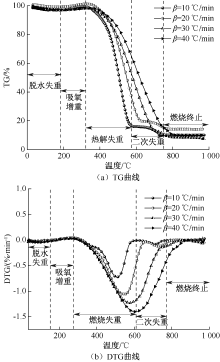
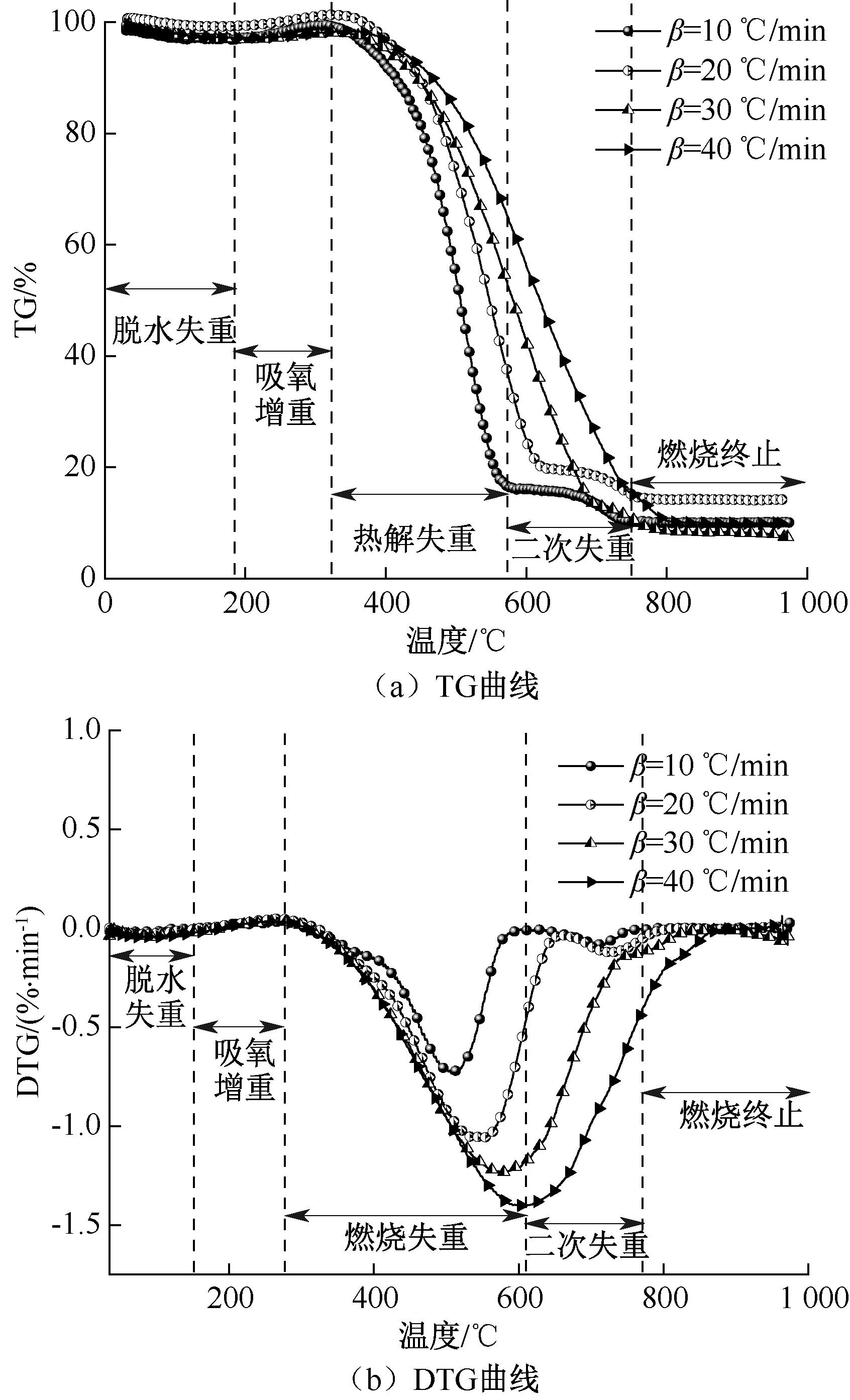
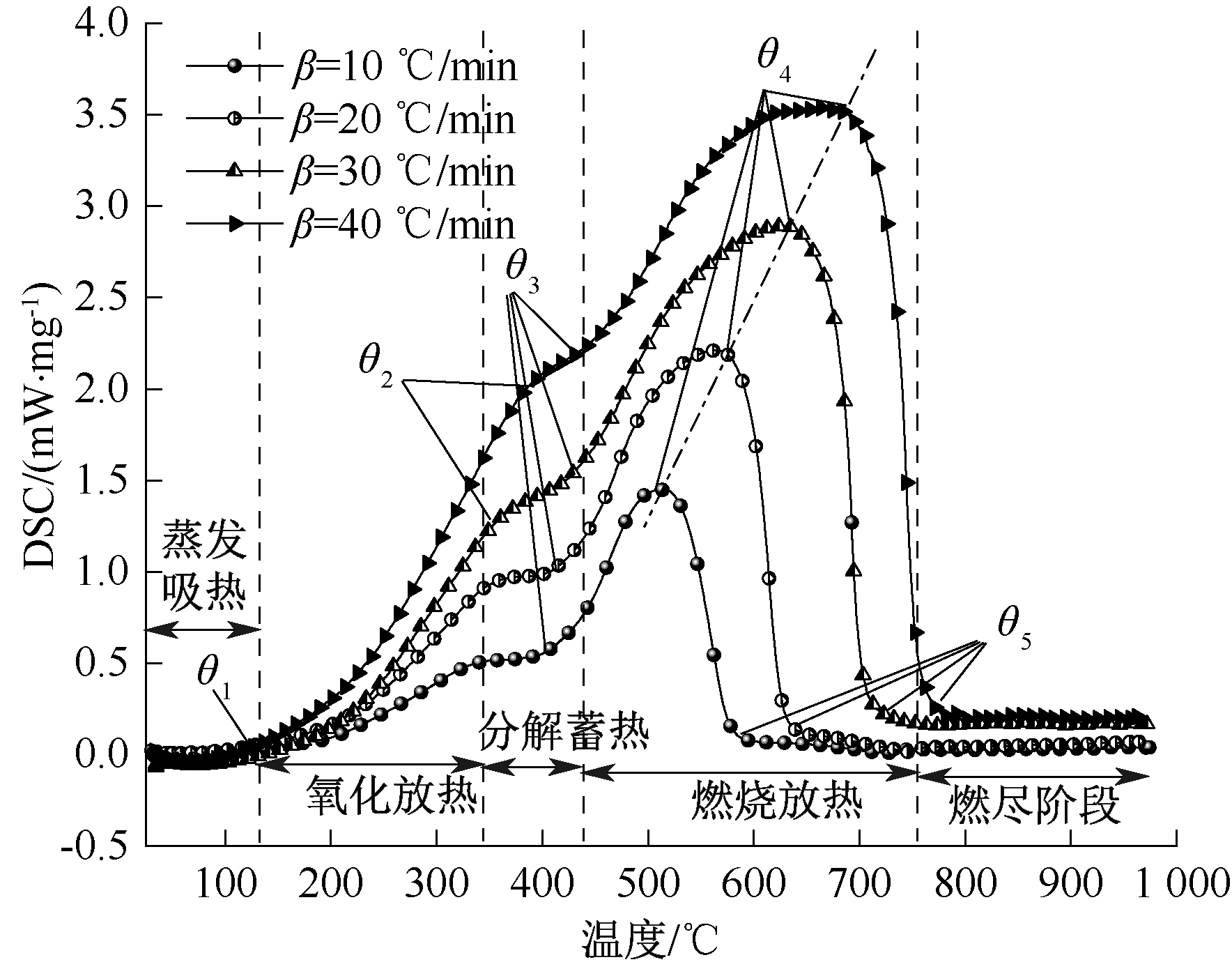
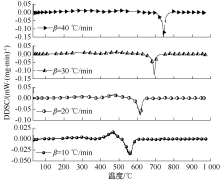
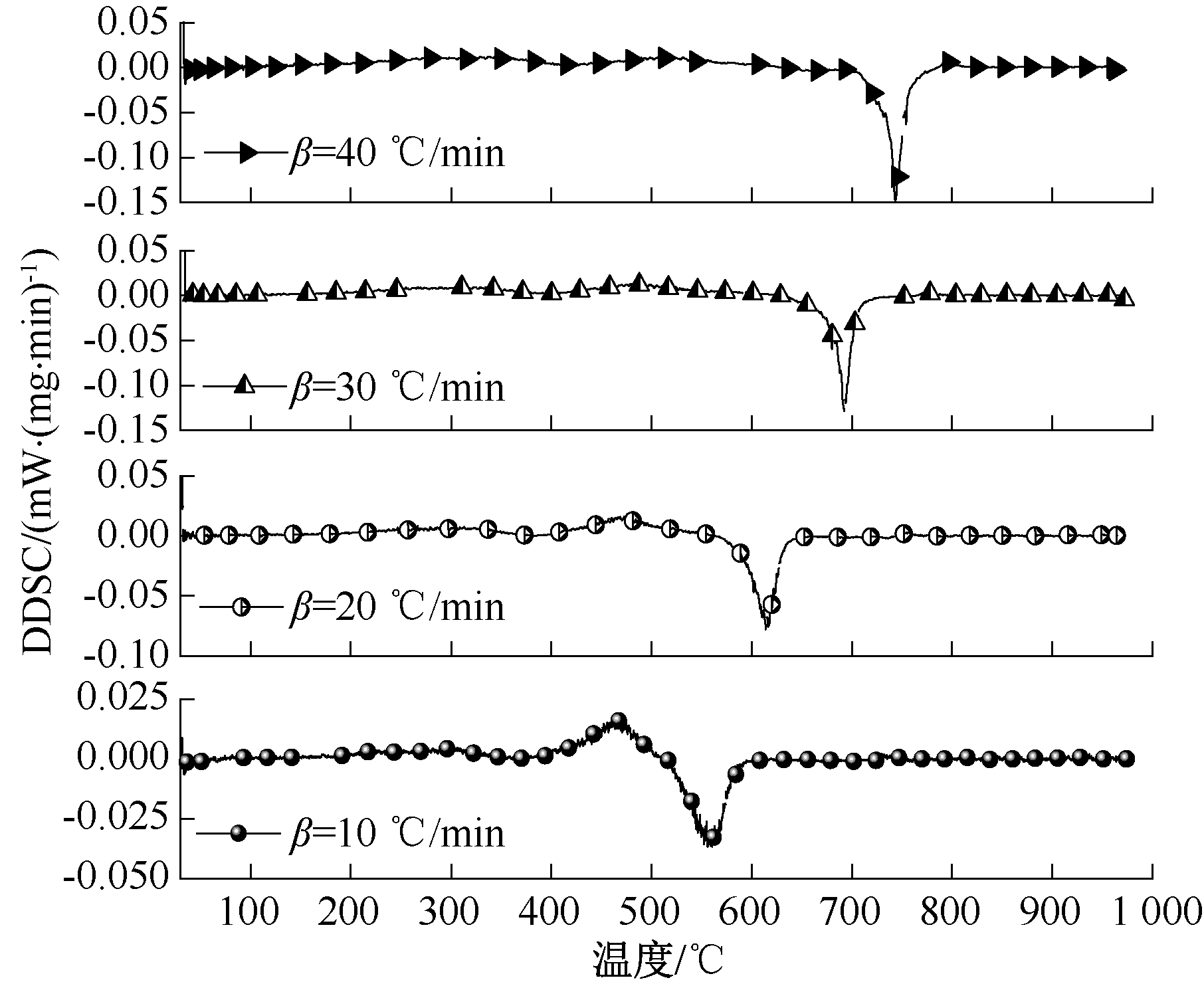
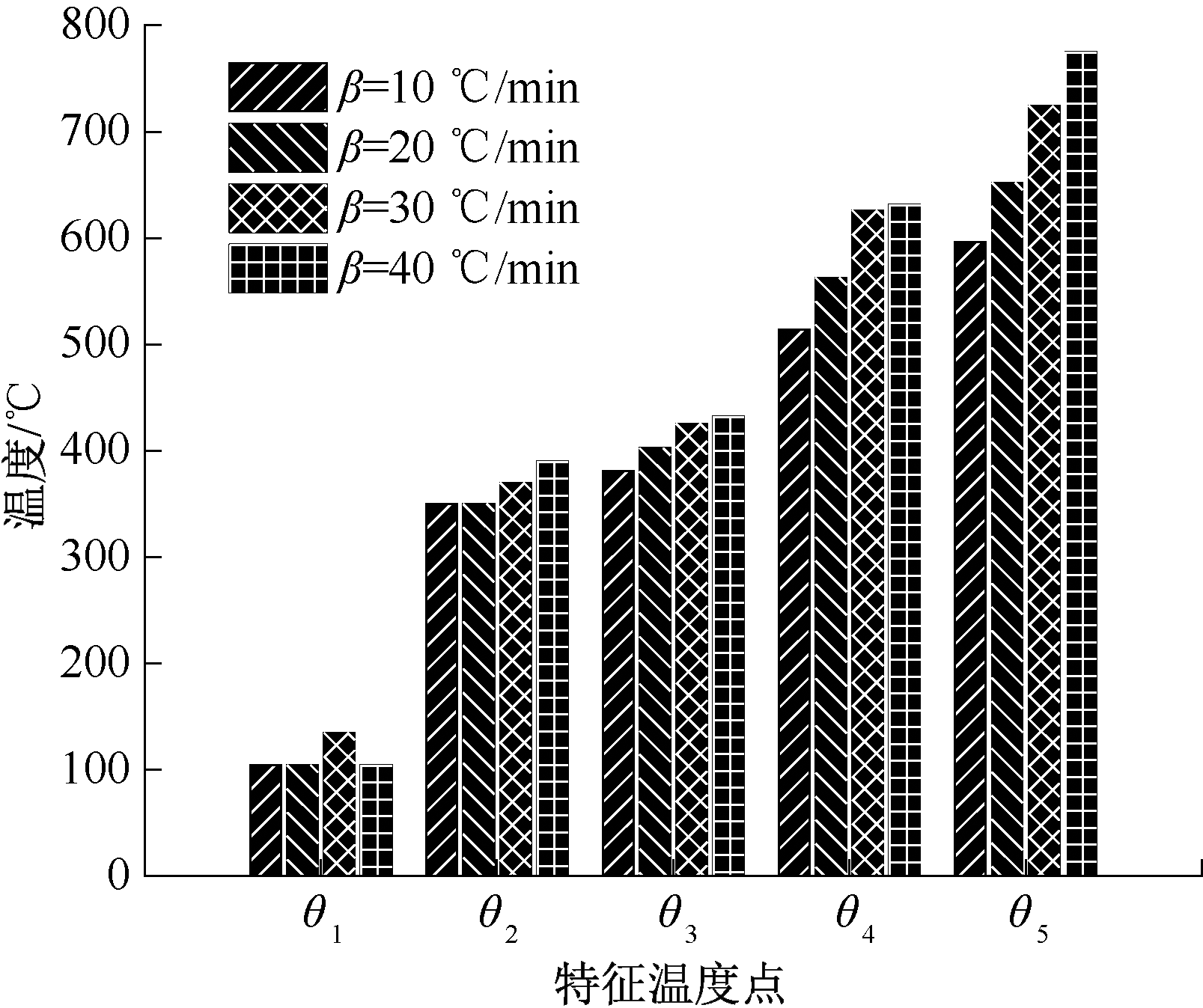
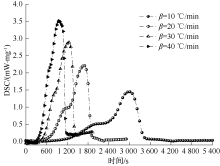
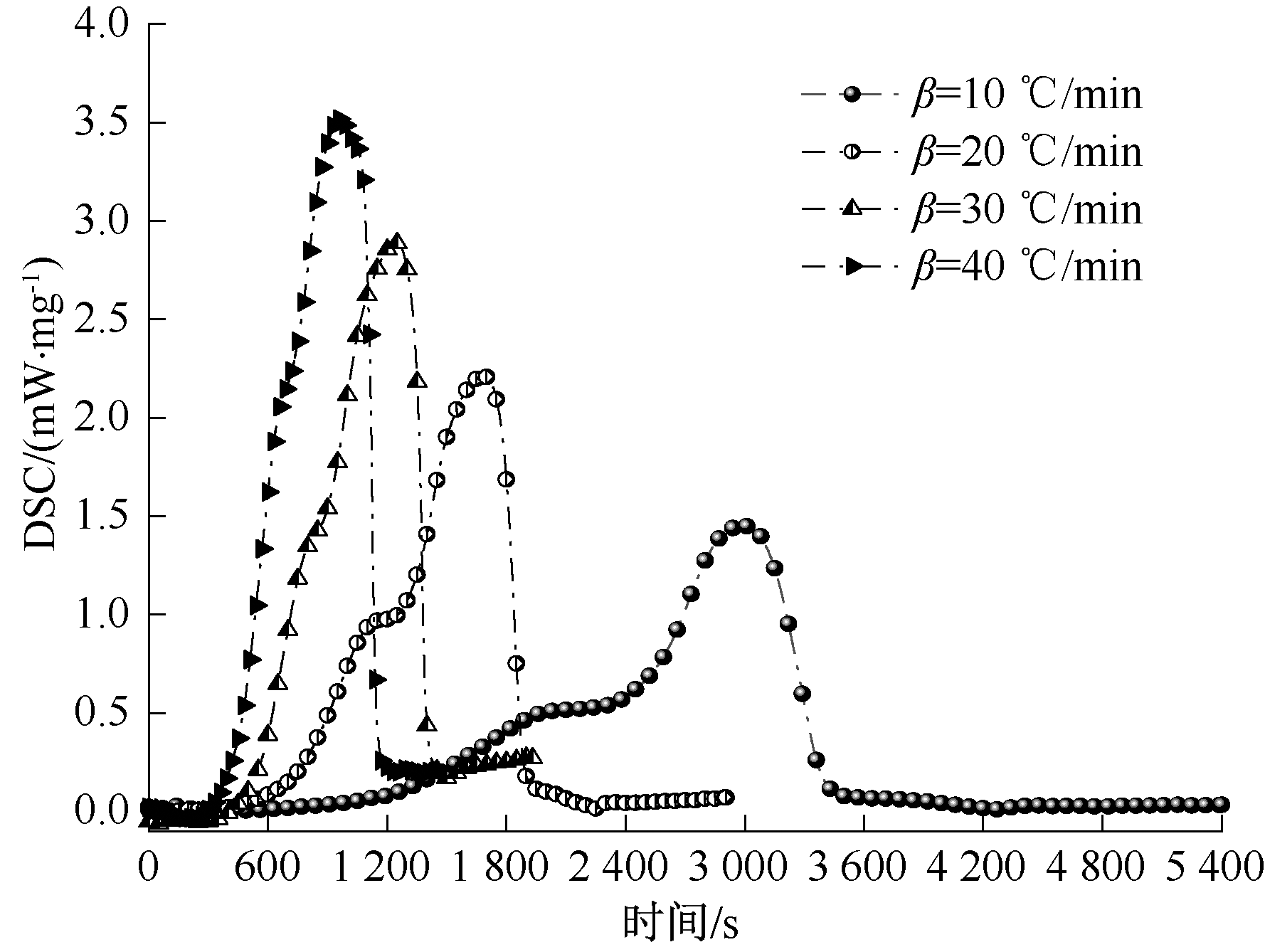
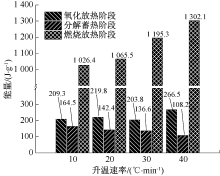
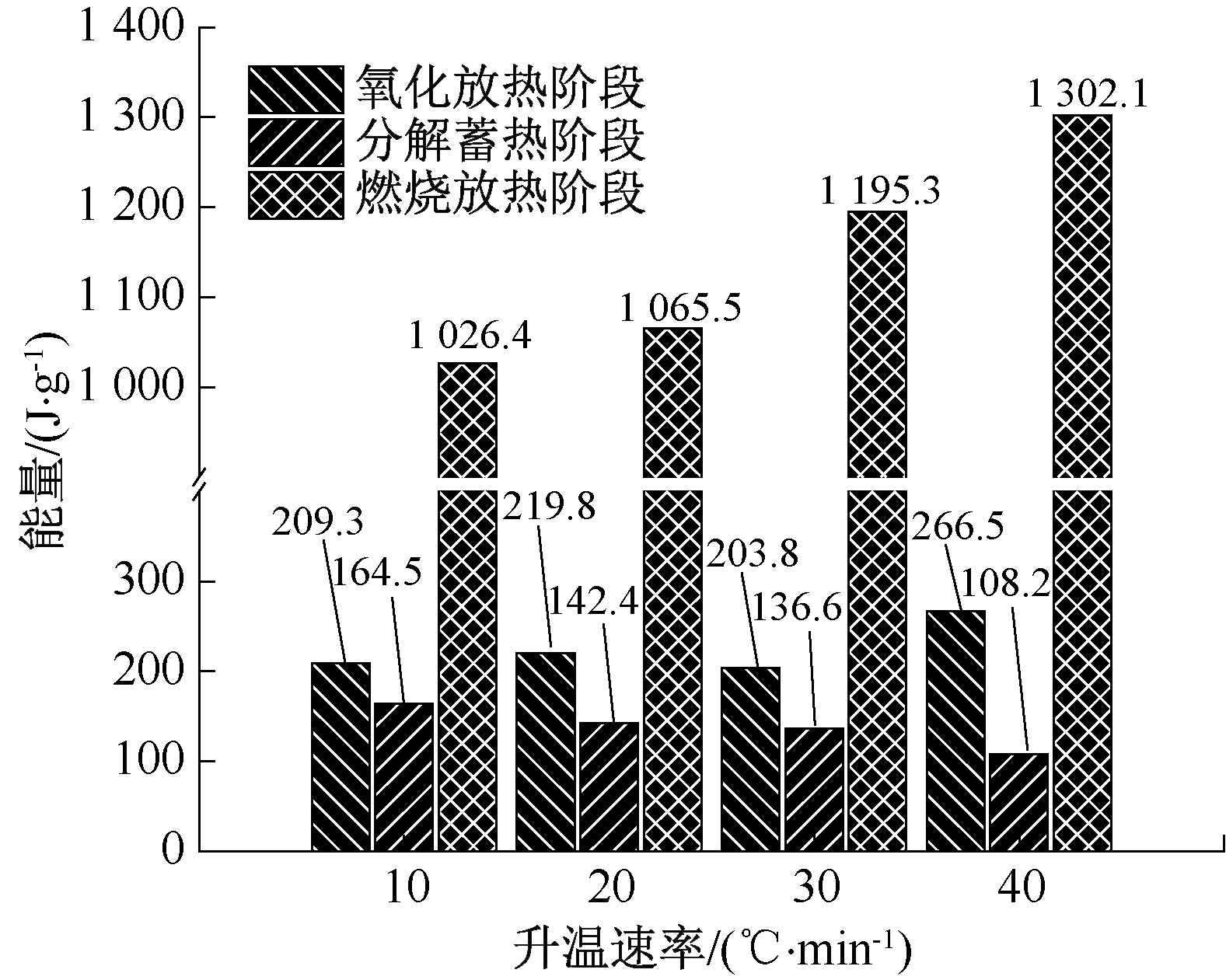
| [1] |
邱立军, 宋德文, 高翠玲, 等. 西北地区不粘煤、长焰煤煤岩特征及某些工艺性质[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2001, 7(4): 49-51.
|
|
QIU Lijun, SONG Dewen, GAO Cuiling, et al. Anthracology character and process property of non-caking coal and long flame coal in northeast region[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2001, 7(4): 49-51.
|
| [2] |
刘壮, 田宜水, 胡二峰, 等. 低阶煤热解影响因素及其工艺技术研究进展[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2021, 27(1): 50-59.
|
|
LIU Zhuang, TIAN Yishui, HU Erfeng, et al. Research progress on influencing factors and technology of low-rank coal pyrolysis[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2021, 27(1): 50-59.
|
| [3] |
王秋红, 靳松灵, 罗振敏, 等. 煤变质程度对煤燃烧动力学参数的影响[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2022, 29(3): 62-70.
|
|
WANG Qiuhong, JIN Songling, LUO Zhenmin, et al. Influence of metamorphism degree on kinetic parameters of coal combustion[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2022, 29(3): 62-70.
|
| [4] |
贾海林, 崔博, 焦振营, 等. 基于TG/DSC/MS技术的煤氧复合全过程及气体产物研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47(10): 3704-3715.
|
|
JIA Hailin, CUI Bo, JIAO Zhenying, et al. Study on the whole process and gas products of coal-oxygen complex re-action based on TG/DSC/MS technology[J]. Jourmal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(10): 3 704-3 715.
|
| [5] |
张嬿妮, 王安鹏, 侯云超, 等. 不同升温速率下烟煤的低温氧化放热特性研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2022, 50(9): 104-113.
|
|
ZHANG Yanni, WANG Anpeng, HOU Yunchao, et al. Study on low temperature oxidation heat release characteristics of bituminous coal at different heating rates[J]. Coal Scienee and Technology, 2022, 50(9): 104-113.
|
| [6] |
王成博, 雷昌奎, 邓存宝. 焦煤氧化燃烧特性参数与热动力学特征[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 709-719.
|
|
WANG Chengbo, LEl Changkui, DENG Cunbao. Oxidation combustion characteristic parameters and thermodynamic of coking coal[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2024, 44(4): 709-719.
|
| [7] |
邓军, 周廷斌, 游先中, 等. 贵州龙凤煤矿无烟煤自燃特性及动力学参数[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 409-417.
|
|
DENG Jun, ZHOU Tingbin, YOU Xianzhong, et al. Spontaneous combustion characteristics and kinetic parameters of anthracite in Guizhou Longfeng coal mine[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2024, 44(3): 409-417.
|
| [8] |
张玉涛, 郭强, 张园勃, 等. 基于相关系数法的煤自燃危险性关联分析及预测[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(1): 125-132.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.01.0774
|
|
ZHANG Yutao, GUO Qiang, ZHANG Yuanbo, et al. Corelation analysis and prediction of coal spontameous combustion riskbased on correlation coeicient method[J]. China Safety Scienee Joumal, 2024, 34(1): 125-132.
|
| [9] |
姜峰, 尚芳兰, 李珍宝, 等. 热重-FTIR法分析不粘煤氧化特性参数[J]. 燃烧科学与技术, 2021, 27(1): 35-42.
|
|
JIANG Feng, SHANG Fanglan, LI Zhenbao, et al. Oxidation characteristic parameters of non-caking coal by TG and FTIR[J]. Journal of Combustion Science and Technology, 2021, 27(1): 35-42.
|
| [10] |
江国栋, 魏利平, 滕海鹏, 等. 基于热重法的准东煤等转化率热解动力学模型[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(4): 1415-1422.
doi: 10.11949/j.issn.0438-1157.20161335
|
|
JIANG Guodong, WEI Liping, TENG Haipeng, et al. A kinetic model based on TGA data for pyrolysis of Zhundong coal[J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(4): 1415-1422.
|
| [11] |
马东, 解庆典, 赵志强, 等. 孟巴矿高地温环境煤孔隙及氧化动力学特征[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(8): 162-169.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.08.0061
|
|
MA Dong, XIE Qingdian, ZHAO Zhiqiang, et al. Characteristics of high temperature environment on coal pore structure andoxidation dynamics of Barapukuria coal mine in Bangladesh[J]. China Safety Scienee Joumal, 2024, 34(8): 162-169.
|
| [12] |
刘洋, 石泽正, 陈朝帅, 等. 热分析获取锅炉内煤着火特性-Part I:比热容、着火温度和着火热[J]. 煤炭学报, 2025, 50(2): 1 303-1 314.
|
|
LIU Yang, SHI Zezheng, CHEN Zhaoshuai, et al. Thermal analysis for obtaining coal ignition characteristics in boilers-Part 1: specific heat capacity, ignition temperature, and ignition heat[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2025, 50(2): 1 303-1 314.
|
| [13] |
臧立彬, 崔虎锋, 李庆春. 弱氧化气氛下烟煤热解特性及热解产物组成[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2020, 48(5): 34-39.
|
|
ZANG Libin, CUI Hufeng, LI Qingchun. Pyrolysis characteristics and pyrolysis product composition of bituminous coal under weak oxidizing atmosphere[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2020, 48(5): 34-39.
|
| [14] |
张玉涛, 杨杰, 李亚清, 等. 氧气浓度和升温速率对煤自燃特性影响[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2023, 23(1): 43-48.
|
|
ZHANG Yutao, YANG Jie, LI Yaqing, et al. Effects of oxygen concentration and heating rate on the characteristics of coal spontaneous combustion[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2023, 23(1): 43-48.
|
| [15] |
张嬿妮, 刘春辉, 舒盼, 等. 弱粘煤低温氧化活性基团与热效应的研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2021, 17(11): 98-104.
|
|
ZHANG Yanni, LIU Chunhui, SHU Pan, et al. Study on low-temperature oxygen active groups and thermal effect of weakly caking coal[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2021, 17(11): 98-104.
|
| [16] |
李伍, 杨文斌, 杜仲华. 淮北煤田石台矿烟煤生烃结构演化研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2021, 49(6): 152-160.
|
|
LI Wu, YANG Wenbin, DU Zhonghua. Study on hydrocarbon generation structure evolution of bituminous coal in Shitai mine, Huaibei coafield[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(6): 152-160.
|
| [17] |
FLYNN J H, WALL L A. A quick, direct method for the determination of activation energy from thermogravimetric data[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part C Polymer Letters, 1966, 4(5): 323-328.
|
| [18] |
KISSINGER H E. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1957, 29(11): 1702-1706.
doi: 10.1021/ac60131a045
|
| [19] |
FRIEDMAN H L. Kinetics of thermal degradation of char-forming plastics from thermogravimetry. application to a phenolic plastic[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part C: Polymer Symposia, 2010, 6(1): 183-195.
doi: 10.1002/polc.v6:1
|
| [20] |
STARINK M J. A new method for the derivation of activation energies from experiments performed at constant heating rate[J]. Thermochimica Acta, 1996, 288(1/2): 97-104.
doi: 10.1016/S0040-6031(96)03053-5
|
| [21] |
候飞, 曹威虎, 王艺, 等. 煤低温氧化动力学参数测试方法对比研究[J]. 工矿自动化, 2021, 47(9): 58-64.
|
|
HOU Fei, CAO Weihu, WANG Yi, et al. Comparative study on test methods of coal low temperature oxidation kinetic parameters[J]. Industry and Mine Automation, 2021, 47(9): 58-64.
|
| [22] |
白斌, 周卫红, 丁毅飞, 等. 纤维素热解动力学分析方法研究[J]. 生物质化学工程, 2017, 51(4): 8-16.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5854.2017.04.002
|
|
BAI Bin, ZHOU Weihong, DING Yifei, et al. Analysis method of cellulose pyrolysis dynamics[J]. Biomass Chemical Engineering, 2017, 51(4): 8-16.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5854.2017.04.002
|
| [23] |
白刚, 周西华, 宋东平, 等. 不同变质程度煤燃烧特性及动力学参数研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27(9): 63-68.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.09.011
|
|
BAI Gang, ZHOU Xihua, SONG Dongping, et al. Research on coal's combustion characteristics and kinetics parameters as a function of its metmorphic degree[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27(9): 63-68.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.09.011
|