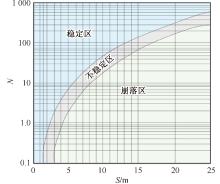
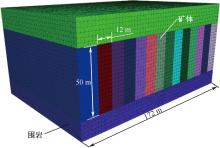
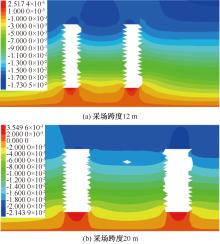
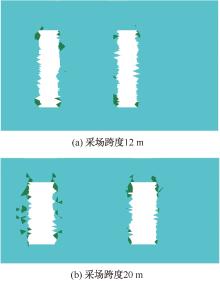
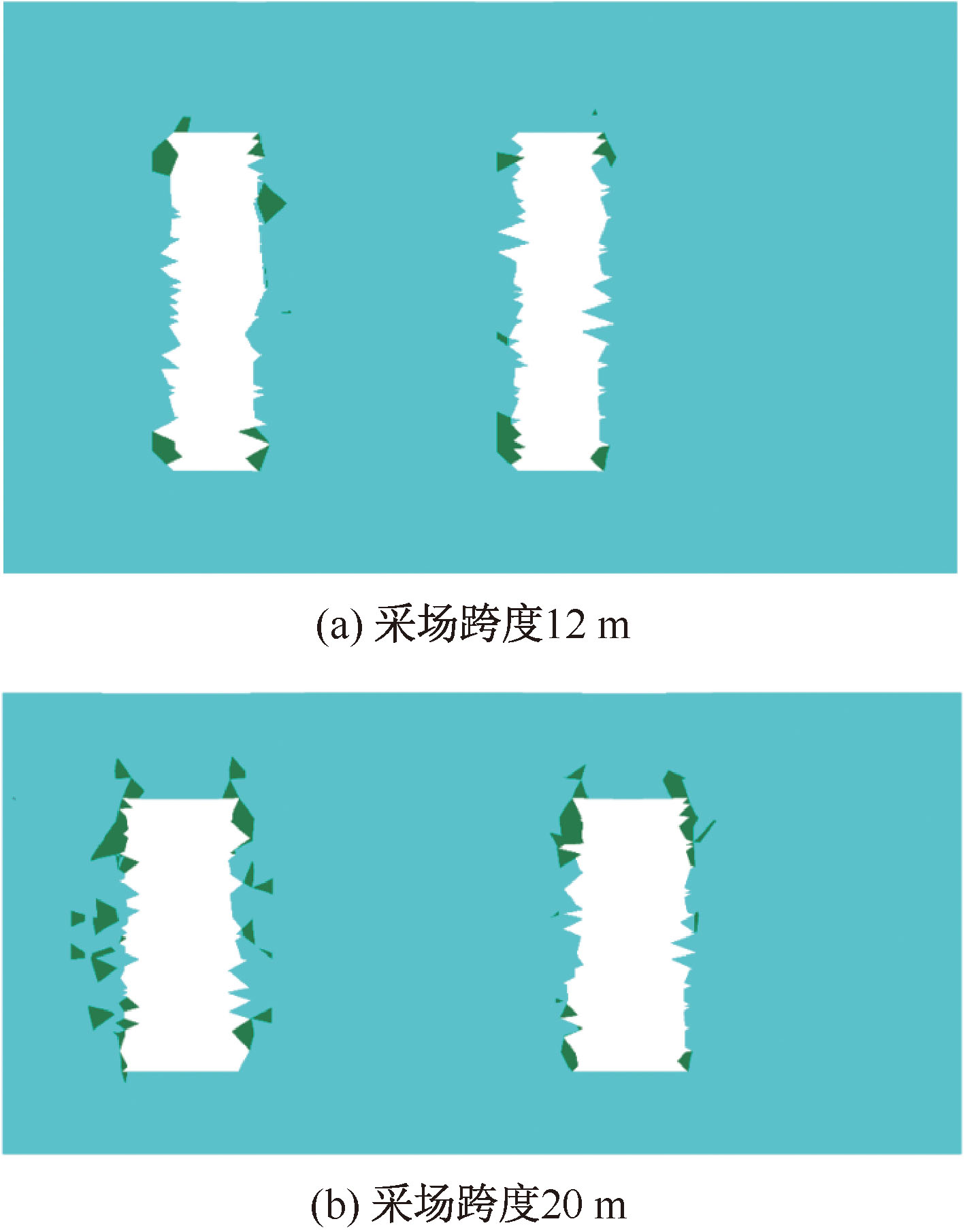
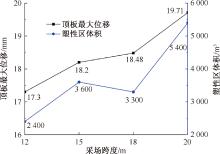
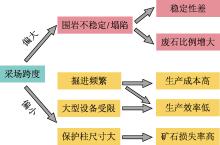
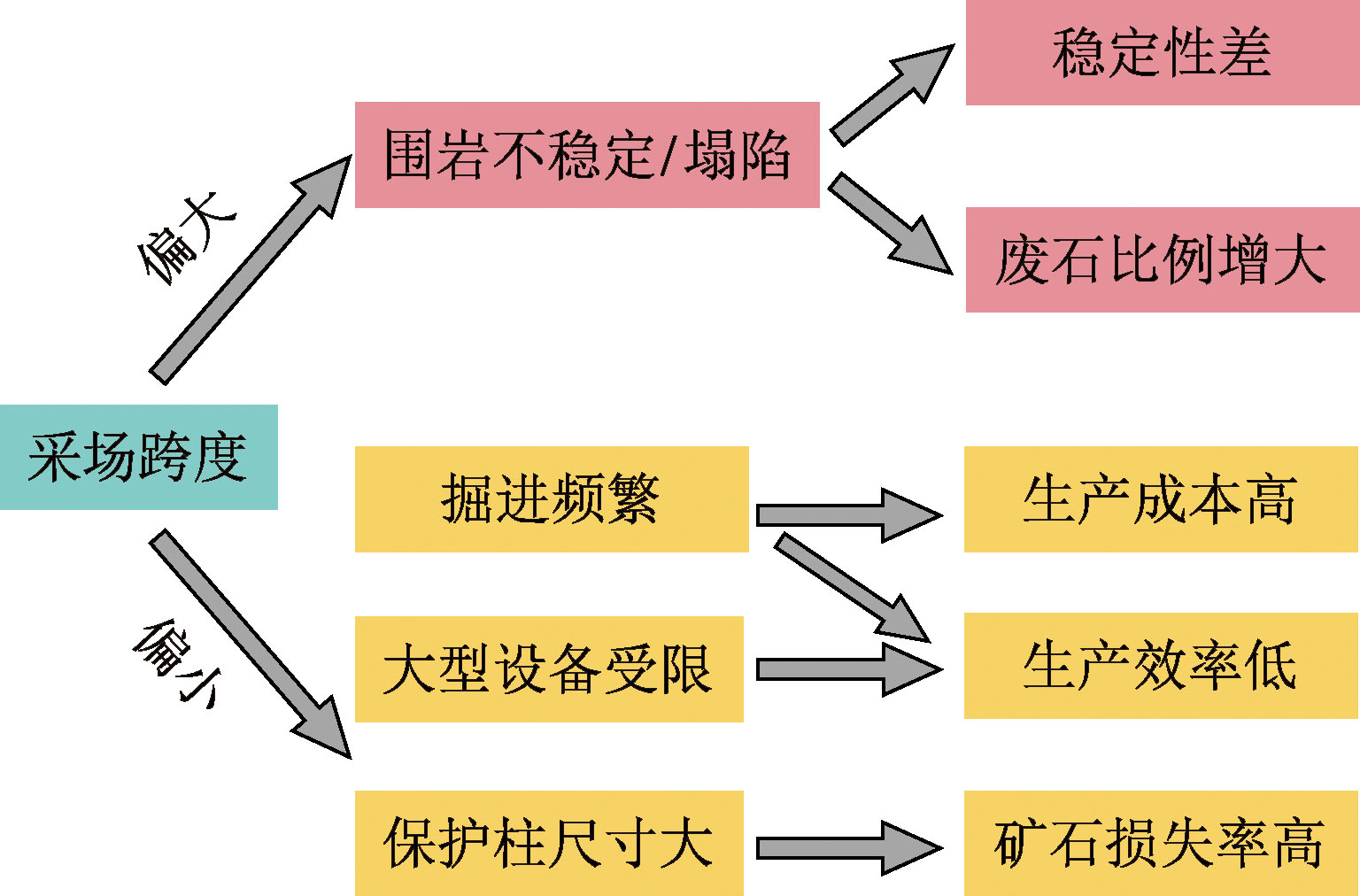
| [1] |
郭文兵, 刘玄, 杨伟强, 等. 断层影响下采动覆岩与地表移动特征[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(12): 38-46.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.12.0126
|
|
GUO Wenbing, LIU Xuan, YANG Weiqiang, et al. Characteristics of mining overburden and surface movement under influence of faults[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(12):38-46.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.12.0126
|
| [2] |
聂培强, 郑永升, 姜千山, 等. 金青顶矿区采场稳定性分析[J]. 黄金, 2025, 46(5): 28-32, 57.
|
|
NIE Peiqiang, ZHENG Yongsheng, JIANG Qianshan, et al. Stope stability analysis in the Jinqingding mining district[J]. Gold, 2025, 46(5): 28-32, 57.
|
| [3] |
SWIFT G, REDDISH D. Stability problems associated with an abandoned ironstone mine[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2002, 61(3): 227-239.
doi: 10.1007/s10064-001-0147-9
|
| [4] |
朱志岗, 侯克鹏, 孙华芬, 等. 基于3种计算方法的采空区顶板稳定性综合分析[J]. 化工矿物与加工, 2020(5): 11-14, 17.
|
|
ZHU Zhigang, HOU Kepeng, SUN Huafen, et al. Comprehensive analysis of roof stability in goaf based on three calculation methods[J]. Industrial Minerals & Processing, 2020(5): 11-14, 17.
|
| [5] |
NOMIKOS P P, SOFIANOS A I, TSOUTRELIS C E. Structural response of vertically multi-jointed roof rock beams[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2002, 39(1): 79-94.
|
| [6] |
杨勇, 张敏思, 张飞, 等. 红岭多金属矿复杂采空区稳定性[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(35): 14982-14987.
|
|
YANG Yong, ZHANG Minsi, ZHANG Fei, et al. Stability of complex lead mined-out area of an polymetallic mine in Hongling[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(35):14982-14987.
|
| [7] |
ZHANG Long, HU Jianhua, WANG Xueliang, et al. Optimization of stope structural parameters based on Mathews stability graph probability model[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2018, 2018(1): DOI: 10.1155/2018/1754328.
|
| [8] |
胡高建, 杨天鸿, 胡忠强, 等. 基于Mathews稳定图等方法的多角度采空区群稳定性分析评价[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2017, 34(2): 348-354.
|
|
HU Gaojian, YANG Tianhong, HU Zhongqiang, et al. Mathews-stability-method-based multi-angle analysis and evaluation of mined-out zones stability[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2017, 34(2): 348-354.
|
| [9] |
王登华, 彭府华, 张智博, 等. 基于微震监测多方法的采空区群稳定性分析[J]. 有色金属:矿山部分, 2023, 75(6): 37-45.
|
|
WANG Denghua, PENG Fuhua, ZHANG Zhibo, et al. Multi-method stability analysis on large-area goaf group based on micro-seismic monitoring[J]. Nonferrous Metals: Mining Section, 2023, 75(6): 37-45.
|
| [10] |
SUM Mingzhi, REN Fengyu, DING Hangxing. Optimization of stope structure parameters based on the mined orebody at the Meishan iron mine[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2021, 2021(1): DOI: 10.1155/2021/8052827.
|
| [11] |
ZHAO Xingdong, ZHOU Xin. Design method and application of stope structure parameters in deep metal mines based on an improved stability graph[J]. Minerals, 2022, 13(1): DOI: 10.3390/min13010002.
|
| [12] |
刘培正, 张传信, 胡永泉, 等. 厚大矿体分段空场嗣后充填采场结构参数优化研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2009(11): 10-13, 123.
|
|
LIU Peizheng, ZHANG Chuanxin, HU Yongquan, et al. Research on the optimization of structural parameters for heavy ore-body by sublevel open-stope with subsequent filling[J]. Metal Mine, 2009(11): 10-13, 123.
|
| [13] |
蔡春林. 软弱直接顶磷矿采场结构参数优化研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2024.
|
|
CAI Chunlin. Research on optimization of structural parameters of weak direct top phosphate mine stopes[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2024.
|
| [14] |
段泽锋, 黄德镛, 贾子月, 等. 某铅锌矿分段凿岩阶段采场法采场稳定性研究[J]. 矿业研究与开发, 2025, 45(1): 71-78.
|
|
DUAN Zefeng, HUANG Deyong, JIA Ziyue, et al. Study on stope stability in a lead-zinc mine mined by sublevel rock-cutting stage room method[J]. Mining Research and Development, 2025, 45(1): 71-78.
|
| [15] |
付士根, 刘岩, 魏杰, 等. 大理石矿采场结构参数的模拟优化研究[J]. 合肥工业大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 43(1): 108-112.
|
|
FU Shigen, LIU Yan, WEI Jie, et al. Research on simulation and optimization of structural parameters of marble mining stope[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology: Natural Science, 2020, 43(1): 108-112.
|
| [16] |
DU Han, LI Xuefeng, HUANG Xuxing, et al. Optimization of stope structural parameters for steeply dipping thick ore bodies: based on the simulated annealing algorithm[J]. Applied Sciences, 2024, 14(24): DOI: 10.3390/app142411597.
|
| [17] |
谢伟, 倪彬, 李乾龙, 等. 基于Mathews图解法的采空区稳定性分析[J]. 金属矿山, 2022(6):40-45.
|
|
XIE Wei, NI Bin, LI Qianlong, et al. Stability analysis of goaf based on Mathews graphic method[J]. Metal Mine, 2022(6):40-45.
|
| [18] |
杨学武. 昆钢马鞍山铁矿2号矿体中厚部分采矿方法优化研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2022.
|
|
YANG Xuewu. Research on optimization of mining methods for the medium-thick part of No.2 ore body of Kungang Maanshan iron mine[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2022.
|
| [19] |
HEIDARZADEH S, SAEIDI A, ROULEAU A. Evaluation of the effect of geometrical parameters on stope probability of failure in the open stoping method using numerical modeling[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2019, 29(3): 399-408.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2018.05.011
|
| [20] |
ZHOU Kunyou, DOU Linming, LI Xuwei, et al. Coal burst and mining-induced stress evolution in a deep isolated main entry area: a case study[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2022, 137: DOI: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2022.106289.
|
| [21] |
曹英莉. 基于CRITIC赋权法的采场结构参数优选模拟研究[J]. 矿业研究与开发, 2021, 41(3): 5-9.
|
|
CAO Yingli. Simulation study on optimization of stope structure parameters based on CRITIC weighting method[J]. Mining Research and Development, 2021, 41(3): 5-9.
|