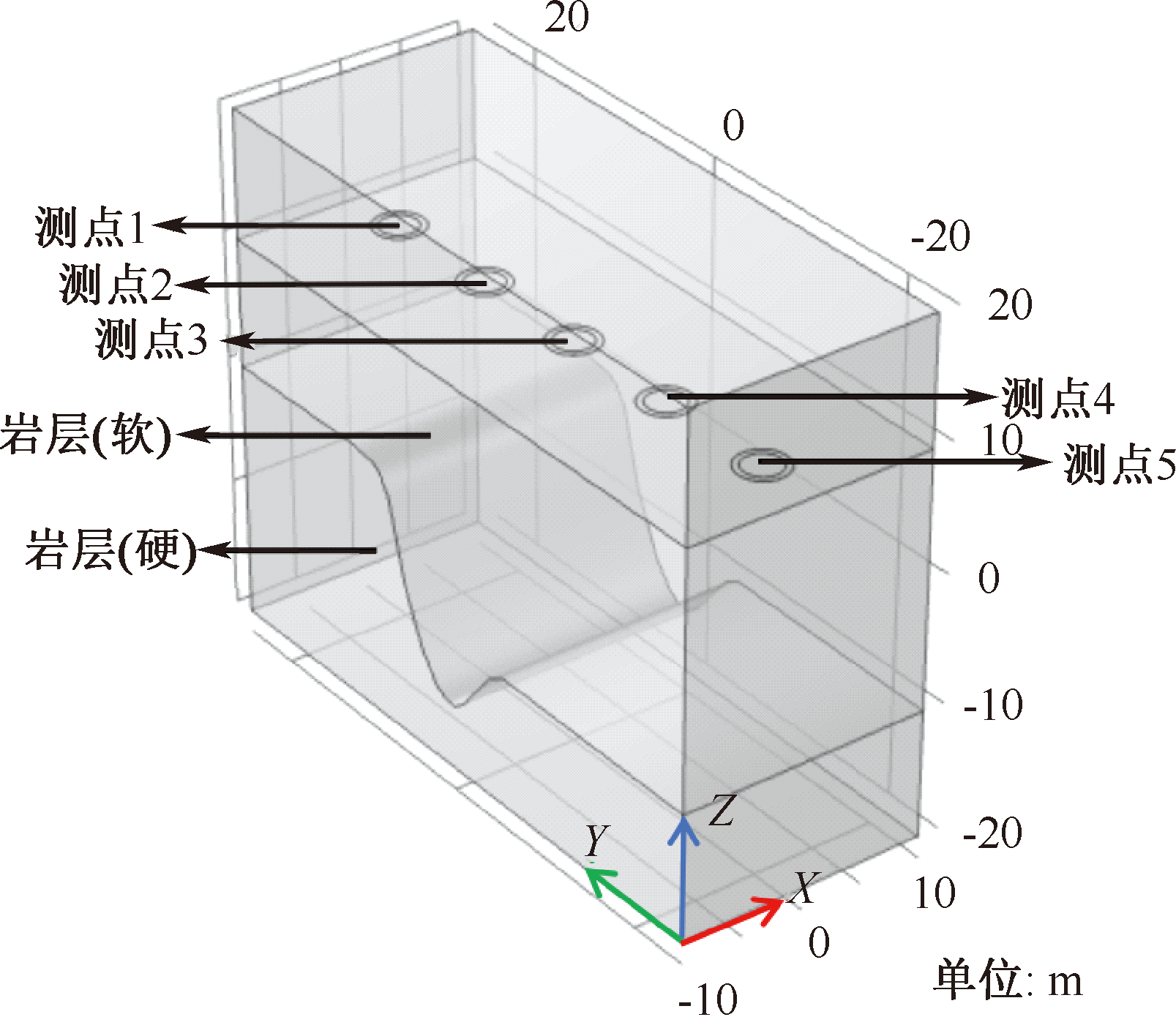
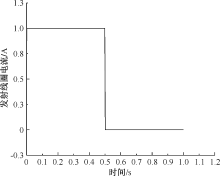
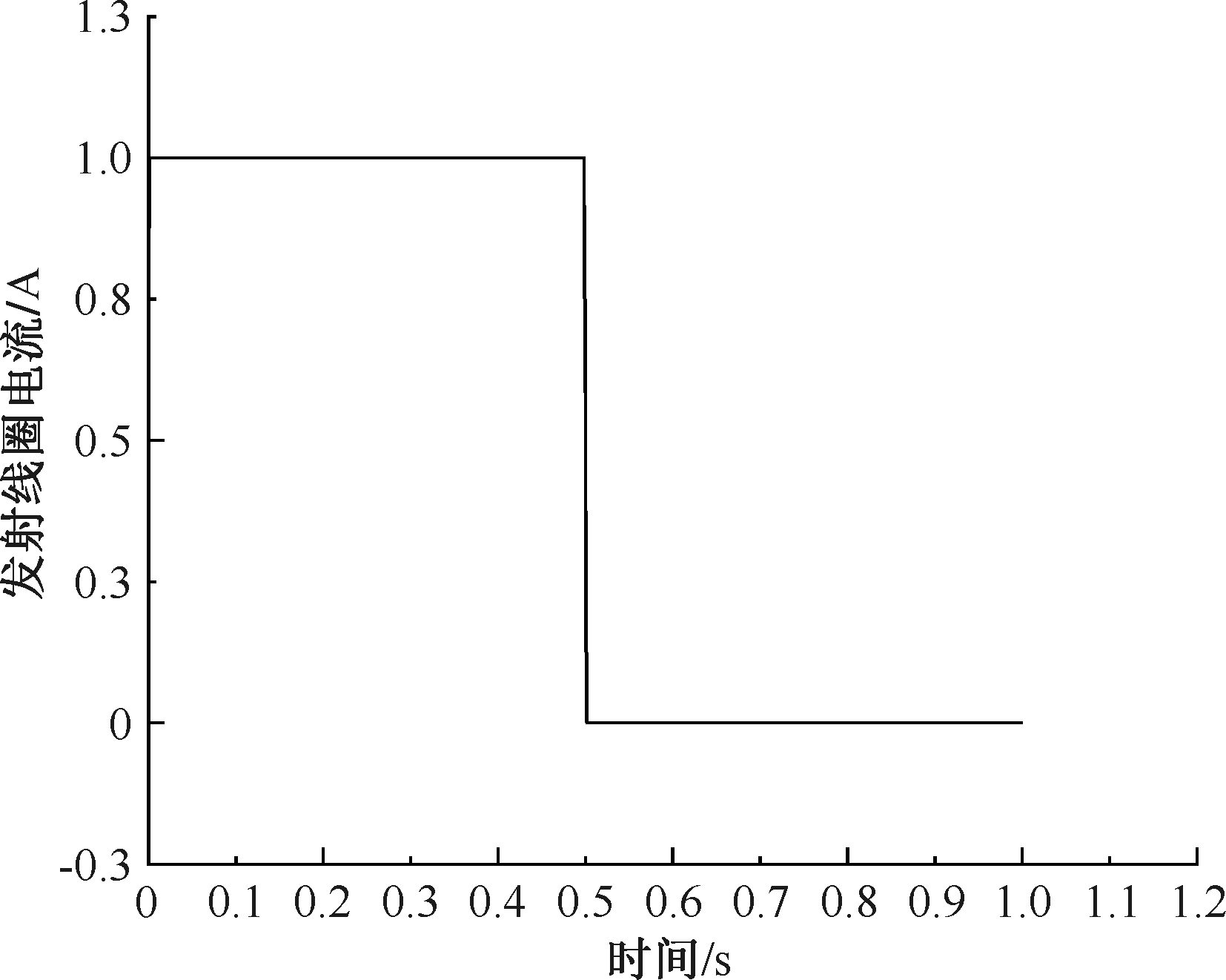
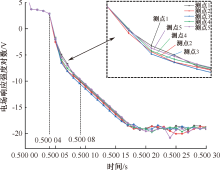
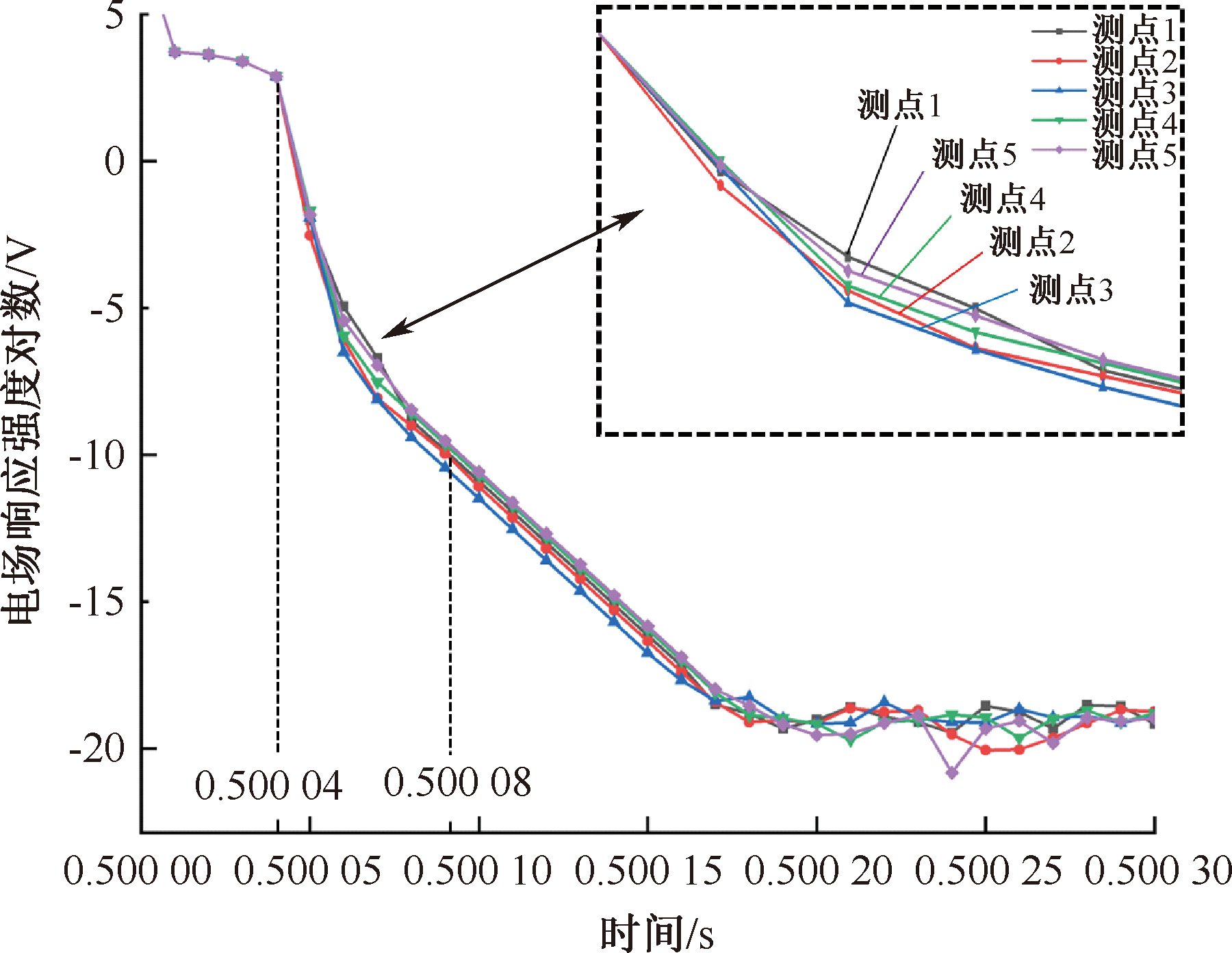
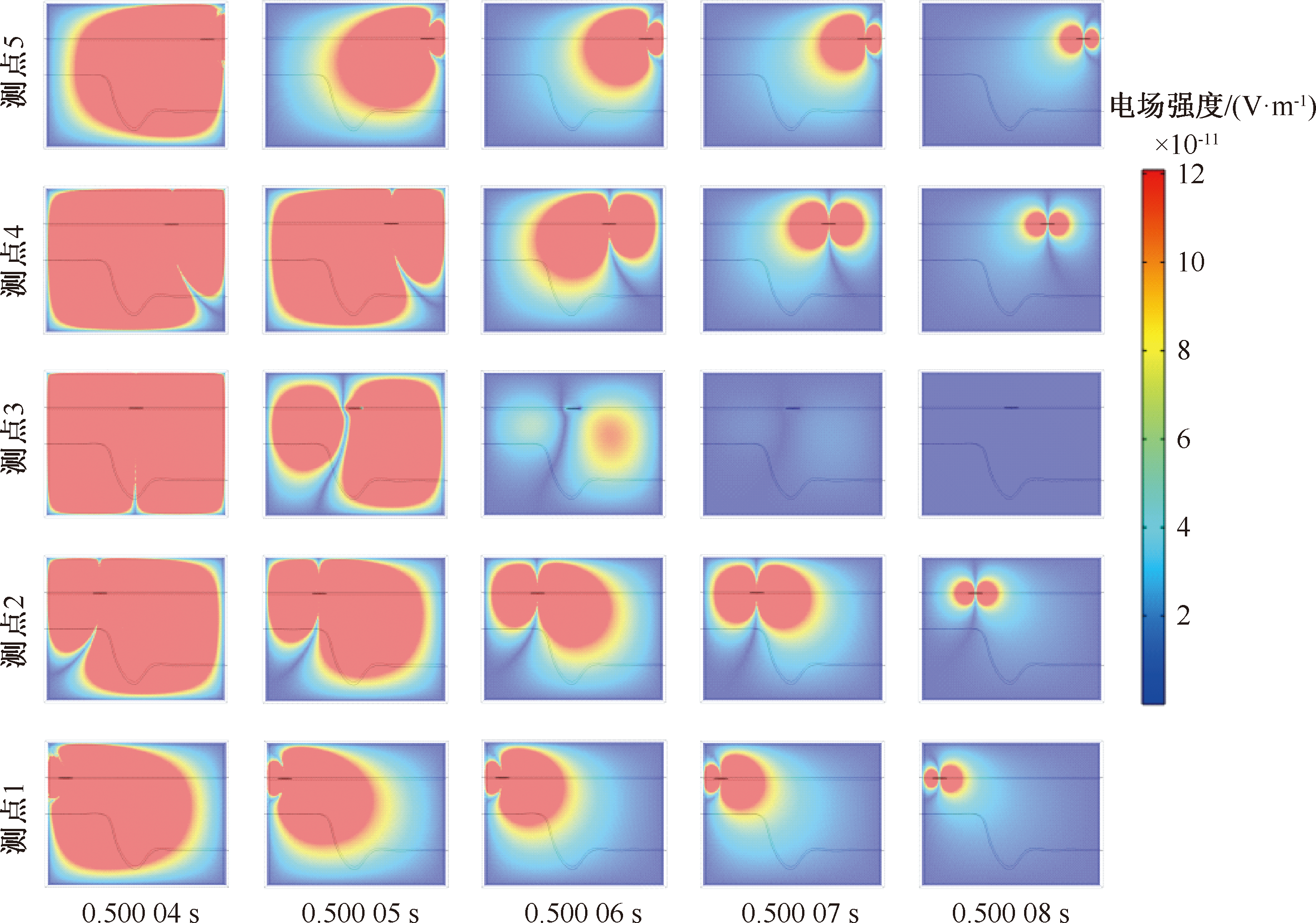
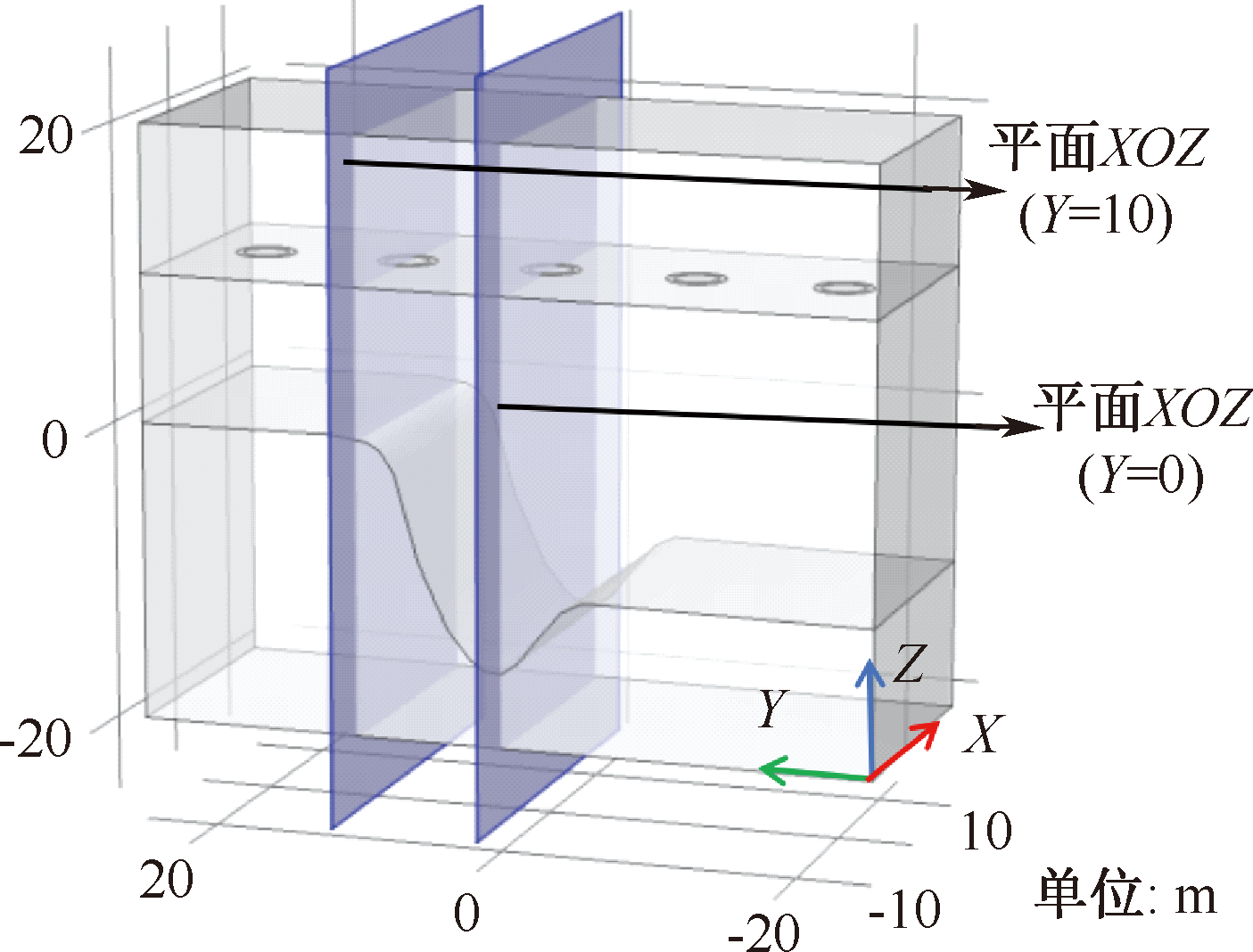
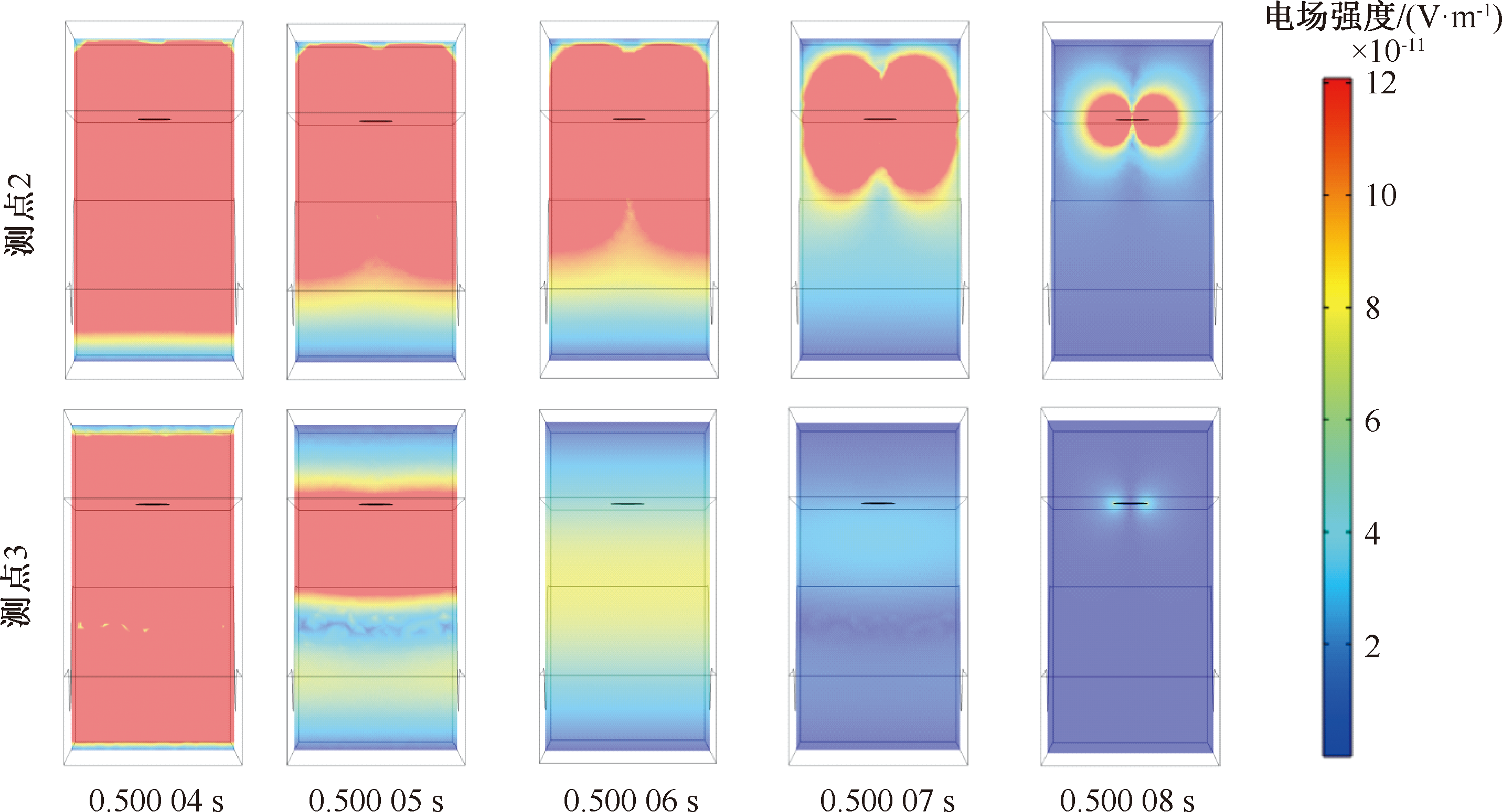
| [1] |
郭卫社. 软硬不均地层盾构技术的思考[J]. 隧道建设, 2016, 36(10):1196-1201.
|
|
GUO Weishe. Reflecting on technologies for shield tunneling in heterogeneous ground[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2016, 36(10): 1196-1201.
|
| [2] |
杜闯东. 基岩破碎带与软硬不均等不良地层盾构掘进技术分析[J]. 隧道建设, 2015, 35(9):920-927.
|
|
DU Chuangdong. Analysis on shield tunneling in fractured bed rock zones and upper-soft lower-hard groun[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2015, 35(9): 920-927.
|
| [3] |
吴瑞祥. 软硬不均地层盾构施工技术研究及地层扰动影响分析[J]. 建设机械技术与管理, 2021, 34(4):62-64,132.
|
|
WU Ruixiang. Shield construction technology in soft and hard stratum and its influence on stratum disturbance law[J]. Construction Machinery Technology & Management, 2021, 34(4): 62-64,132.
|
| [4] |
王青松, 张拥军, 康与超. 青岛上软下硬复合地层隧道开挖变形规律研究[J]. 北方交通, 2024(1):73-76.
|
|
WANG Qingsong, ZHANG Yongjun, KANG Yuchao. Research on the deformation law of tunnel excavation in Qingdao's upper soft and lower hard composite strata[J]. Northern Communications, 2024 (1): 73-76.
|
| [5] |
刘畅. 基于上软下硬地层开挖风险处理及效果评价分析[J]. 价值工程, 2024, 43(6):27-29.
|
|
LIU Chang. Risk management and effect evaluation analysis of excavation in upper soft and lower hard strata[J]. Value Engineering, 2024, 43(6): 27-29.
|
| [6] |
伍小刚, 李天斌, 张中, 等. 传统瞬变电磁法的改进及其在隧道超前地质预报中的应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2021, 48(1):163-170.
|
|
WU Xiaogang, LI Tianbin, ZHANG Zhong, et al. Improvement of the traditional transient electromagnetic method and its application to advanced geological forecast of tunnel[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(1): 163-170.
|
| [7] |
梁庆华. 矿井全空间小线圈瞬变电磁探测技术及应用研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2012.
|
|
LIANG Qinghua. The technology and application of mine full-space transient electromagnetic detection by small coil[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2012.
|
| [8] |
高晓耕. 斜井上部流砂层塌陷空洞纳米瞬变电磁法探测[J]. 中国煤炭, 2016, 42(8):25-29.
|
|
GAO Xiaogeng. Research on detecting collapse holes in quicksand layer above inclined shaft by NanoTEM[J]. China Coal, 2016, 42(8): 25-29.
|
| [9] |
张子强. 瞬变电磁法在隧道工程地质风险预测与评估中的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2021, 18(5):671-677.
|
|
ZHANG Ziqiang. Application of transient electromagnetic method in geological risk prediction and assessment of tunnel engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2021, 18(5): 671-677.
|
| [10] |
李辉, 韩自强, 陈棚. 瞬变电磁法在公路隧道地下水预报中的应用[J]. 隧道建设:中英文, 2019, 39(增1):355-360.
|
|
LI Hui, HAN Ziqiang, CHEN Peng. Application of transient electromagnetic method in groundwater prediction of highway tunnel[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2019, 39(S1): 355-360.
|
| [11] |
郑洪斌, 赵学敏. 基于COMSOL模拟的瞬变电磁法在隧道超前地质预报中的应用[J]. 公路, 2023, 68(6):469-474.
|
|
ZHENG Hongbin, ZHAO Xuemin. Application of transient electromagnetic method in tunnel advanced geological prediction based on COMSOL simulation[J]. Highway, 2023, 68(6): 469-474.
|
| [12] |
王春源, 张桓, 马洪亮, 等. 浅埋深线圈瞬变电磁场超前探测响应及应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(5):75-81.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.05.1294
|
|
WANG Chunyuan, ZHANG Huan, MA Hongliang, et al. Advanced detection response and application of transient electromagnetic field of shallow buried deep coil[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(5): 75-81.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.05.1294
|
| [13] |
GUO Changang, TAN Tingjiang, MA Liuzhu, et al. Response and application of full-space numerical simulation based on finite element method for transient electromagnetic advanced detection of mine water[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(22):DOI: 10.3390/SU142215024.
|
| [14] |
CHENG Jiulong, CHEN Ding, XUE Guoqiang, et al. Synthetic aperture imaging in advanced detection of roadway using mine transient electromagnetic method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(2):190-198.
doi: 10.1002/cjg2.2016.59.issue-2
|
| [15] |
薛国强, 李貅, 底青云. 瞬变电磁法理论与应用研究进展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2007(4):1195-1200.
|
|
XUE Guoqiang, LI Xiu, DI Qingyun. The progress of TEM in theory and application[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2007(4):1195-1200.
|
| [16] |
张军. 瞬变电磁精细探测方法在隧道地质预报中的应用研究[J]. 能源与环保, 2019, 41(6):33-38,42.
|
|
ZHANG Jun. Application study on TEM fine detection method in tunnel geological prediction[J]. China Energy and Environmental Protection, 2019, 41(6): 33-38,42.
|
| [17] |
牛之琏. 时间域电磁法原理[M]. 长沙: 中南工业大学出版社, 1992:5-30.
|
| [18] |
孙静. 青岛市海滩沉积地貌及质量评价[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012.
|
|
SUN Jing. Sedimentary geomorphology of beaches in Qingdao city and their quality rating[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2012.
|