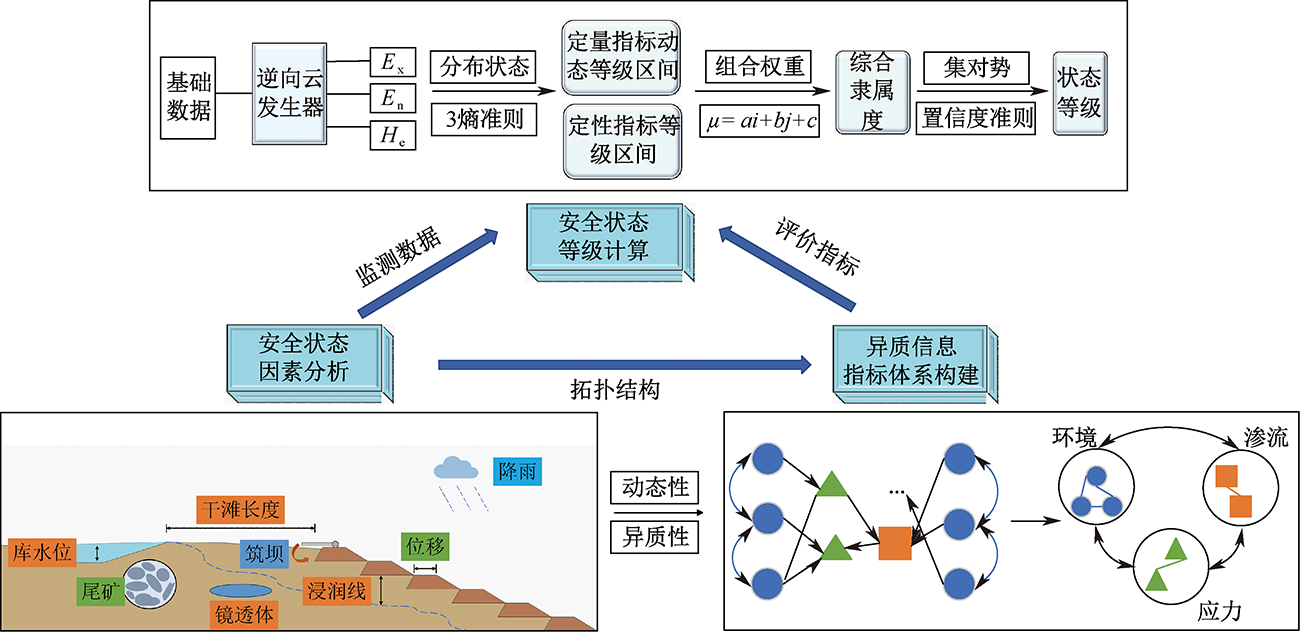
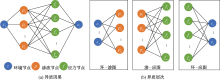
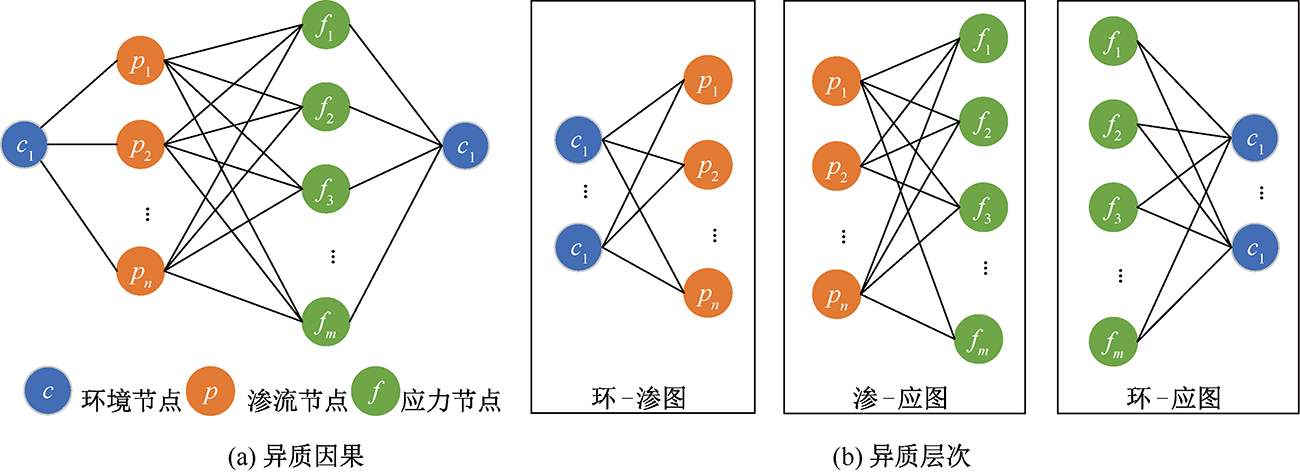
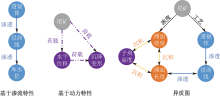
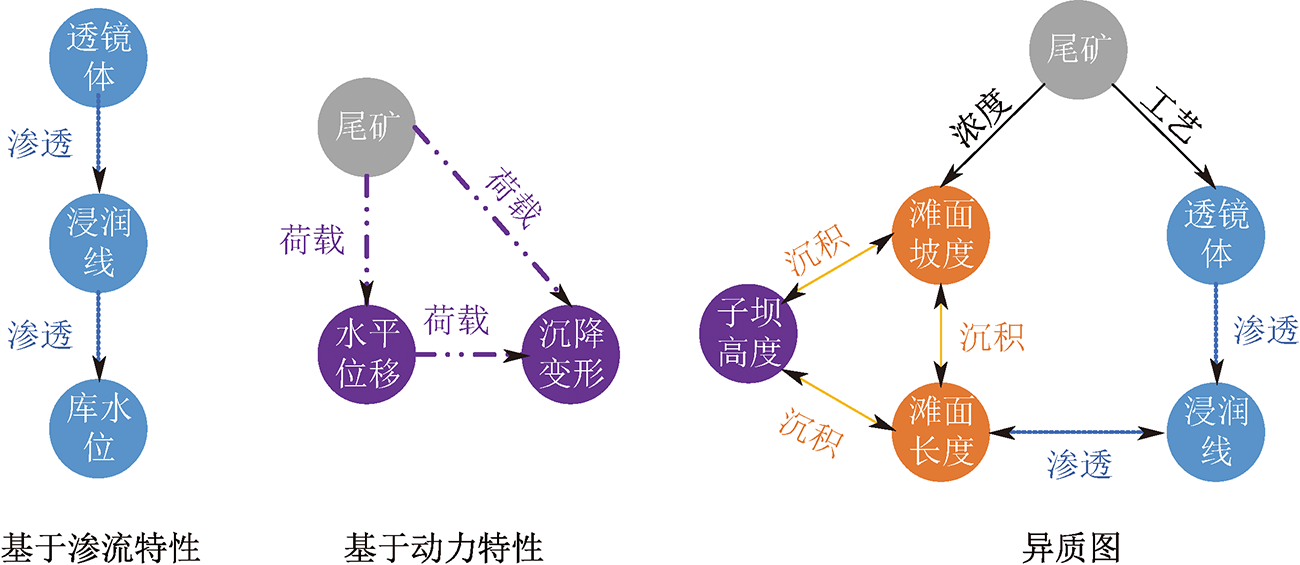
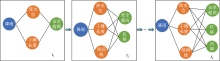
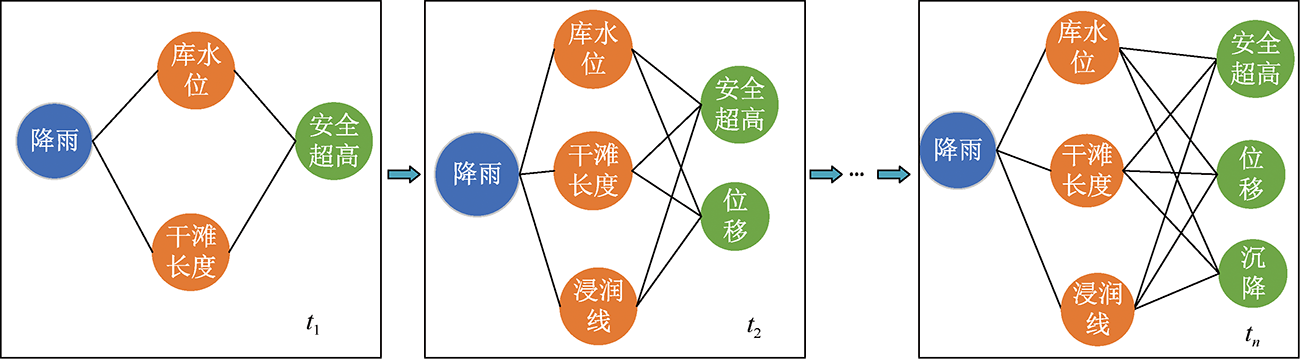
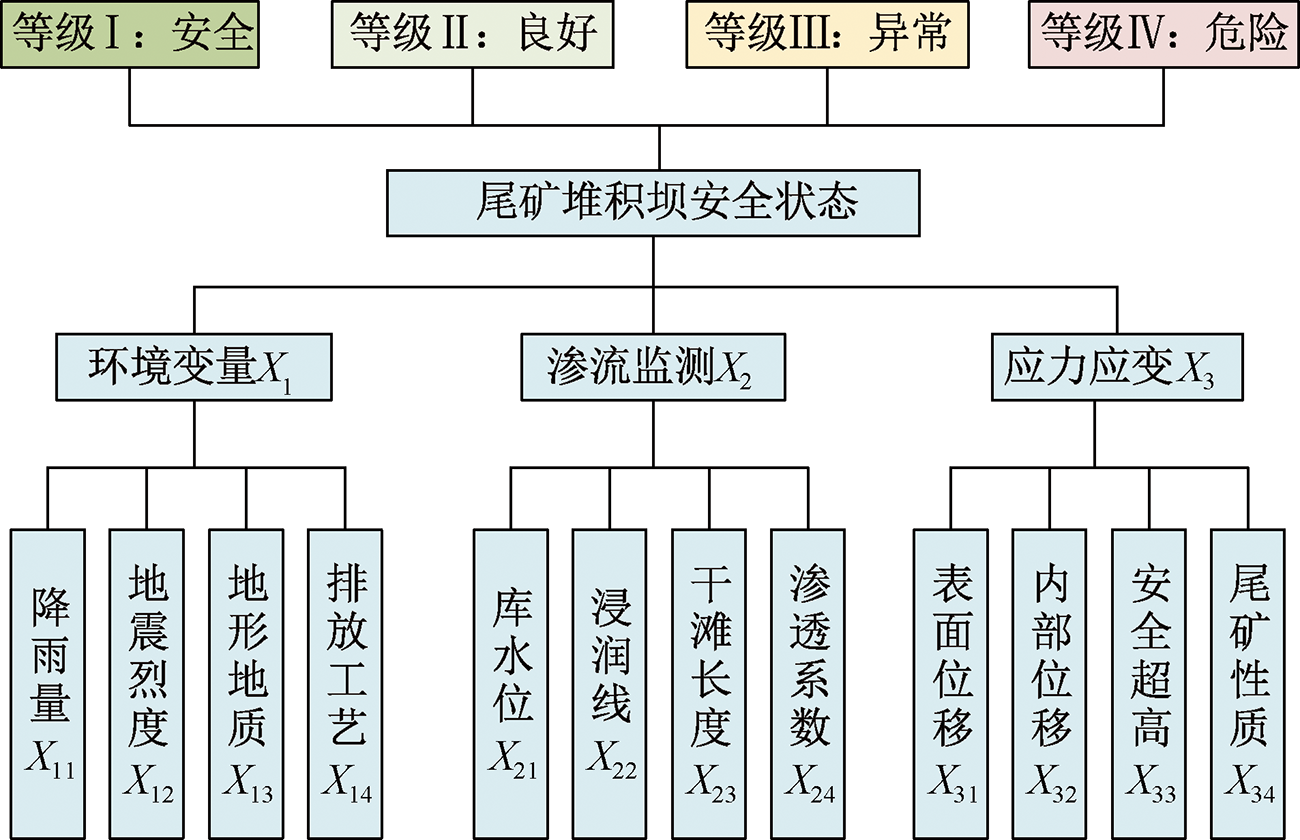
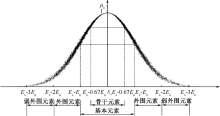
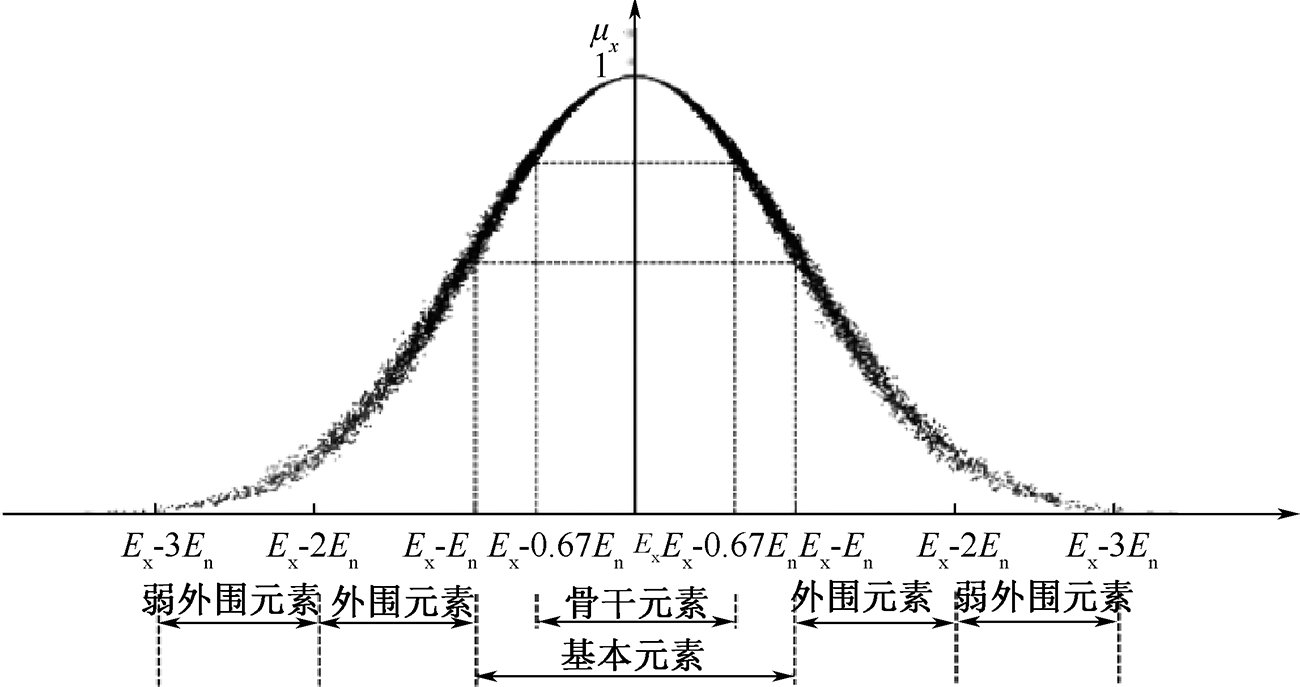
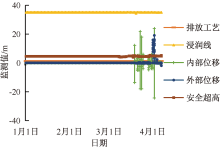
| [1] |
OWEN J R, KEMP D, LÈBRE E, et al. Catastrophic tailings dam failures and disaster risk disclosure[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2020, 42:101361-101 371.
|
| [2] |
CLARKSON L, WILLIAMS D. An overview of conventional tailings dam geotechnical failure mechanisms[J]. Mining Metallurgy & Exploration, 2021, 38(3): 1305-1328.
|
| [3] |
BAKER E. Mine tailings storage: safety is no accident[M]. Nairobi and Arendal: United Nations Environment Programme and GRID-Arendal, 2017:1-37.
|
| [4] |
LUMBROSO D, MCELROY C, GOFF C, et al. The potential to reduce the risks posed by tailings dams using satellite-based information:ScienceDirect[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2019, 38:101209-101 222.
|
| [5] |
DU Zheyuan, GE Linlin, NG A H M, et al. Risk assessment for tailings dams in Brumadinho of Brazil using InSAR time series approach[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 717:137125-137 138.
|
| [6] |
BUSELLI G, LU Kanglin. Groundwater contamination monitoring with multichannel electrical and electromagnetic methods[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2001, 48(1):11-23.
|
| [7] |
蒋卫东, 李夕兵, 邱更生. 基于最大Lyapunov指数分析的尾矿坝浸润线控制混沌方法[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2003, 3(5):16-20.
|
|
JIANG Weidong, LI Xibing, QIU Gengsheng. A new method for chaos-controlling of seepage line in tailings dam based on analysis of largest Lyapunov exponent[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2003, 3(5):16-20.
|
| [8] |
WANG Ligang, YANG Xiaocong, HE Manchao. Research on safety monitoring system of tailings dam based on internet of things[C]. Institute of Physics.International Symposium on Application of Materials Science and Energy Materials, Part 1 of 2, 2018:716-722.
|
| [9] |
杨春和, 张超, 李全明, 等. 大型高尾矿坝灾变机制与防控方法[J]. 岩土力学, 2021, 42(1):1-17.
|
|
YANG Chunhe, ZHANG Chao, LI Quanming, et al. Disaster mechanism and prevention methods of large-scale high tailings dam[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(1):1-17.
|
| [10] |
颜学军. 上游法尾矿堆筑坝坝体沉积规律探讨[J]. 稀有金属与硬质合, 2008, 36(2):54-58.
|
|
YAN Xuejun. Investigation on the depositing law of tailings dam by upstream damming[J]. Rare Metals and Cemented Carbides, 2008, 36(2):54-58.
|
| [11] |
张东明, 郑彬彬, 尹光志, 等. 高浓缩分级尾矿上游法堆坝及模型试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2016, 37(7):1832-1838,1 867.
|
|
ZHANG Dongming, ZHENG Binbin, YIN Guangzhi, et al. Model tests on upstream dam-building method using concentrated and classified tailings[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(7):1832-1838,1 867.
|
| [12] |
李辉, 易富, 张佳. 基于因素空间的尾矿坝稳定性综合评价[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(12): 28-34.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.12.005
|
|
LI Hui, YI Fu, ZHANG Jia. Comprehensive stability evaluation of tailing dam based on factor space[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(12): 28-34.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.12.005
|
| [13] |
潘科, 许开立, 刘琛. 基于三角模糊理论的尾矿库风险评价研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2012, 12(2):242-245.
|
|
PAN Ke, XU Kaili, LIU Chen. Risk evaluation model of tailings pond based on the triangular fuzzy theory[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2012, 12(2): 242-245.
|
| [14] |
戴剑勇, 王雯雯, 黄晓庆. 基于网络云模型的尾矿库溃坝安全评估[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2022, 22(1):1-7.
|
|
DAI Jianyong, WANG Wenwen, HUANG Xiaoqing. Safety assessment of tailings reservoir dam break based on network cloud model[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2022, 22(1):1-7.
|
| [15] |
柯丽华, 黄畅畅, 李全明, 等. 尾矿库安全态势分析及其敏感因素研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2021(11):165-172.
|
|
KE Lihua, HUANG Changchang, LI Quanming, et al. Safety situation analysis and sensitive factors study of tailings pond[J]. Metal Mine, 2021(11): 165-172.
|
| [16] |
DONG Kai, YANG Dewei, YAN Jihao, et al. Anomaly identification of monitoring data and safety evaluation method of tailings dam[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2022, 10: 1 016 458-1 016 470.
|
| [17] |
刘迪, 卢才武, 连民杰, 等. 基于贝叶斯决策的尾矿坝干滩长度预警研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(增1):120-126.
|
|
LIU Di, LU Caiwu, LIAN Minjie, et al. Dry beach length pre-warning of tailings dam based on Bayesian decision[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(S1):120-126.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.S1.0650
|
| [18] |
SITHARAM T G, HEGDE A M. Stability analysis of rock-fill tailing dam: an Indian case study[J]. International Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 11(4): 332-342.
|
| [19] |
BAUDRIT C, TAILLANDIER F, CURT C, et al. Graph based knowledge models for capitalizing, predicting and learning: a proof of concept applied to the dam systems[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2022, 52: 101 551-101 571.
|
| [20] |
杨春和, 张超, 马昌坤, 等. 高应力条件下尾矿破碎特性及坝体稳定性研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2022, 18(2):20-26.
|
|
YANG Chunhe, ZHANG Chao, MA Changkun, et al. Study on tailings breakage characteristics and dam stability under high stress conditions[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2022, 18(2):20-26.
|
| [21] |
曾纪涵, 章光, 吴浩, 等. 改进POT模型下尾矿坝综合预警值确定方法[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(5):134-139.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.05.1699
|
|
ZENG Jihan, ZHANG Guang, WU Hao, et al. Determination method of comprehensive early-warning indexes for tailing dam based on improved POT model[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(5):134-139.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.05.1699
|
| [22] |
李全明, 段志杰, 于玉贞, 等. 尾矿坝沉积结构特征与性能演化规律研究进展[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2022, 18(2):6-19.
|
|
LI Quanming, DUAN Zhijie, YU Yuzhen, et al. Research progress on deposition structure characteristics and performance evolution law of tailings dam[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2022, 18(2):6-19.
|
| [23] |
赵冰, 王光进, 刘文连, 等. 尾矿库坝体三维渗流场的数值模拟与试验分析[J]. 有色金属工程, 2020, 10(8):99-106.
|
|
ZHAO Bing, WANG Guangjin, LIU Wenlian, et al. Numerical simulation and experimental analysis of three-dimensional seepage field in tailings dam body[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2020, 10(8):99-106.
|
| [24] |
GB 39496—2020,尾矿库安全规程[S].
|
|
GB 39496-2020, Safety regulation for tailings pond[S].
|
| [25] |
阳雨平, 黄丕森, 陈国国. 基于改进FIM-未确知测度的尾矿库风险评价模型及应用[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2021, 21(3):996-1004.
|
|
YANG Yuping, HUANG Pisen, CHEN Guoguo. Safety evaluation of tailings pond based on FIM-optimization unascertained measure[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2021, 21(3):996-1004.
|