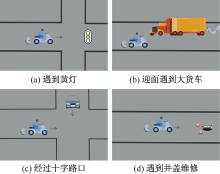
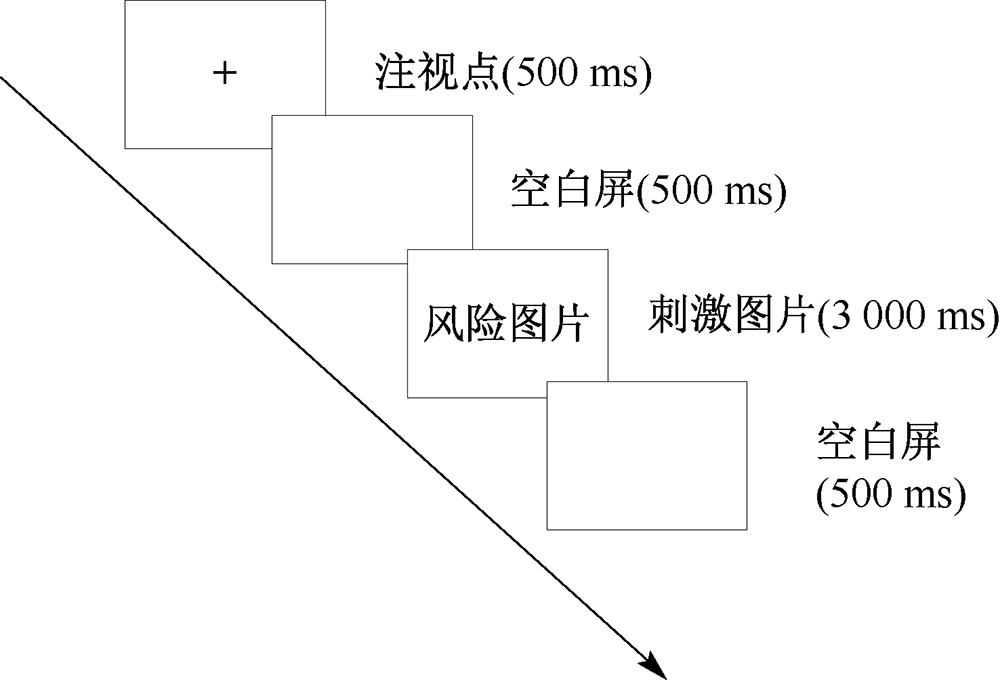
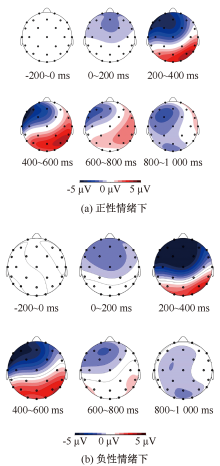
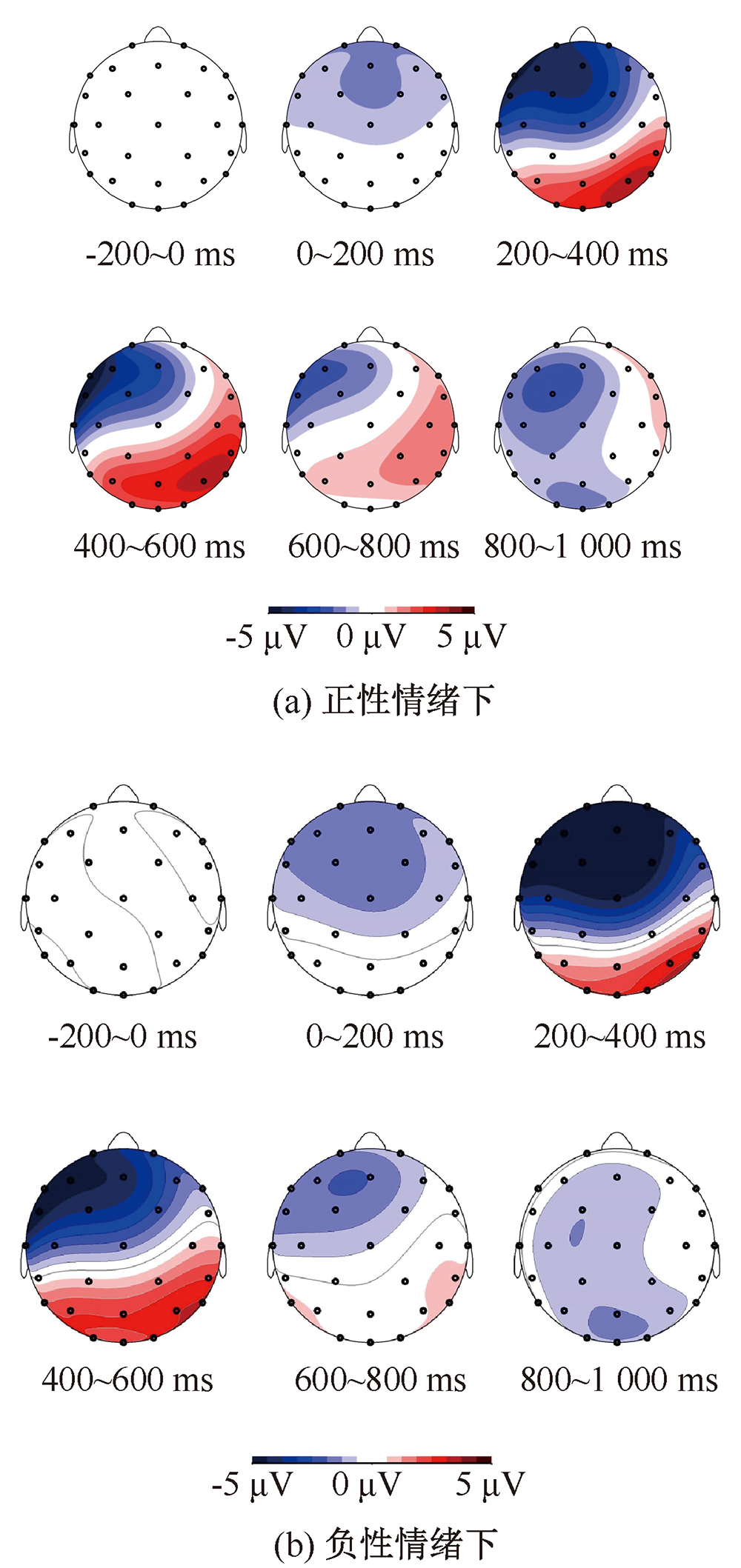
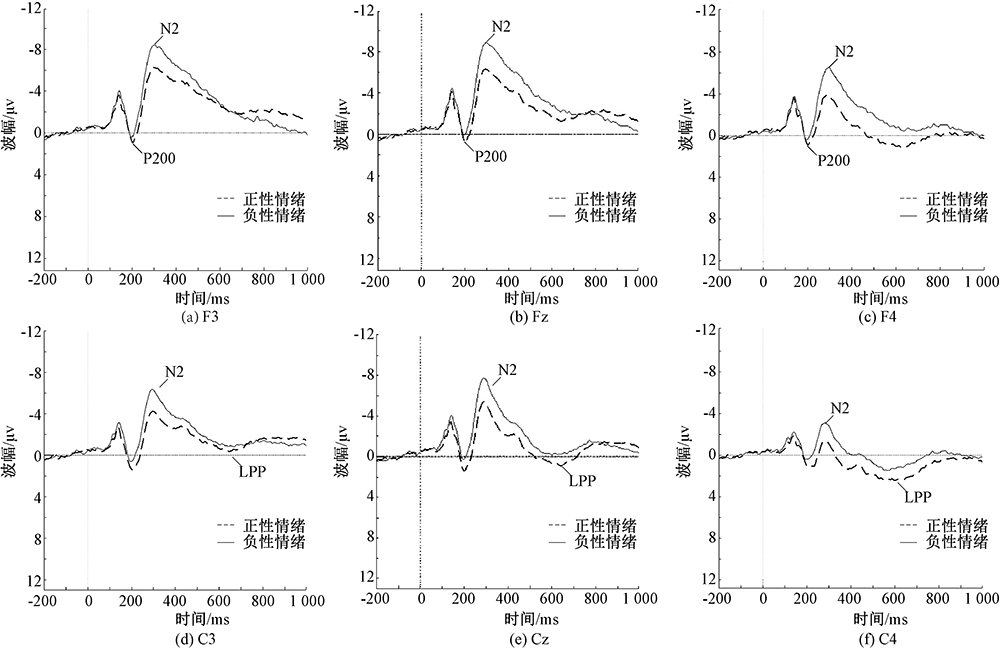
| [1] |
黄成军. 安全行为的心理分析[J]. 安全、健康和环境, 2004, 4(12):23-26.
|
|
HUANG Chengjun. Psychoanalysis of safety action[J]. Safety Healthy & Environment, 2004, 4(12):23-26.
|
| [2] |
HOLLNAGEL E. Human reliability analysis: context and control[M]. London: Academic Press, 1993:135-159.
|
| [3] |
付净, 韩子鹏, 刘辉, 等. 面对突发安全事故人的安全行为决策探究[J]. 吉林化工学院学报, 2011, 28(9):105-108.
|
|
FU Jing, HAN Zipeng, LIU Hui, et al. Research on people's safety behavior decision when facing unexpected safety accident[J]. Journal of Jilin Institute of Chemical Technology, 2011, 28(9):105-108.
|
| [4] |
刘菲. 大型群众性活动安全管理研究:以上海外滩踩踏事件为视角[J]. 湖北警官学院学报, 2015, 28(5):36-39.
|
| [5] |
阳剑兰, 武影慧. 基于“安全阀理论”的城市公交司乘冲突应急管理研究:以重庆“10·28”公交坠江事件为例[J]. 交通企业管理, 2019, 34(5):86-89.
|
| [6] |
SCHWARZ N, CLORE G L. Mood, misattribution, and judgments of well-being: informative and directive functions of affective states[J]. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 1983, 45(3):513-523.
doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.45.3.513
|
| [7] |
周湛菁. 性别、情绪效价和情绪唤醒度对风险决策的影响[D]. 长沙: 湖南师范大学, 2016.
|
|
ZHOU Zhanjing. Effects of gender, emotional valence and emotional arousal on risk decision-making[D]. Changsha: Hunan Normal University, 2016.
|
| [8] |
王丽. 情绪和任务框架对风险决策倾向的影响[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆师范大学, 2014.
|
|
WANG Li. Emotional and tasks framework impact on risk decision-making tendency[D]. Wulumuqi: Xinjiang Normal University, 2014.
|
| [9] |
JOHNSON E J, TVERSKY A. Affect, generalization, and the perception of risk[J]. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 1983, 45(1): 20-31.
doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.45.1.20
|
| [10] |
毕玉芳. 情绪对自我和他人风险决策影响的实验研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2006.
|
|
BI Yufang. The experimental research on the impact of emotion on self-other risk decision-making[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2006.
|
| [11] |
朱序. 应急情境诱发的情绪影响应急决策偏好及脑自动信息加工的研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2015.
|
| [12] |
ISEN A M, PATRICK R. The effect of positive feelings on risk taking: when the chips are down[J]. Organizational Behavior and Human Performance, 1983, 31(2):194-202.
doi: 10.1016/0030-5073(83)90120-4
|
| [13] |
KAHNEMAN D. Thinking, fast and slow[M]. New York: Random House Audio, 2011:22-25.
|
| [14] |
LOEWENSTEIN G F, WEBER E U, HSEE C K, et al. Risk as feelings[J]. Psychological Bulletin, 2001, 127(2):267-286.
doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.127.2.267
pmid: 11316014
|
| [15] |
张舒, 余亚琦, 史秀志. 安全风险决策阶段性模型构建:神经科学探索[J]. 科技促进发展, 2020, 16(12):1639-1646.
|
|
ZHANG Shu, YU Yaqi, SHI Xiuzhi. Phased model construction for safety risk decision based on neuroscience[J]. Science and Technology for Development, 2020, 16(12):1639-1646.
|
| [16] |
李磊, 王文涛, 施云航, 等. 基于眼动实验的情绪对驾驶员注意力的影响[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2021, 41(1):70-74.
|
|
LI Lei, WANG Wentao, SHI Yunhang, et al. Influences of emotion on drivers' attention based on eye movement experiment[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2021, 41(1):70-74.
|
| [17] |
王春雪, 吕淑然. 情绪对安全标志识别影响研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2016, 26(3):15-20.
|
|
WANG Chunxue, LYU Shuran. Research on effect of emotions on recognition of safety sign[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2016, 26(3):15-20.
|
| [18] |
吴博聪. 消极情绪对年轻驾驶员危险识别的影响[D]. 大连: 辽宁师范大学, 2021.
|
|
WU Bocong. The Influence of negative emotion on hazard detection of young drivers[D]. Dalian: Liaoning Normal University, 2021.
|
| [19] |
李琰, 毛钰, 张燕. 建筑工人应急行为影响机制[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(10):1-7.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.10.001
|
|
LI Yan, MAO Yu, ZHANG Yan. Influence mechanism of construction workers' emergency behavior[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(10):1-7.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.10.001
|
| [20] |
常淑芝, 孙延林. 认知负荷与情绪对篮球运动员风险决策框架效应的影响[J]. 天津体育学院学报, 2021, 36(5):569-573.
|
|
CHANG Shuzhi, SUN Yanlin. Influence of cognitive load and emotion on framing effect in risk decision-making of basketball players[J]. Journal of Tianjin University of Sport, 2021, 36(5):569-573.
|
| [21] |
陆翠薇, 夏璐, 李德阳, 等. 偶然情绪的效价和强度对风险决策的交互影响[J]. 中国健康心理学杂志, 2021, 29(11):1746-1752.
|
|
LU Cuiwei, XIA Lu, LI Deyang, et al. Interactive influence of the valence and intensity of accidental emotions on risk decision-making[J]. China Journal of Health Psychology, 2021, 29(11):1746-1752.
|
| [22] |
张舒, 黄云芳, 史秀志. 神经安全学建设背景与基础分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(5):98-105.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.05.015
|
|
ZHANG Shu, HUANG Yunfang, SHI Xiuzhi. Background and foundation analysis of construction of neuro-safety science[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(5):98-105.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.05.015
|
| [23] |
金晶. 安全标志信号词风险信息处理实验研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2011.
|
|
JIN Jing. The risk information processing for warning signal words: an experimental study[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2011.
|
| [24] |
CARRETIÉ L, MARTÍN-LOECHES M, HINOJOSA J A, et al. Emotion and attention interaction studied through event-related potentials[J]. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 2001, 13(8):1109-1128.
pmid: 11784449
|
| [25] |
CARRETIÉ L, MERCADO F, TAPIA M, et al. Emotion, attention, and the 'negativity bias', studied through event-related potentials[J]. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 2001, 41(1):75-85.
pmid: 11239699
|
| [26] |
李夏. 情绪影响风险决策的ERP研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江理工大学, 2013.
|
|
LI Xia. An event-related potentials study of mood affect risk decision-making: take happy and angry for example[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Sci-tech University, 2013.
|
| [27] |
WEINBERG A, HAJCAK G. The late positive potential predicts subsequent interference with target processing[J]. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 2011, 23:2994-3007.
doi: 10.1162/jocn.2011.21630
pmid: 21268668
|
| [28] |
FLAISCH T, STOCKBURGER J, SCHUPP H. Affective prime and target picture processing: an ERP analysis of early and late interference effects[J]. Brain Topography, 2008, 20:183-191.
doi: 10.1007/s10548-008-0045-6
pmid: 18335309
|
| [29] |
BRADLEY M M, LANG P J. Measuring emotion: the self-assessment manikin and the semantic differential[J]. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 1994, 25(1):49-59.
doi: 10.1016/0005-7916(94)90063-9
pmid: 7962581
|
| [30] |
李芳, 朱昭红, 白学军. 高兴和悲伤电影片段诱发情绪的有效性和时间进程[J]. 心理与行为研究, 2009, 7(1):32-38.
|
|
LI Fang, ZHU Zhaohong, BAI Xuejun. The duration of happiness and sadness induced by emotional film editing[J]. Studies of Psychology and Behavior, 2009, 7(1):32-38.
|
| [31] |
谢韵梓, 阳泽. 不同情绪诱发方法有效性的比较研究[J]. 心理与行为研究, 2016, 14(5):591-599.
|
|
XIE Yunzi, YANG Ze. A comparative study on the validity of different mood induction procedures (MIPs)[J]. Studies of Psychology and Behavior, 2016, 14(5):591-599.
|
| [32] |
代琨琦. 情绪反应的持续时间研究:以图片材料为例[D]. 信阳: 信阳师范学院, 2013.
|
|
DAI Kunqi. The duration of the emotion:take picture as an example[D]. Xinyang: Xinyang Normal University, 2013.
|
| [33] |
舒良超. 基于决策神经科学的不确定决策机理研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2009.
|
| [34] |
何玲. 情绪与情绪调节策略对不同感觉寻求运动员冲动行为的影响[D]. 北京: 北京体育大学, 2019.
|
|
HE Ling. The impact of emotion and emotional regulation strategies on different sensation seeking athletes' impulsive behavior[D]. Beijing: Beijing Sport University, 2019.
|
| [35] |
DENNIS T A, CHEN Chaocheng. Trait anxirty and conflict monitoring following threat: an ERP study[J]. Psychophysiology, 2009, 46(1):122-131.
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2008.00758.x
|
| [36] |
MA Qingguo, WANG Xiaoyi, DAI Shenyi, et al. Event-related potential N270 correlates of brand extension[J]. Neuroreport, 2007, 18(10):1031-1034.
pmid: 17558290
|
| [37] |
YANG Juan, LI Hong, ZHANG Ye, et al. The neural basis of risky decision-making in a blackjack task[J]. Neuroreport, 2007, 18(14):1507-1510.
pmid: 17712284
|
| [38] |
WICKENS C D. Engineering psychology and human performance 2th[M]. New York: Harper-collins, 1992:173-199.
|