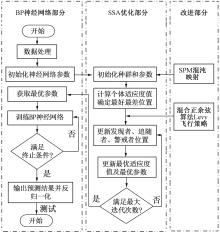
| [1] |
钱枫林, 崔健. BP神经网络模型在应急需求预测中的应用:以地震伤亡人数预测为例[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2013, 23(4): 20-25.
|
|
QIAN Fenglin, CUI Jian. Application of bp neural network analysis in forecasting emergency demand:a case study on earthquake casualty forecasting[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2013, 23(4): 20-25.
|
| [2] |
程琼琼. 基于GA的BP神经网络的地震应急物资需求预测[D]. 成都: 西南财经大学, 2016.
|
|
CHENG Qiongqiong. The forecast of earthquake emergency material demand based on GA optimization BP neural network[D]. Chengdu: Southwestern University of Finance and Economics, 2016.
|
| [3] |
樊睿. 基于PSO-BP神经网络的大型地震应急物资需求预测研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2020.
|
|
FAN Rui. Demand forecasting of large-scale earthquake emergency materials based on PSO-BP neural network[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2020.
|
| [4] |
王松松. 基于FOA-BP神经网络的地震应急物资需求预测研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州交通大学, 2022.
|
|
WANG Songsong. Research on earthquake emergency material demand forecast based on FOA-BP neural network[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2022.
|
| [5] |
张淞, 黄猛, 刘帅, 等. 基于网络信息与BP神经网络的应急物资需求预测研究:以积石山县6.2级地震为例[J]. 防灾科技学院学报, 2024, 26(3): 76-85.
|
|
ZHANG Song, HUANG Meng, LIU Shuai, et al. Emergency material demand prediction based on network information and BP neural network: taking Jishishan MS6. 2 earthquake,Gansu in 2023 as an example[J]. Journal of Institute of Disaster Prevention, 2024, 26(3): 76-85.
|
| [6] |
薛建凯. 一种新型的群智能优化技术的研究与应用:麻雀搜索算法[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2020.
|
|
XUE Jiankai. Research and application of a novel swarm intelligence optimization technique: sparrow search algorithm[D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2020.
|
| [7] |
吉露, 曹斌. 数据空间中一种基于步进的后映射(SPM)迭代方法[J]. 智能计算机与应用, 2021, 11(9): 22-27.
|
|
JI Lu, CAO Bin. An iterative method of step-by-step post-mapping (SPM) in data space[J]. Intelligent Computer and Applications, 2021, 11(9): 22-27.
|
| [8] |
徐松金, 龙文. 求解高维优化问题的改进正弦余弦算法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2018, 35(9): 2 574-2 577.
|
|
XU Songjin, LONG Wen. Improved sine cosine algorithm for solving high-dimensional optimization problems[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2018, 35(9): 2 574-2 577.
|
| [9] |
毛清华, 张强, 毛承成, 等. 混合正弦余弦算法和Lévy飞行的麻雀算法[J]. 山西大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 44(6): 1 086-1 091.
|
|
MAO Qinghua, ZHANG Qiang, MAO Chencheng, et al. Mixing sine and cosine algorithm with Lévy flying chaotic sparrow algorithm[J]. Journal of Shanxi University: Natural Science Edition, 2021, 44(6): 1 086-1 091.
|
| [10] |
周军, 孔菁菁. 多策略改进的麻雀搜索算法及其应用[J]. 东北师大学报:自然科学版, 2024, 56(4): 81-88.
|
|
ZHOU Jun, KONG Jingjing. Multi-strategy improved sparrow search algorithm and its application[J]. Journal of Northeast Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 2024, 56(4): 81-88.
|
| [11] |
国家统计局. 国家数据[EB/OL]. (2024-05-06). https://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.htm?cn=C01&zb=A0C0G&sj=2024.
|
| [12] |
EM-DAT. EM-DAT data entry procedures[EB/OL].[2024-05-06].https://public.emdat.be.
|
| [13] |
郭子雪, 韩瑞, 齐美然. 基于多元模糊回归的应急物资需求预测模型[J]. 河北大学学报:自然科学版, 2017, 37(4): 337-342.
|
|
GUO Zixue, HAN Rui, QI Meiran. Predictive method of emergency supplies demand based on multiple fuzzy linear regression model[J]. Journal of Hebei University: Natural Science Edition, 2017, 37(4): 337-342.
|
| [14] |
郭继东, 杨月巧. 地震应急物资需求预测的模糊案例推理技术[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2017, 13(2): 176-180.
|
|
GUO Jidong, YANG Yueqiao. Study on fuzzy case-based reasoning (FCBR) for demand forecast of emergency material in earthquake[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2017, 13(2): 176-180.
|
| [15] |
于汐, 孙思行, 张浩然, 等. 重特大地震应急物资需求预测方法研究进展[J]. 中国应急管理科学, 2022 (12): 66-76.
|
|
YU Xi, SUN Sihang, ZHANG Haoran, et al. Research progress of emergency materials demand forecasting method for major earthquake[J]. Journal of Chinese Emergency Management Science, 2022 (12): 66-76.
|
| [16] |
魏孝文. 震后应急物资需求预测及企业供应优化研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2021.
|
|
WEI Xiaowen. Research on the demand prediction of emergency materials and optimal scheduling of enterprise supply after the earthquake[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2021.
|
| [17] |
徐琳. 破坏性地震震后初期应急物资需求预测[D]. 成都: 四川大学, 2021.
|
|
XU Lin. Prediction of emergency materials demand for destructive earthquakes in the initial post earthquake period[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan University, 2021.
|
| [18] |
王小纯, 牟海波. 震后应急物资分配-运输问题研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2021, 18(4): 1 043-1 049.
|
|
WANG Xiaochun, MU Haibo. Research on allocation-transportation problem of emergency materials in post-earthquake[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2021, 18(4): 1 043-1 049.
|
| [19] |
唐红亮, 吴柏林, 胡旺, 等. 基于粒子群优化的地震应急物资多目标调度算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(3): 737-745.
|
|
TANG Hongliang, WU Bolin, HU Wang, et al. Earthquake emergency resource multiobjective schedule algorithm based on particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Electronics and Information Technology, 2020, 42(3): 737-745.
|
| [20] |
刘贾贾, 李凤, 刘龙, 等. 基于案例推理的地震应急物资需求预测[J]. 高原地震, 2020, 32(3): 69-74.
|
|
LIU Jiajia, LI Feng, LIU Long, et al. Prediction of earthquake emergency material demand based on case-based reasoning[J]. Plateau Earthquake Research, 2020, 32(3): 69-74.
|
| [21] |
周梦, 吕志刚, 邸若海, 等. 基于小样本数据的BP神经网络建模[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2022, 22(7): 2 754-2 760.
|
|
ZHOU Meng, LYU Zhigang, DI Ruohai, et al. BP neural network modeling based on small sample data[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2022, 22(7): 2 754-2 760.
|
| [22] |
蔡荣辉, 崔雨轩, 薛培静. 三层BP神经网络隐层节点数确定方法探究[J]. 电脑与信息技术, 2017, 25(5): 29-33.
|
|
CAI Ronghui, CUI Yuxuan, XUE Peijing. Research on the methods of determining the number of hidden nodes in three-layer BP neural network[J]. Computer and Information Technology, 2017, 25(5): 29-33.
|
| [23] |
聂高众, 高建国, 苏桂武, 等. 地震应急救助需求的模型化处理:来自地震震例的经验分析[J]. 资源科学, 2001, 23(1): 69-76.
|
|
NIE Gaozhong, GAO Jianguo, SU Guiwu, et al. Models on rapid jugement for the emergent rescue needs during earthquake:by analysis on post earthquake events[J]. Resources Science, 2001, 23(1): 69-76.
|
| [24] |
陈涛, 许燕蓉, 龙厚印. 面向地震灾害的应急物资需求预测[J]. 上海大学学报:自然科学版, 2022, 28(6): 946-956.
|
|
CHEN Tao, XU Yanrong, LONG Houyin. Demand prediction of emergency supplies for earthquake disaster[J]. Journal of Shanghai University: Natural Science Edition, 2022, 28(6): 946-956.
|
| [25] |
邓砚, 苏桂武, 聂高众. 中国地震应急地区系数的初步研究[J]. 灾害学, 2008, 23(1): 140-144.
|
|
DENG Yan, SU Guiwu, NIE Gaozhong. The preliminary study on the regional index (RI) of earthquake emergency response (EER) of China[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2008, 23(1): 140-144.
|