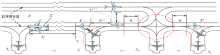
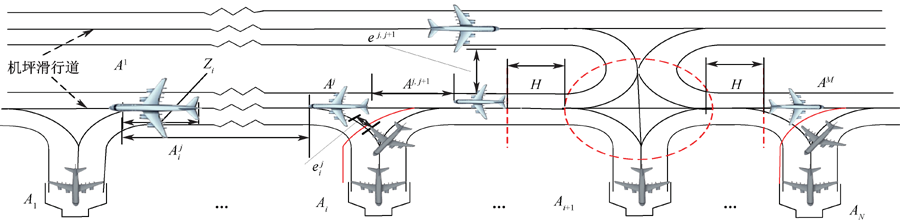
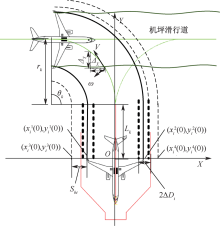
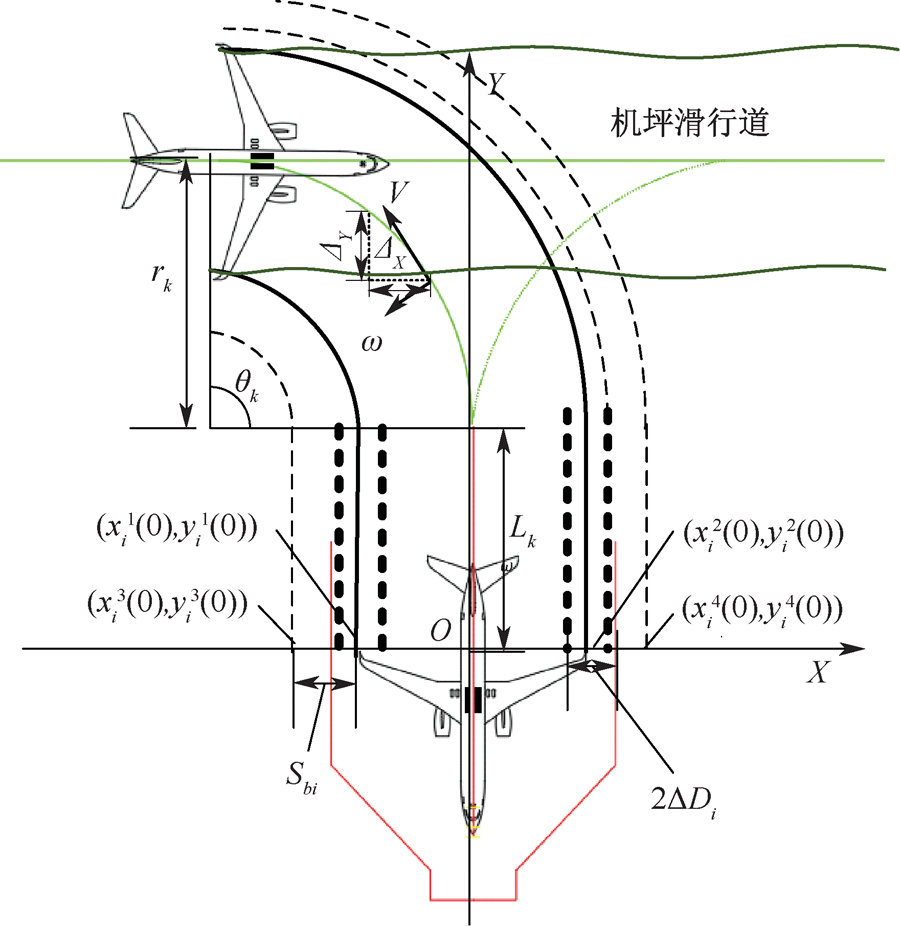
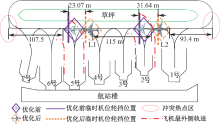
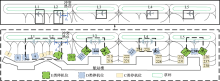
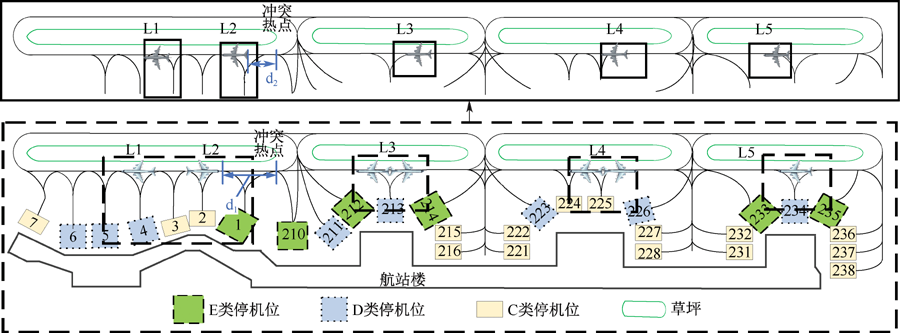
| [1] |
ALOMAR I, TOLUJEW J, MEDVEDEVS A. Analysis of riga international airport flight delays[C]. International Conference on Reliability and Statistics in Transportation and Communication, 2017: 519-529.
|
| [2] |
VERMA S, LEE H, MARTIN L, et al. Evaluation of a tactical surface metering tool for Charlotte Douglas international airport via human-in-the-loop simulation[C]. 2017 IEEE/AIAA 36th Digital Avionics Systems Conference(DASC), 2017: 1-10.
|
| [3] |
蒋洪迅, 马仁义. 面向靠桥率及道口冲突率的航班-机位指派问题优化模型及其启发式算法研究[J]. 系统科学与数学, 2021, 41(1):75-98.
doi: 10.12341/jssms14097
|
|
JIANG Hongxun, MA Renyi. Rates of closed-bridge and crossing-collision oriented optimizationModel on aircraft-gate assignment and its heuristics[J]. Journal of Systems Science and Mathematical Sciences, 2021, 41(1):75-98.
doi: 10.12341/jssms14097
|
| [4] |
李云鹏, 张则强, 管超, 等. 停机位分配问题的整数规划模型及启发式求解方法[J]. 系统工程, 2020, 38(1):103-112.
|
|
LI Yunpeng, ZHANG Zeqiang, GUAN Chao, et al. Integer programming model and heuristic method for gate assignment problem[J]. Systems Engineering, 2020, 38(1):103-112.
|
| [5] |
杨新湦, 安琪. 基于最小扰动的停机位及滑行路径临时改派策略[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2017, 39(2):23-27,60.
|
|
YANG Xinsheng, AN Qi. Reassignment strategy of airport gate and taxiing route based on minimum disturbance[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2017, 39(2):23-27,60.
|
| [6] |
TANG Chinghui. A gate reassignment model for the taiwan taoyuan airport under temporary gate shortages and stochastic flight delays[J]. IEEE Trans. Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part A, 2011, 41(4):637-350.
doi: 10.1109/TSMCA.2010.2089512
|
| [7] |
余洲, 张兆宁. 基于模糊数的机场滑行冲突预测方法[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(3):90-95.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.03.0938
|
|
YU Zhou, ZHANG Zhaoning. A prediction method of airport taxiing conflicts based on fuzzy numbers[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(3):90-95.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.03.0938
|
| [8] |
康瑞, 杨凯. 航空器逆向滑行冲突风险评估模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(10):39-45.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.10.006
|
|
KANG Rui, YANG Kai. Risk assessment model of aircraft opposite taxiing conflict[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(10):39-45.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.10.006
|
| [9] |
LUO Xiao, TANG Yong, WU Honggang, et al. Real-time adjustment strategy for conflict-free taxiing route of A-SMGCS aircraft on airport surface[C]. IEEE International Conference on Mrchatronics & Automation, 2020:929-934.
|
| [10] |
MH 5001—2021, 民用机场飞行区技术标准[S].
|
|
MH 5001-2021, Aerodrome technical standards[S].
|
| [11] |
中国民用航空局. 中国民用航空局航班备降工作规则[L].2020-04-17.
|
| [12] |
ŠPETLÍK M, BREZINA J. Groundwater contaminant transport solved by Monte Carlo methods accelerated by deep learning meta-model[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(15):DOI:10.3390/APP12157382.
|
| [13] |
谷润平, 吕智鸿, 魏志强. 多跑道独立进近中的TCAS告警风险仿真与分析[J]. 飞行力学, 2021, 39(3):48-53.
|
|
GU Runping, LYU Zhihong, WEI Zhiqiang. Simulation and analysis of TCAS warning risk inmulti-runway independent approach[J]. Flight Dynamics, 2021, 39(3):48-53.
|
| [14] |
SHI Kaize, PENG Xueping, LU Hao, et al. Application of social sensors in natural disasters emergency management: a review[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 2022, 10(6):3143-3158.
doi: 10.1109/TCSS.2022.3211552
|
| [15] |
石昊, 赵育善, 师鹏. 航天器近距离相对运动的轨迹偏差分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2017, 43(3):636-644.
|
|
SHI Hao, ZHAO Yushan, SHI Peng. Analysis of trajectory deviation for spacecraft relative motion in close-range[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017, 43(3):636-644.
|