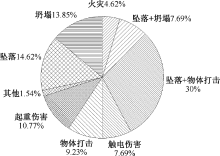
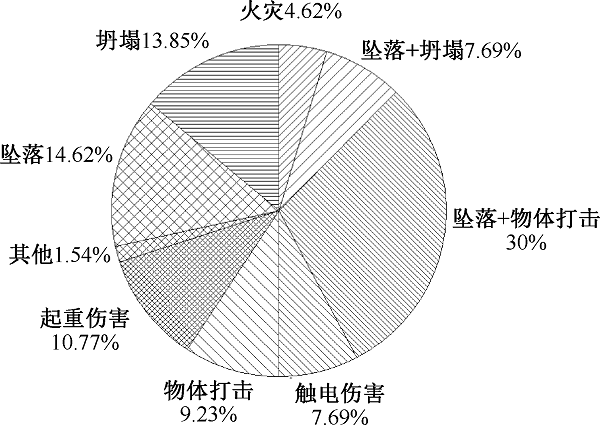
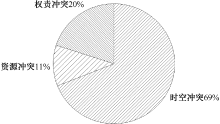
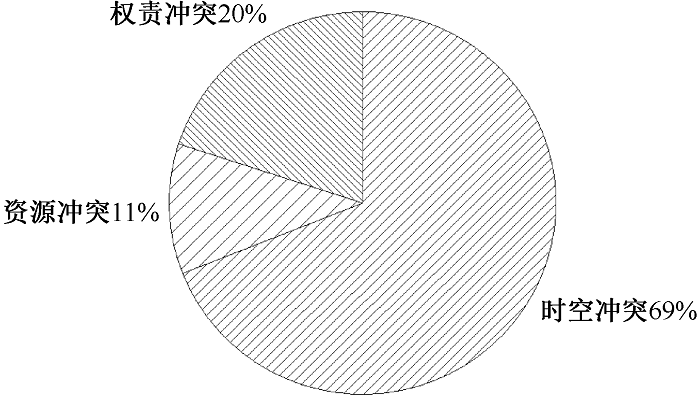
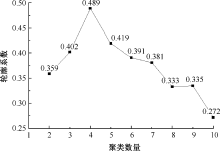
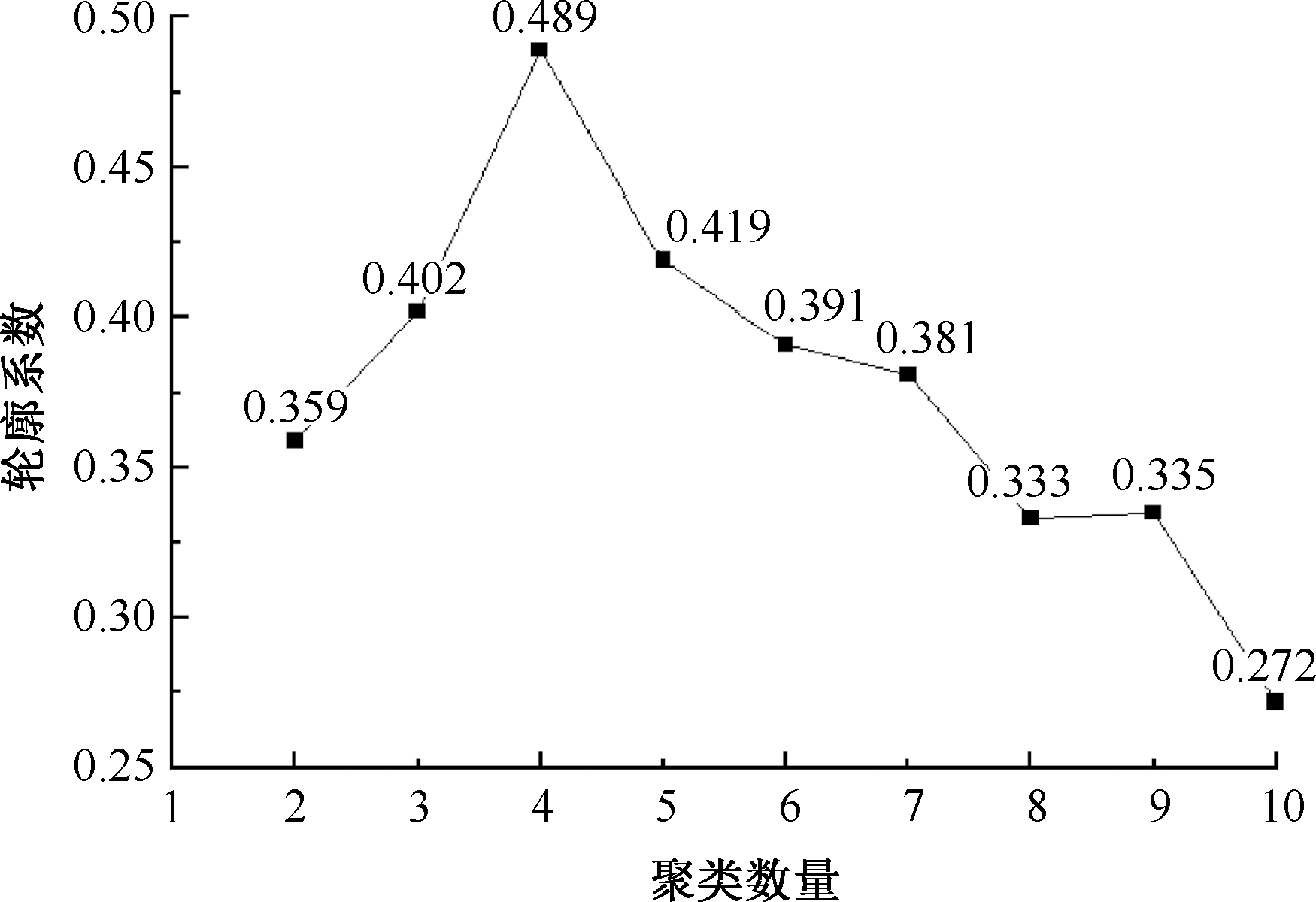
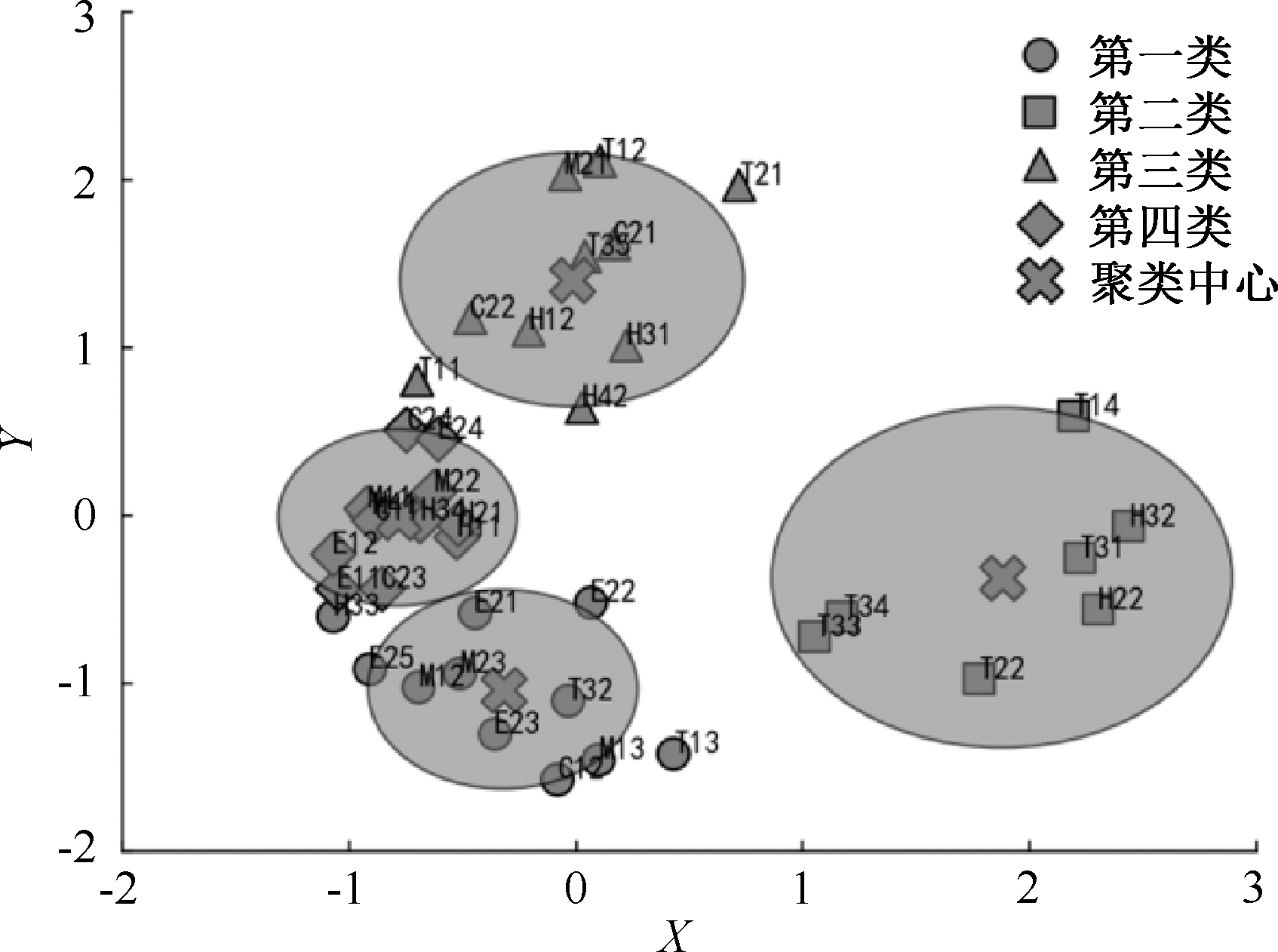
| [1] |
YEO C, BHANDARI J, ABBASSI R, et al. Dynamic risk analysis of offloading process in floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) platform using Bayesian network[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2016,41:259-269.
|
| [2] |
AKINCI B, FISCHEN M, LEVITT R, et al. Formalization and automation of time-space conflict analysis[J]. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 2002, 16(2):124-134.
|
| [3] |
MOON H, DAWOOD N, KANG L, et al. Development of workspace conflict visualization system using 4D object of work schedule[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2014, 28(1):50-65.
|
| [4] |
胡超, 赵春菊, 周宜红, 等. 高拱坝仓面施工时空冲突分析与调整方法研究[J]. 水力发电学报, 2017, 36(5):19-27.
|
|
HU Chao, ZHAO Chunju, ZHOU Yihong, et al. Time-space conflict analysis and adjustment methods for pouring concrete of higharch dams[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2017, 36(5):19-27.
|
| [5] |
王建平, 聂本武, 李智. 三峡升船机立体交叉作业的风险控制措施研究[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2013, 20(1):147-150.
|
|
WANG Jianping, NIE Benwu, LI Zhi. Research on the risk control countermeasures of the grade separation operation of ship lift in three gorges[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2013, 20(1):147-150.
|
| [6] |
江新, 吴园莉. 水电工程项目群交叉作业风险演化机理研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2015, 25(12):157-163.
|
|
JIANG Xin, WU Yuanli. Research on evolution mechanisms of risks in hydropower project group cross operation[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2015, 25(12):157-163.
|
| [7] |
屈静, 张明星, 张明, 等. 基于压气站场的交叉作业安全风险评价模型研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2022, 22(3):1163-1169.
|
|
QU Jing, ZHANG Mingxing, ZHANG Ming, et al. Research on the safety risk control mode of compressor field based on cross operation[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2022, 22(3):1163-1169.
|
| [8] |
ROZENFELD O, SACKS R, ROSENFELD Y, et al. Construction job safety analysis[J]. Safety Science, 2010, 48(4):491-498.
|
| [9] |
应急管理部办公厅. 生产安全事故调查报告编制指南(试行)[EB/OL]. (2023-03-16). https://www.mem.gov.cn/gk/zfxxgkpt/fdzdgknr/202303/t20230316_444990.shtml.
|
| [10] |
方雪, 谢朝武, 黄锐. 扎根理论下国内漂流旅游安全事故成因机制[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(4):23-29.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.04.004
|
|
FANG Xue, XIE Chaowu, HUANG Rui. Formation mechanism of safety accidents in domestic drifting tourism based on GT[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(4):23-29.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.04.004
|
| [11] |
闫淑敏, 杨小丽. 基于扎根理论的高校科研人员创新动力研究[J]. 科技管理研究, 2019, 39(1):39-45.
|
|
YAN Shumin, YANG Xiaoli. Research on innovation motivation of scientific research personnel in colleges and universities based on grounded theory[J]. Science and Technology Management Research, 2019,39(1): 39-45.
|
| [12] |
AYHAN B U, DOĞAN N B, TOKDEMIR O B. An association rule mining model for the assessment of the correlations between the attributes of severe accidents[J]. Journal of Civil Engineering and Management, 2020,26(4):315-330.
|
| [13] |
周林, 平西建, 徐森, 等. 基于谱聚类的聚类集成算法[J]. 自动化学报, 2012, 38(8):1335-1342.
|
|
ZHOU Lin, PING Xijian, XU Sen, et al. Cluster ensemble based on spectral clustering[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(8):1335-1342.
|
| [14] |
梅睿, 吕志勇, 顾文, 等. 基于主成分分析和谱聚类的短期风功率预测[J]. 现代电力, 2023, 40(1):35-41.
|
|
MEI Rui, LYU Zhiyong, GU Wen, et al. Short-term wind power prediction based on principal component analysis and spectral clustering[J]. Modern Electric Power, 2023, 40(1):35-41.
|
| [15] |
胡长明, 刘一衡, 黄华, 等. AHP-改进物元法在整体钢平台顶升模架体系安全风险评估中的应用[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2024, 24(1):33-41.
|
|
HU Changming, LIU Yiheng, HUANG Hua, et al. Application of AHP improved matter-element method in safety risk assessment of integral steel platform jacking formwork system[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2024, 24(1):33-41.
|
| [16] |
KAPLAN S G B J. On the quantitative definition of risk[J]. Risk Analysis, 1981, 1(1):11-27.
|
| [17] |
郑彬彬, 冯婷婷, 王佳贺, 等. 基于文本挖掘的城镇燃气事故致因及关联分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(7):190-195.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.07.1644
|
|
ZHENG Binbin, FENG Tingting, WANG Jiahe, et al. Causes and correlation analysis of urban gas accidents based on text mining[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(7):190-195.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.07.1644
|
| [18] |
李鑫, 阳富强. 危化品事故人为因素关联规则挖掘与分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(11):134-139.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.11.2387
|
|
LI Xin, YANG Fuqiang. Human factor association rules mining and analysis for hazardous chemical accidents[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(11):134-139.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.11.2387
|
| [19] |
应急管理部. 北京丰台长峰医院“4·18”重大火灾事故调查报告[EB/OL]. (2023-10-25). https://www.mem.gov.cn/gk/zfxxgkpt/fdzdgknr/202310/t20231025_466731.shtml.
|