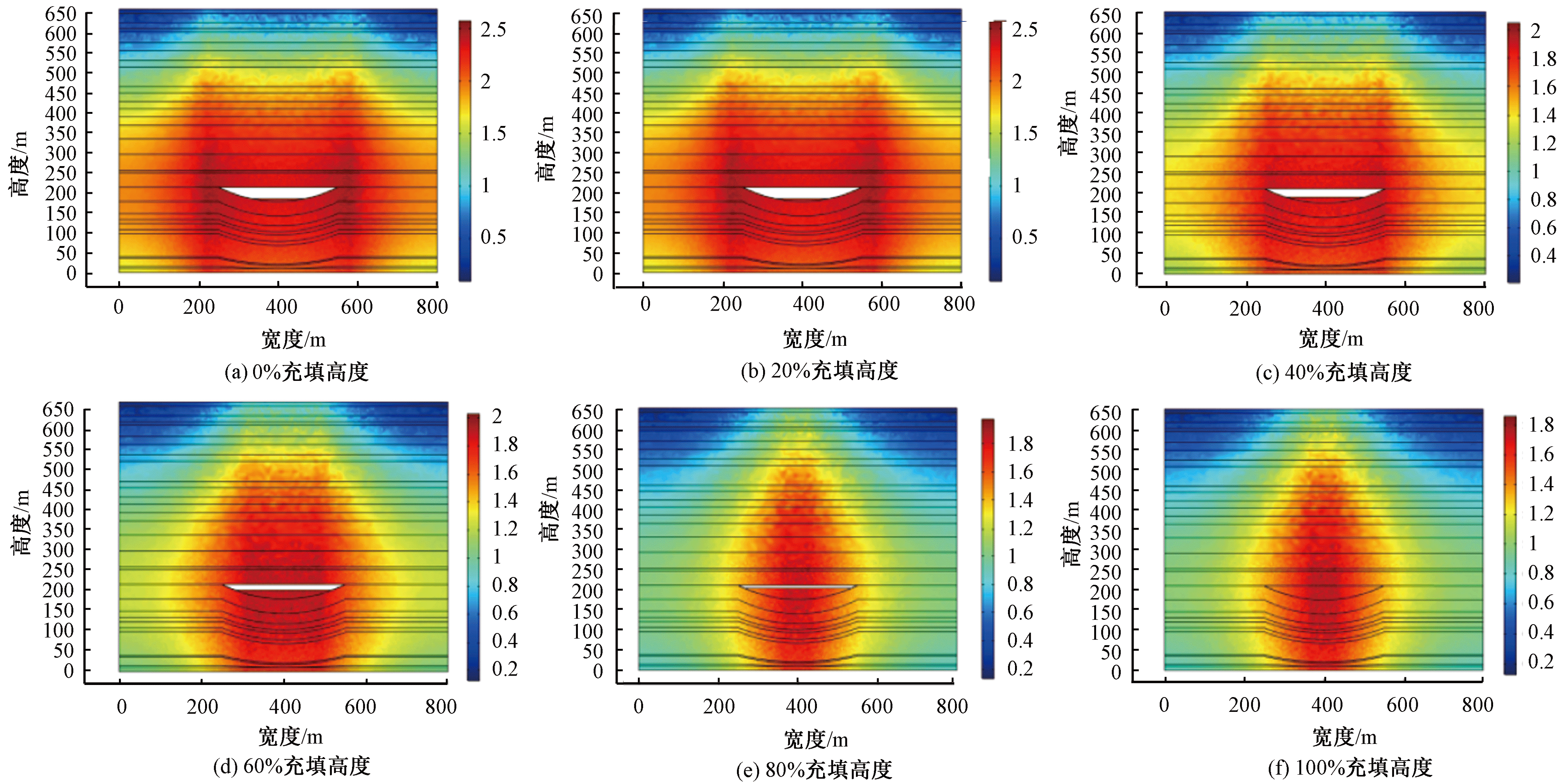
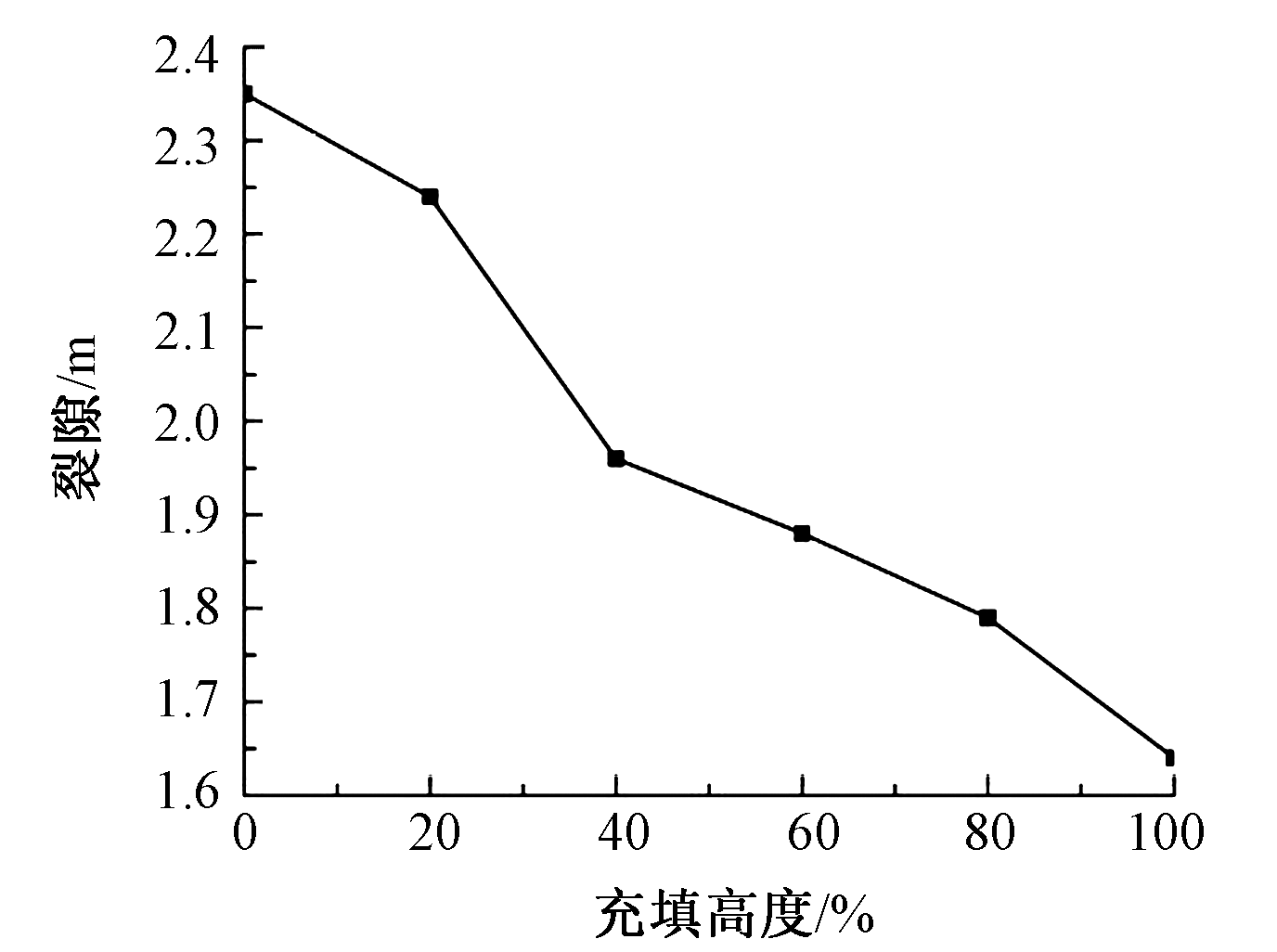
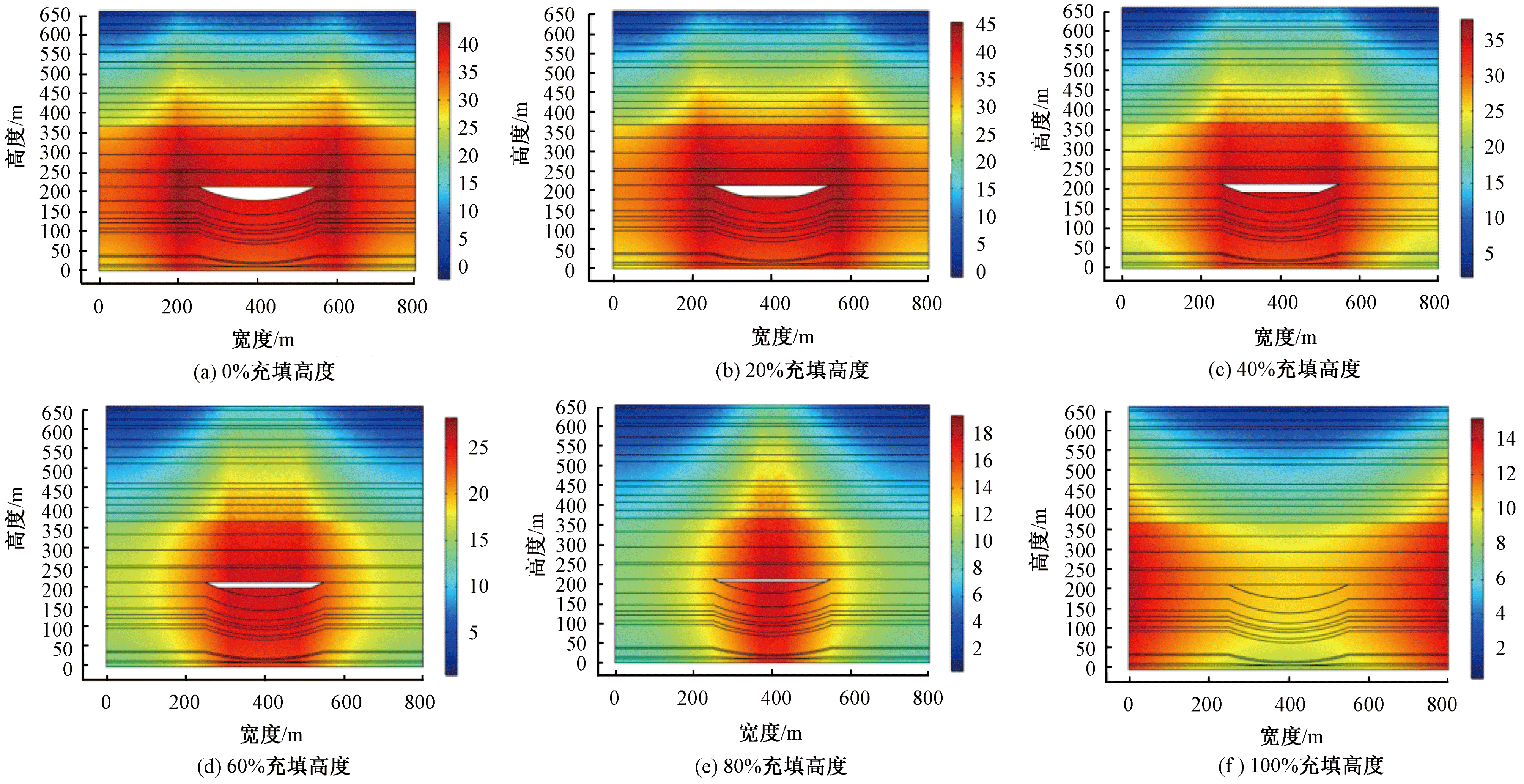
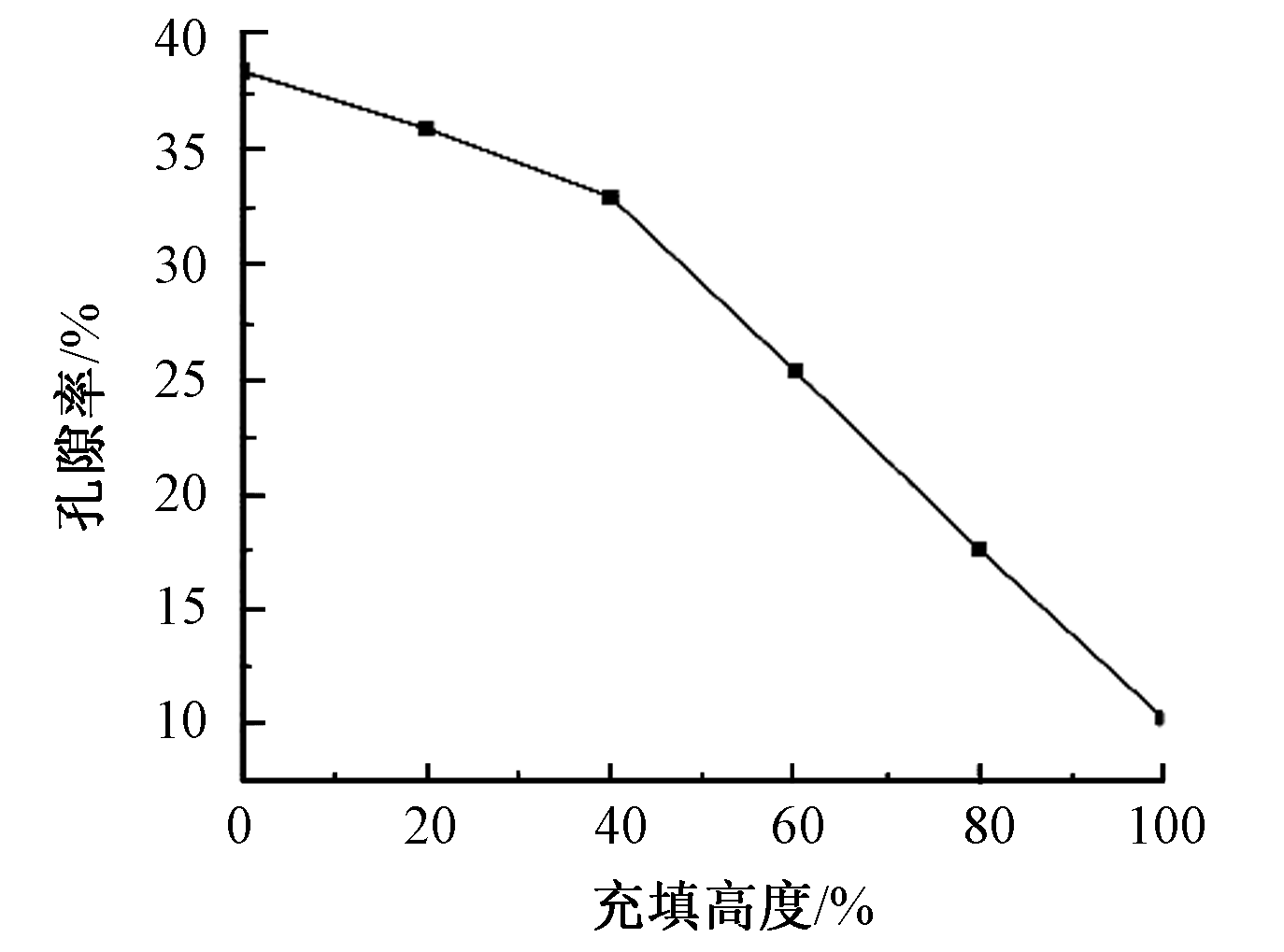
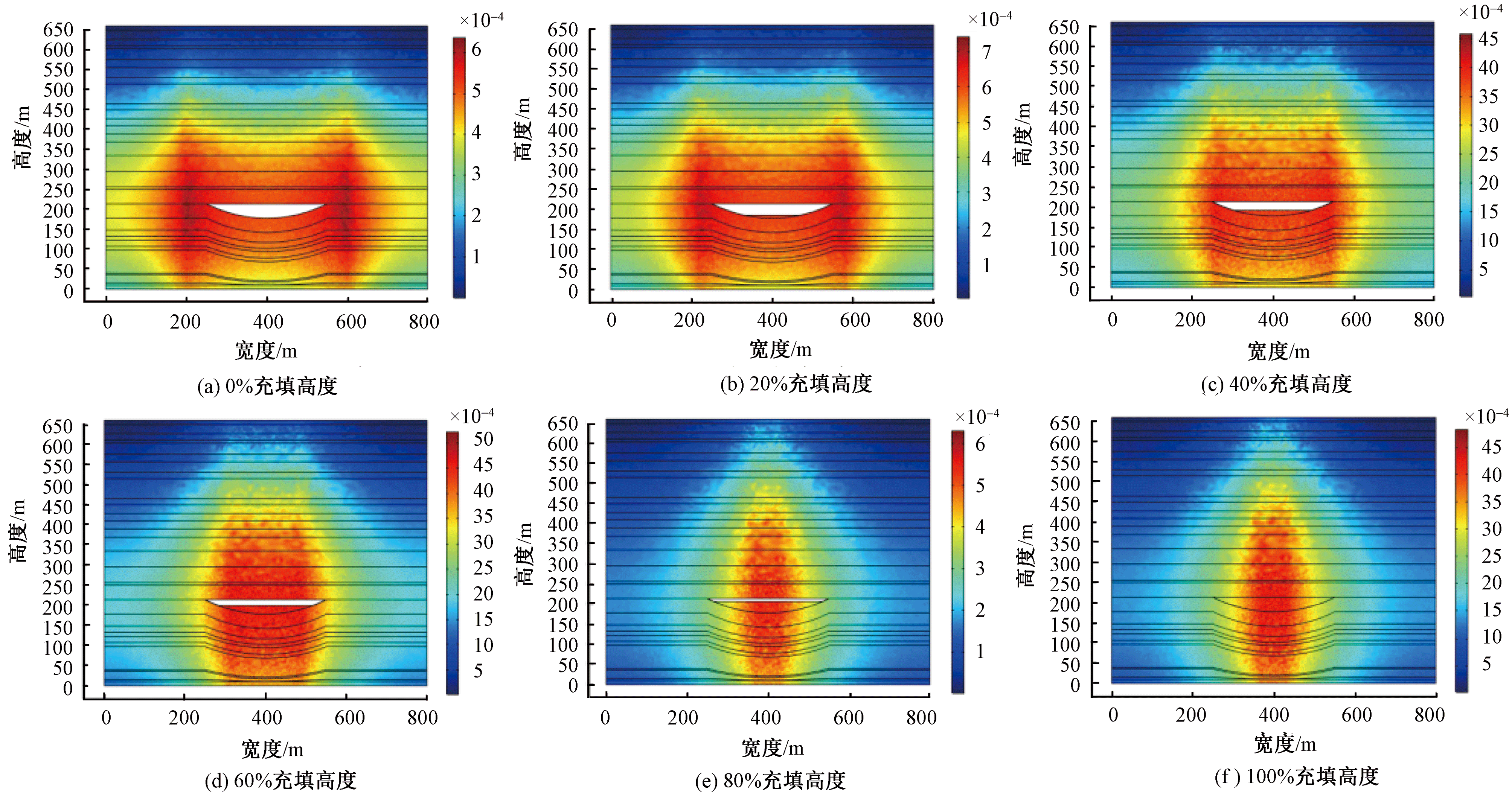
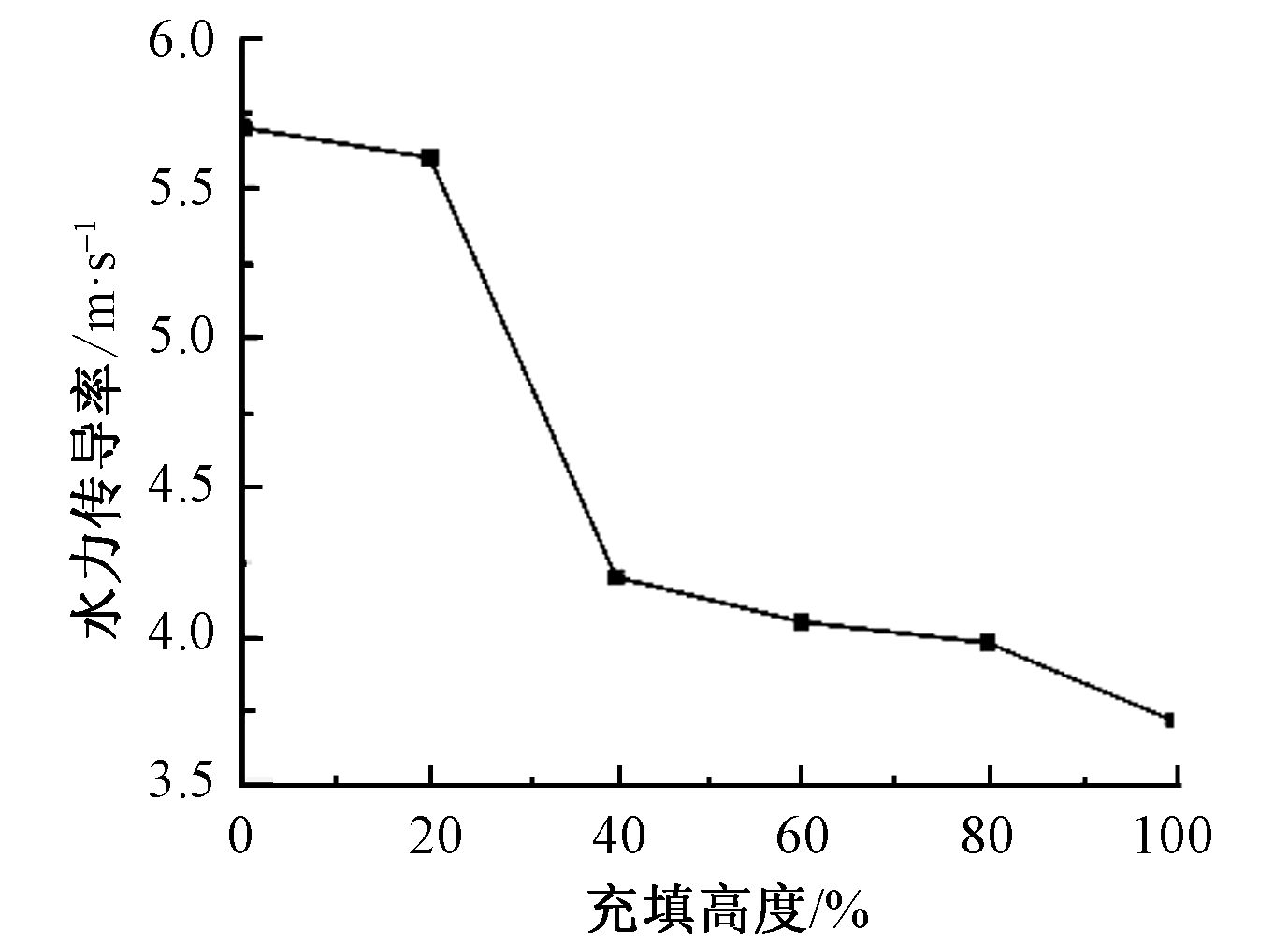
| [1] |
王志强, 郭晓菲, 高运, 等. 华丰煤矿覆岩离层注浆减沉技术研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2014, 33(增1):3249-3 255.
|
|
WANG Zhiqiang, GUO Xiaofei, GAO Yun, et al. Study of grouting technology of overburden-separation to reduce ground subsidence in Huafeng coal mine[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(S1):3249-3 255.
|
| [2] |
周英豪, 王文杰, 卢西洲, 等. 岩爆灾害博弈论组合赋权预测模型及应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(7):105-112.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.07.0620
|
|
ZHOU Yinghao, WANG Wenjie, LU Xizhou, et al. Combination weighting prediction model and application of rock burst disaster based on game theory[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(7):105-112.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.07.0620
|
| [3] |
姜岩, 高延法. 矿山开采塌陷环境治理方法[J]. 矿业研究与开发, 1997(1):14-16.
|
|
JIANG Yan, GAO Yanfa. The method on control and treatment of subsidence in mining[J]. Mining Research and Development, 1997(1):14-16.
|
| [4] |
doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2022.0371
|
|
ZUO Jianping, YU Meilu, SUN Yunjiang, et al. Analysis of fracture mode transformation mechanism and mechanical model with different thickness rock strata[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022:Doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2022.0371.
doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2022.0371
|
| [5] |
姚文涛, 寇天昊, 樊斌, 等. 采动覆岩离层注浆对矿井安全的影响评价[J]. 煤炭技术, 2022, 41(8):170-174.
|
|
YAO Wentao, KOU Tianhao, FAN Bin, et al. Influence evaluation of mining-induced strata separation grouting on mine safety[J]. Coal Technology, 2022, 41(8):170-174.
|
| [6] |
宁掌玄, 张红珠, 冯美生. 采动覆岩离层注浆的相似材料及数值模拟[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 29(3):369-372.
|
|
NING Zhangxuan, ZHANG Hongzhu, FENG Meisheng. Similar materials and numerical simulation on grouting in overlying strata of mining face[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University:Natural Science, 2010, 29(3):369-372.
|
| [7] |
徐睿, 谢亚涛, 周坤鹏. 煤炭绿色保水开采[J]. 矿业快报, 2008(6):20-22,32.
|
|
XU Rui, XIE Yatao, ZHOU Kunpeng. Green water preserved mining of coal[J]. Modern Mining, 2008(6):20-22,32.
|
| [8] |
牟兆刚. 覆岩离层注浆工程有关技术问题探讨: 以夏店煤矿为例[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2021, 33(12):50-55.
|
|
MU Zhaogang. Probe into overburden abscission layer grouting engineering related technical jssues-a case study of xiadian coalmine[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2021, 33(12):50-55.
|
| [9] |
肖民. 榆神矿区榆树湾矿保水开采注浆离层参数研究[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2006.
|
|
XIAO Min. Study on parameters of water-preserved-mining grouting bed-separation in yushuwan mine yushen coalfield[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2006.
|
| [10] |
刘玉德. 沙基型浅埋煤层保水开采技术及其适用条件分类[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2008.
|
|
LIU Yude. The technology and usable conditions' classification of aquifer-protective mining in shallow sand-bedrock-coal seam[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2008.
|