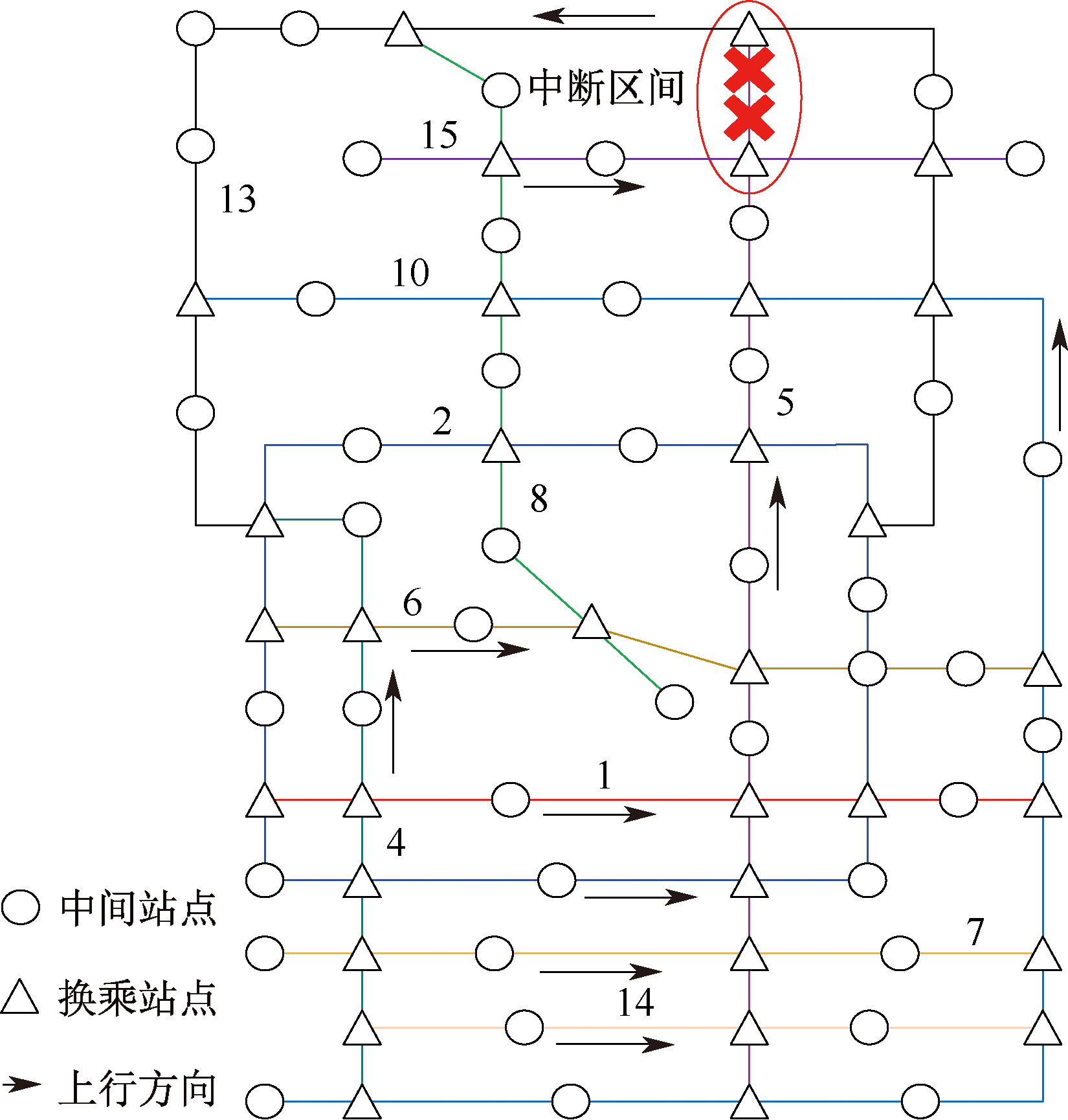
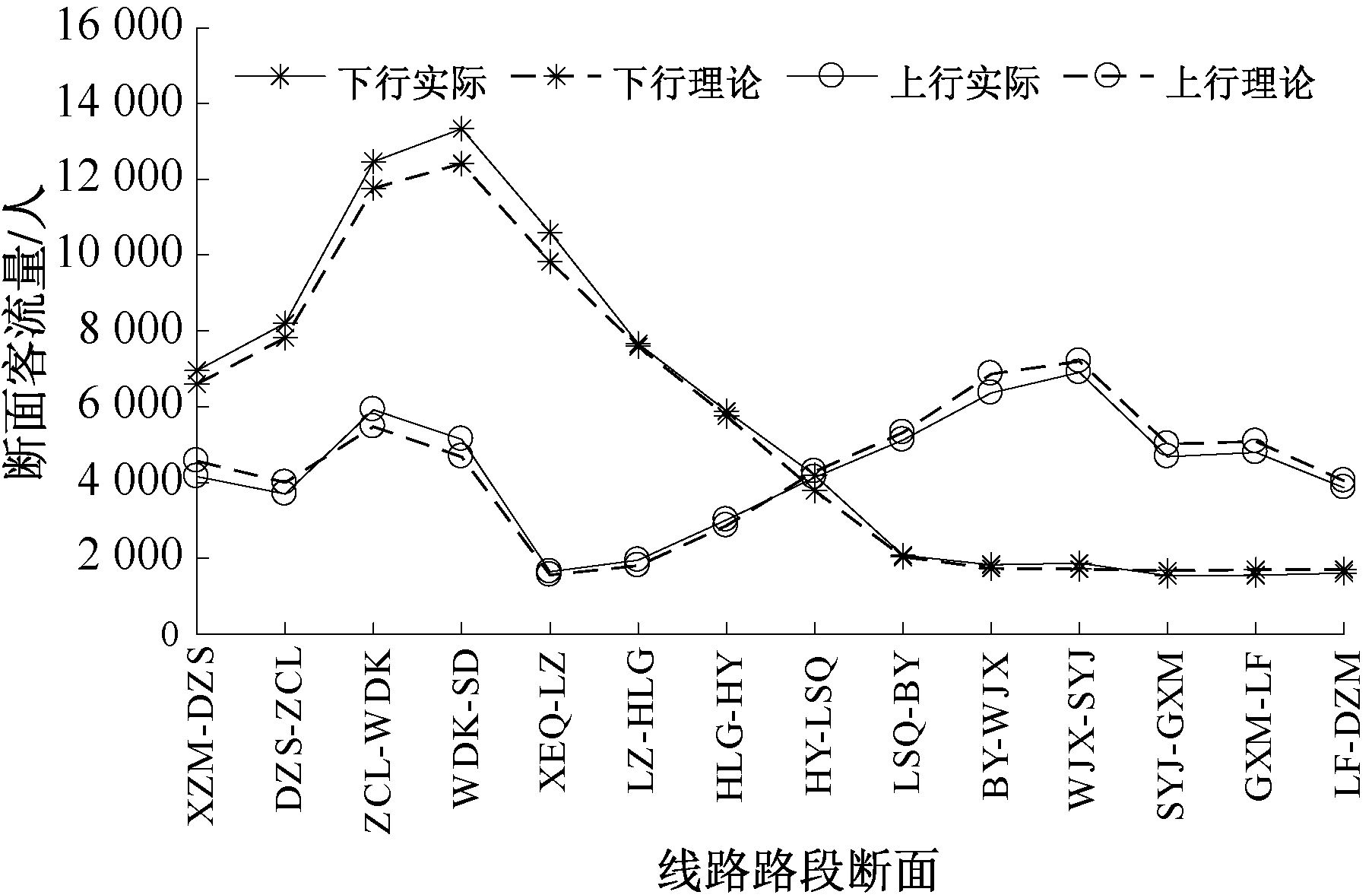
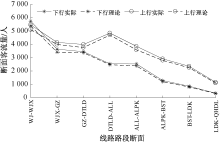
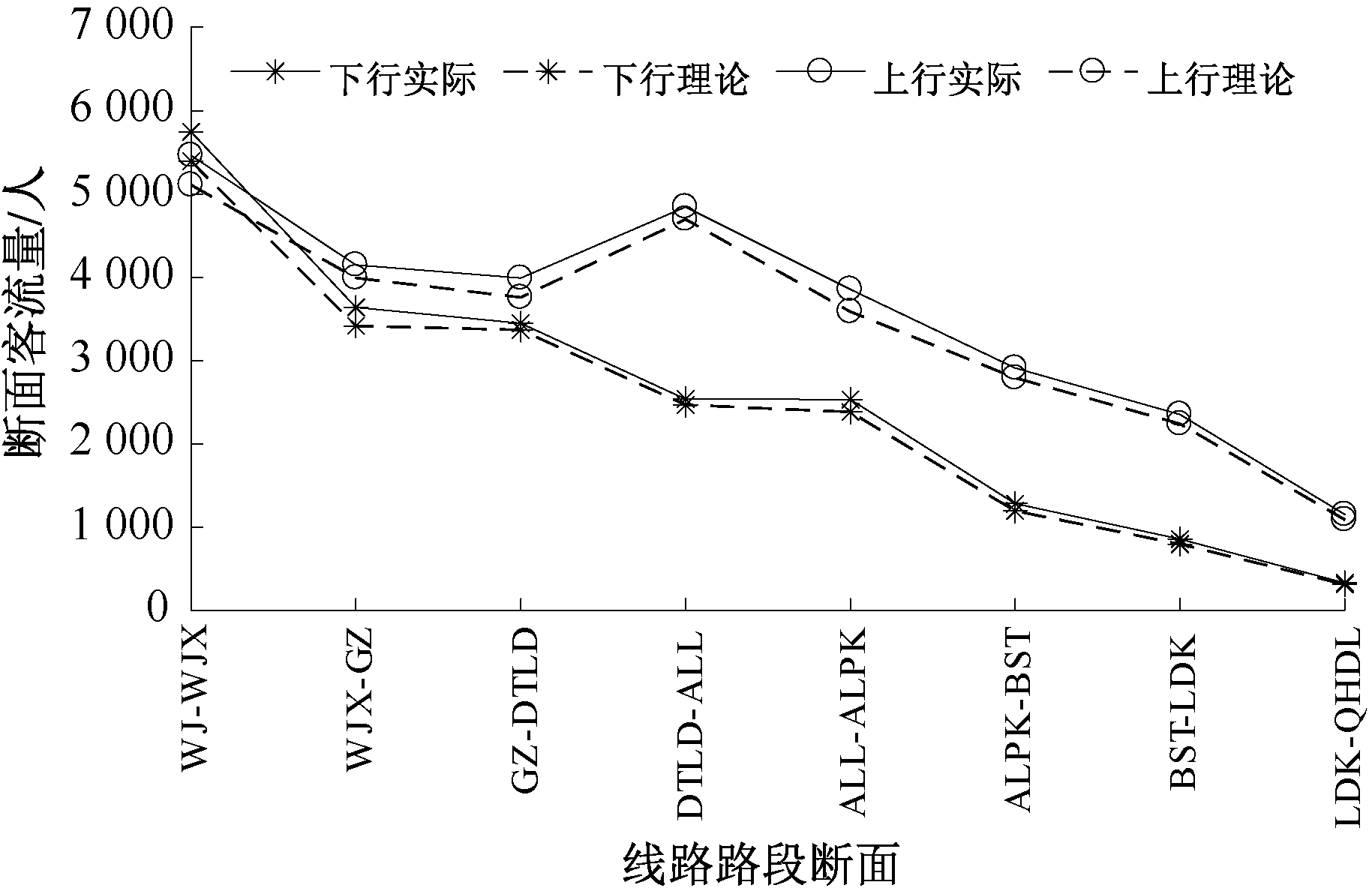
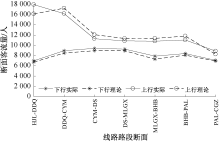
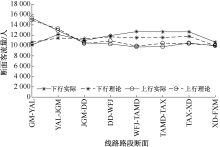
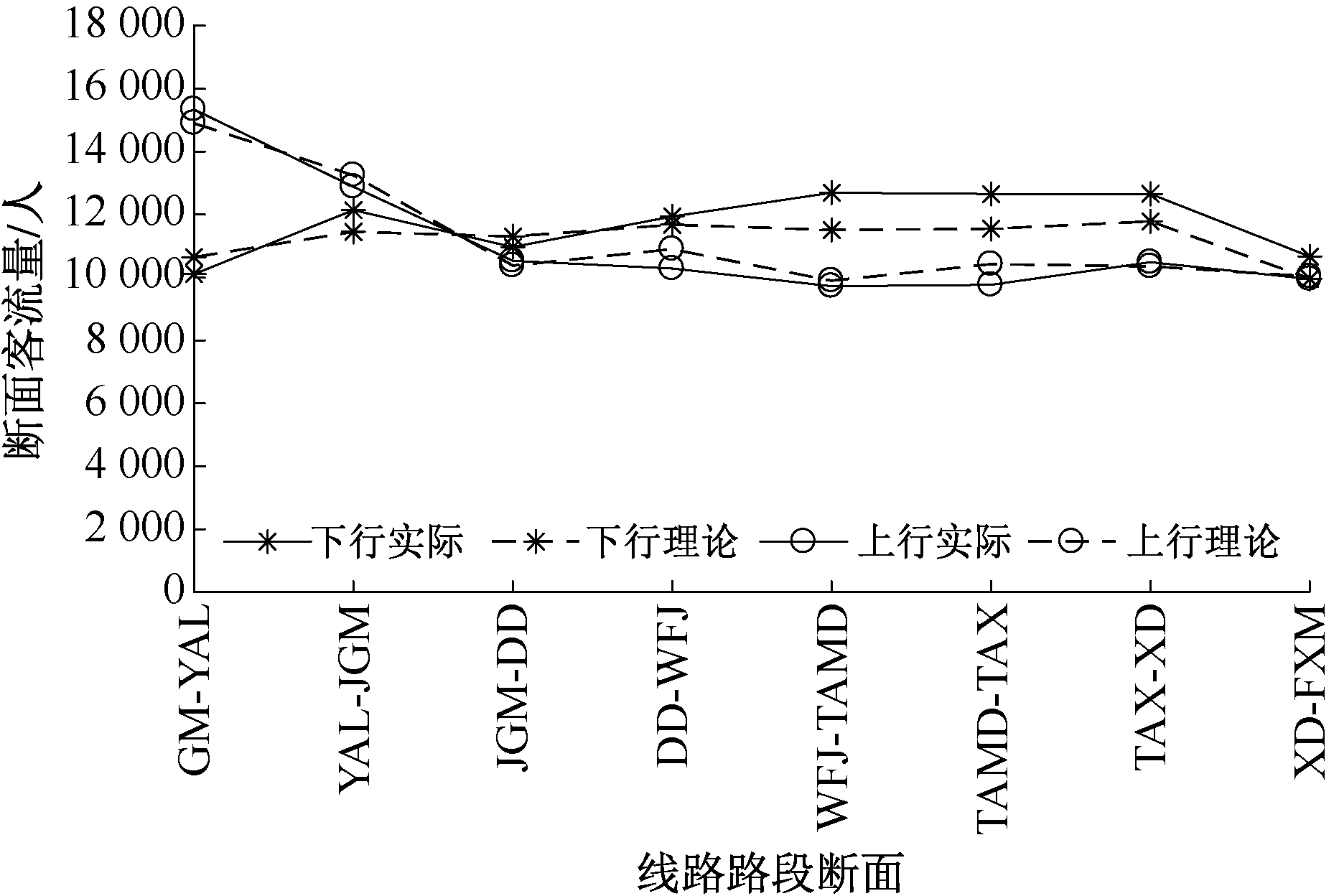
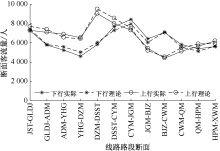
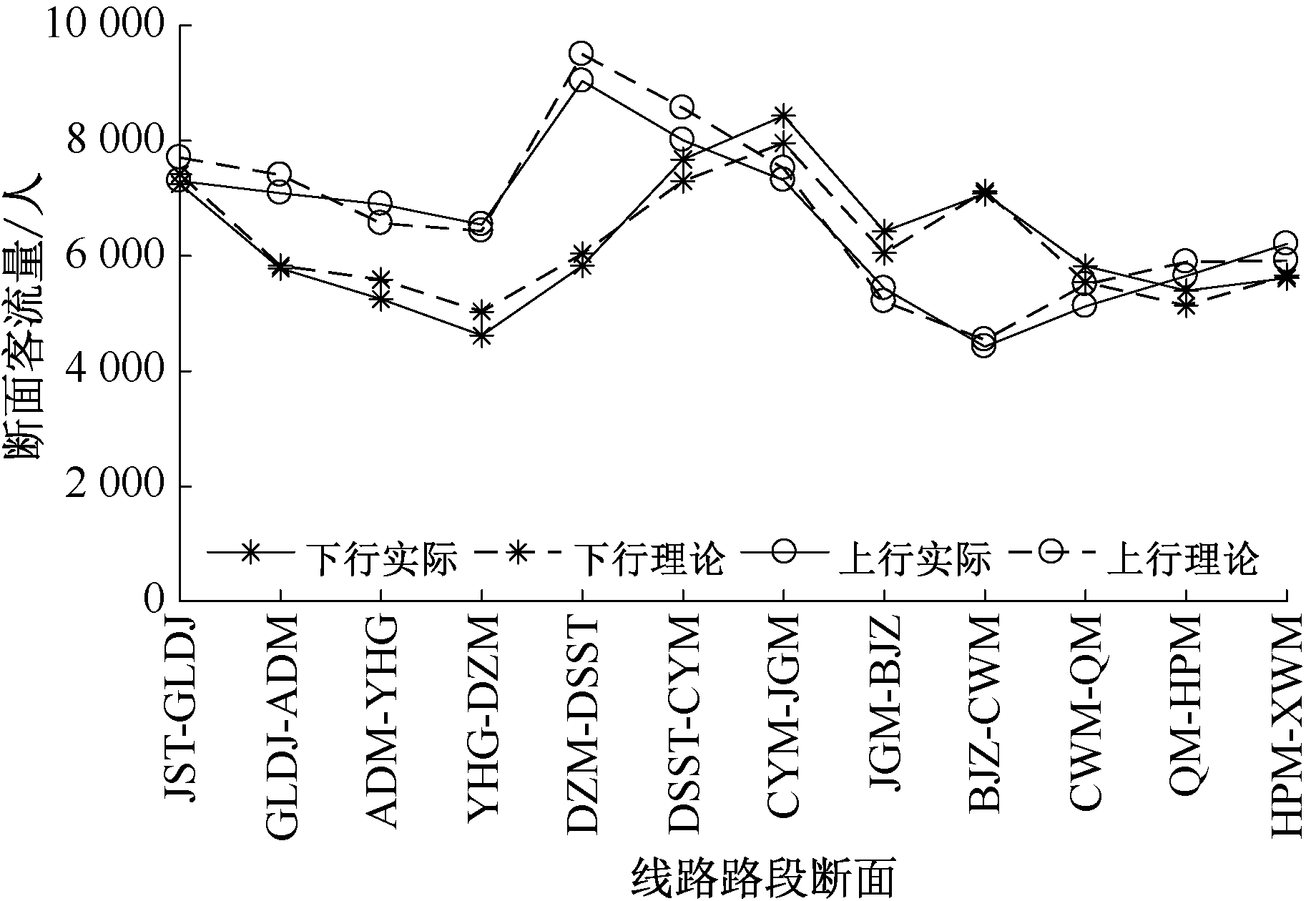
| [1] |
SCHMCKER J D, FONZONE A, SHIMAMOTO H, et al. Frequency-based transit assignment considering seat capacities[J]. Transportation Research:Part B, 2011, 45(2): 392-408.
doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2010.07.002
|
| [2] |
LI Dewei, GAO Yufang, LI Ruoyi, et al. Hybrid random regret minimization and random utility maximization in the context of schedule-based urban rail transit assignment[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2018: DOI: 10.1155/2018/9789316.
doi: 10.1155/2018/9789316
|
| [3] |
POULHES A. Dynamic assignment model of trains and users on a congested urban-rail line[J]. Journal of Rail Transport Planning & Management, 2020, 14: DOI: 10.1016/j.jrtpm.2020.100178.
doi: 10.1016/j.jrtpm.2020.100178
|
| [4] |
陈培文, 高德辉. 考虑路径尺度的城市轨道交通客流分配[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(12): 4884-4889.
|
|
CHEN Peiwen, GAO Dehui. Passenger flow assignment method of urban rail transit based on path size[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(12): 4884-4889.
|
| [5] |
ZHOU Yu, YANG Hai, WANG Yun, et al. Integrated line configuration and frequency determination with passenger path assignment in urban rail transit networks[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 2021, 145: 134-151.
doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2021.01.002
|
| [6] |
倪少权, 杨皓男, 彭强. 基于乘客路径选择的多制式轨道交通客流分配[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2021, 21(1):108-115.
|
|
NI Shaoquan, YANG Haonan, PENG Qiang. Passenger flow distribution of regional multi-standard rail transit based on passenger route selection[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2021, 21(1): 108-115.
|
| [7] |
陈锦渠, 殷勇, 鞠子奇. 基于仿真的城市轨道交通客流分配[J]. 计算机仿真, 2022, 39(2):73-77, 202.
|
|
CHEN Jinqu, YIN Yong, JU Ziqi. Passenger flow assignment of urban rail transit based on simulation[J] Computer Simulation, 2022, 39(2): 73-77, 202.
|
| [8] |
SHANG Pan, YANG Liya, YAO Yu, et al. Integrated optimization model for hierarchical service network design and passenger assignment in an urban rail transit network: a Lagrangian duality reformulation and an iterative layered optimization framework based on forward-passing and backpropagation[J]. Transportation Research Part C, 2022, 144: DOI: 10.1016/j.trc.2022.103877.
doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2022.103877
|
| [9] |
罗凌燕, 沈斐敏, 刘毅, 等. 地铁站突发事件疏散路径选择影响因素研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2016, 26(7): 169-174.
|
|
LUO Lingyan, SHEN Feimin, LIU Yi, et al. Research on factors influencing selection of evacuation route in an emergency in subway station[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2016, 26(7): 169-174.
|
| [10] |
ZENG Lu, LIU Jun, QING Yong. Passenger flow dynamic assignment model of urban mass transit and its application during interval interrupted operation[J]. Journal of Southeast University: English Edition, 2017, 33(1): 115-122.
|
| [11] |
杨景峰, 朱大鹏. 突发事件下铁路系统客流动态分配模型研究[J]. 铁道运输与经济, 2021, 43(6): 21-27.
|
|
YANG Jingfeng, ZHU Dapeng. Research on the dynamic allocation model of railway system passenger flow in an emergency[J]. Railway Transport and Economy, 2021, 43(6): 21-27.
|
| [12] |
贾飞, 孟学雷, 贾宝通, 等. 突发公共卫生事件下高速铁路客流分配研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(6): 153-160.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.06.020
|
|
JIA Fei, MENG Xuelei, JIA Baotong, et al. Research on passenger flow assignment for high-speed railway under public health emergencies[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(6): 153-160.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.06.020
|
| [13] |
吴祥云, 刘灿齐. 轨道交通客流量均衡分配模型与算法[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2004, 32(9): 1158-1162.
|
|
WU Xiangyun, LIU Canqi. Traffic equilibrium assignment model specially for urban railway network[J]. Journal of Tongji University: Natural Science, 2004, 32(9): 1158-1162.
|
| [14] |
四兵锋, 毛保华, 刘智丽. 无缝换乘条件下城市轨道交通网络客流分配模型及算法[J]. 铁道学报, 2007, 29(6): 12-18.
|
|
SI Bingfeng, MAO Baohua, LIU Zhili. Passenger flow assignment model and algorithm for urban railway traffic network under the condition of seamless transfer[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2007, 29(6): 12-18.
|
| [15] |
马驷, 李昌浚, 应恒, 等. 基于AFC数据的客流路径选择[J]. 综合运输, 2019, 41(9): 50-56.
|
|
MA Si, LI Changjun, YING Heng, et al. Passenger flow path selection based on AFC data[J]. China Transportation Review, 2019, 41(9): 50-56.
|
| [16] |
李志纯, 黄海军. 随机交通分配中有效路径的确定方法[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2003, 3(1): 28-32.
|
|
LI Zhichun, HUANG Haijun. Determining the efficient paths in stochastic traffic assignment[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2003, 3(1): 28-32.
|
| [17] |
PRELEC D. The probability weighting function[J]. Econometrica, 1998, 66(3): 497-527.
doi: 10.2307/2998573
|
| [18] |
刘剑锋. 基于换乘的城市轨道交通网络流量分配建模及其实证研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2012.
|
|
LIU Jianfeng. Transfer-based modeling flow assignment with empirical analysis for urban rail transit network[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2012.
|
| [19] |
XU Hongli, ZHOU Jing, XU Wei. A decision-making rule for modeling travelers' route choice behavior based on cumulative prospect theory[J]. Transportation Research Part C, 2011, 19(2): 218-228.
doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2010.05.009
|