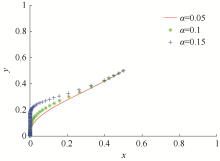
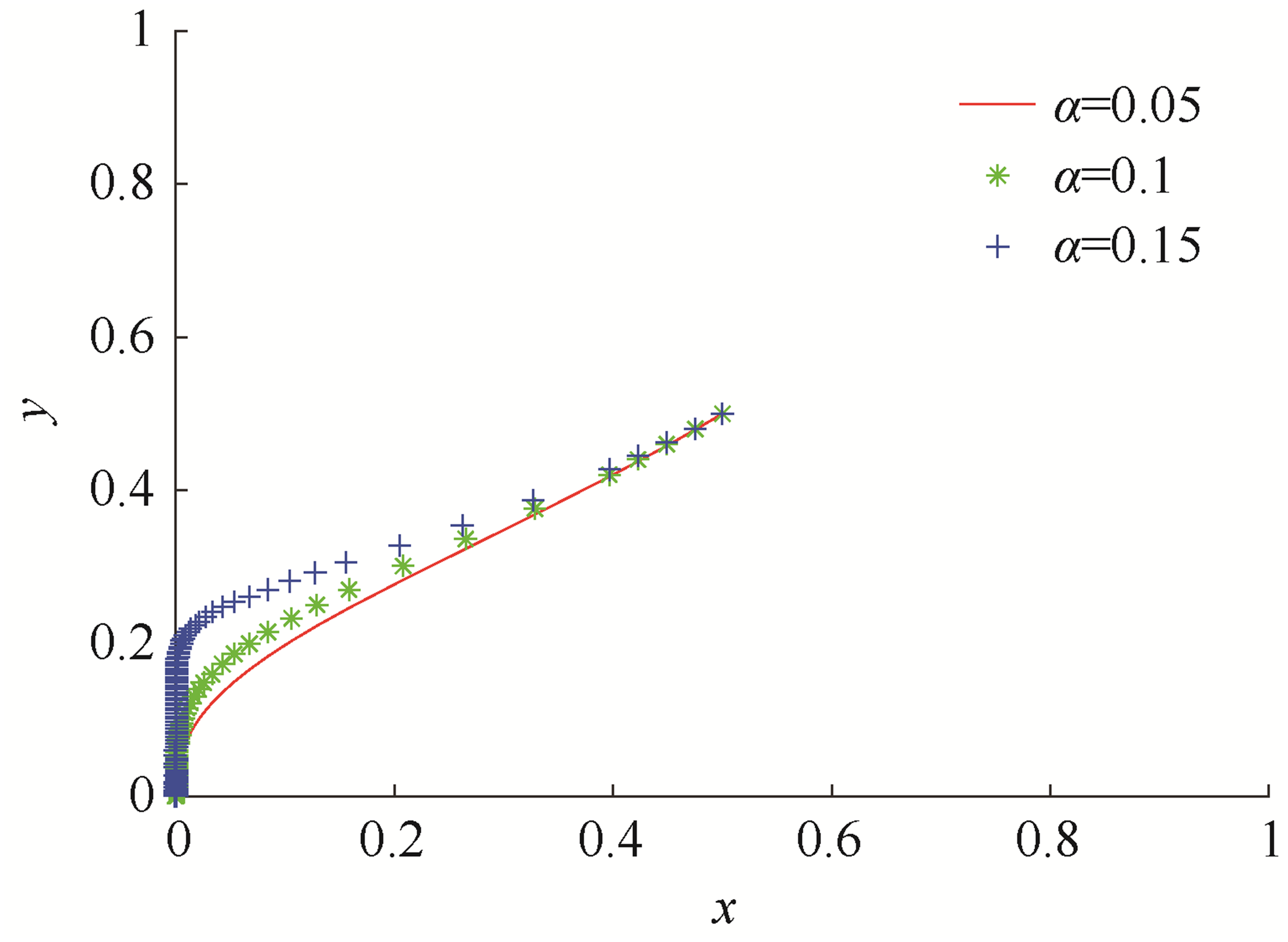
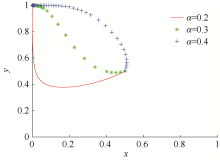
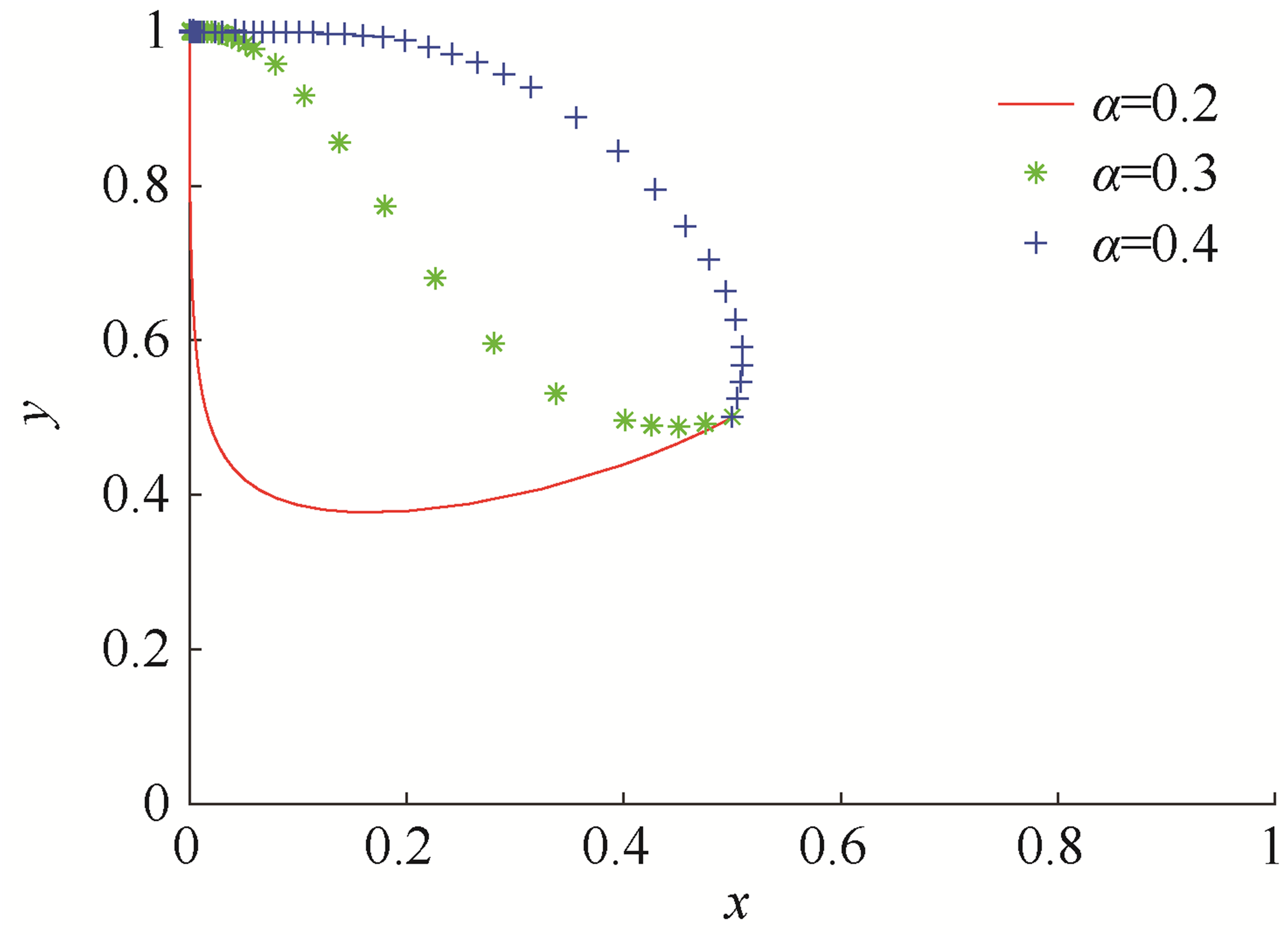
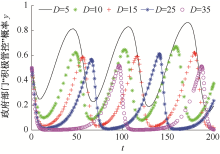
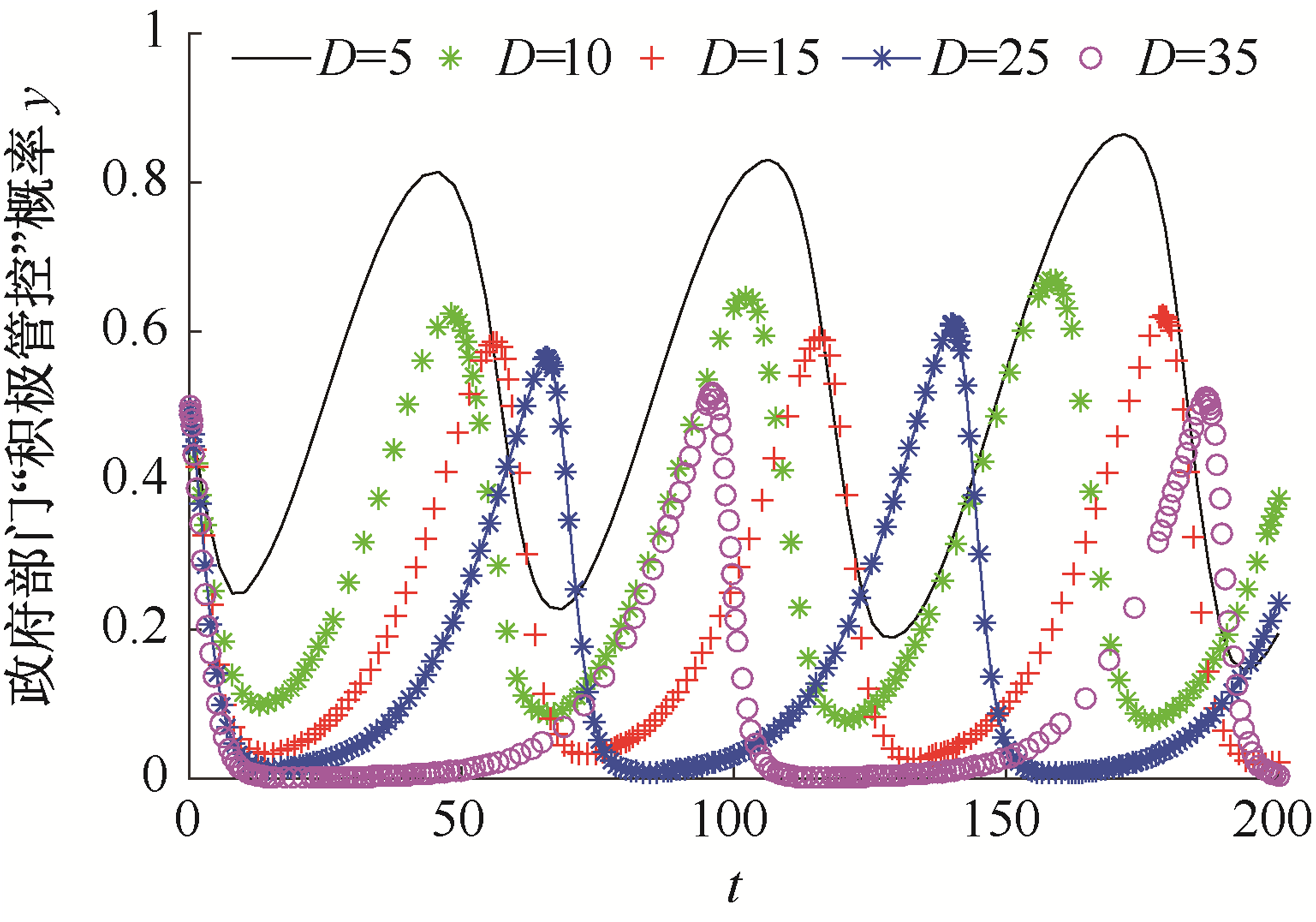
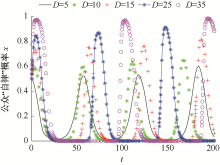
| [1] |
SU Yifeng, WU Chengha, LEE T F. Public health emergency response in Taiwan[J]. Health Security, 2017, 15(2):137-143.
doi: 10.1089/hs.2016.0108
pmid: 28418737
|
| [2] |
KIM Y, KU Minyoung, OH S S. Public health emergency response coordination: putting the plan into practice[J]. Journal of Risk Research, 2019, 123(3): 1-18.
|
| [3] |
曹策俊, 朱彦青, 张帆顺, 等. 考虑信任的公私合作监管演化博弈分析:以新冠病毒医疗垃圾管理为例[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(7):38-47.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.07.006
|
|
CAO Cejun, ZHU Yanqing, ZHANG Fanshun, et al. Evolutionary game analysis of public-private cooperative supervision considering trust: taking medical waste management generated from COVID-19 as example[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31 (7): 38-47.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.07.006
|
| [4] |
田方圆, 田水承, 李红霞, 等. 新冠疫情下民众心理特征与应急管理体系完善[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(11):30-36.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.11.005
|
|
TIAN Fangyuan, TIAN Shuicheng, LI Hongxia, et al. Psychological symptoms of public under COVID-19 outbreak and improvement of emergency management system[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(11): 30-36.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.11.005
|
| [5] |
FRASER C, DONNELLY C A, CAUCHEMEREZ S, et al. Pandemic potential of a strain of influenza A (H1N1): early findings[J]. Science, 2009, 324(5934):1557-1561.
doi: 10.1126/science.1176062
pmid: 19433588
|
| [6] |
SIRAKOULIS G C, KARAFYLLIDIS I, THANAILAKIS A. A cellular automaton model for the effects of population movement and vaccination on epidemic propagation[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2000, 133(3):209-223.
doi: 10.1016/S0304-3800(00)00294-5
|
| [7] |
刘德海, 王维国, 孙康. 基于演化博弈的重大公共卫生事件情景预测模型与防控措施[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2012, 32(5):937-946.
doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(2012)5-937
|
|
LIU Dehai, WANG Weiguo, SUN Kang. Scenario forecasting model and prevention-control measurements of important public health event based evolutionary game[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2012, 32(5):937-946.
|
| [8] |
王立贵, 孔雨微, 宋宏彬, 等. 基于疫情数据分析的传染病模拟仿真平台构建[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2020, 36(2):223-226.
|
|
WANG Ligui, KONG Yuwei, SONG Hongbin, et al. Construction of a surveillance-data based simulation platform for analysis of infectious disease epidemics[J]. Chinese Journal of Public Health, 2020, 36(2):223-226.
|
| [9] |
许智琪, 程郁琨, 姚双良. 突发公共卫生事件中地方政府与社会公众间的演化博弈研究[J]. 运筹学学报, 2021, 25(4):1-14.
|
|
XU Zhiqi, CHEN Yukun, YAO Shuangliang. Evolutionary analysis on cooperative behavior of local government and the public in the public health emergencies[J]. Operations Research Transactions, 2021, 25(4):1-14.
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.16381/j.cnki.issn1003-207x.2020.0587
|
|
LIANG Xi, CHEN Qingqing. Study on the major epidemic prevention and control under the mechanism of government dynamic reward and punishment[J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2021:DOI: 10.16381/j.cnki.issn1003-207x.2020.0587.
doi: 10.16381/j.cnki.issn1003-207x.2020.0587
|
| [11] |
庞天睿, 郑彤. 寄宿制学校新冠病毒肺炎疫情防控及传染风险分析[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2022, 54(2):73-80.
|
|
PANG Tianrui, ZHENG Tong. COVID-19 prevention and control measures and infection risks in a boarding school[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2022, 54(2):73-80.
|
| [12] |
TAYLOR P D, JONKER L B. Evolutionary stable strategies and game dynamics[J]. Mathematical Biosciences, 1978, 40(1/2):145-156.
doi: 10.1016/0025-5564(78)90077-9
|
| [13] |
沙雪良. 防控疫情不力,湖北公开4起问责、处理官员10人[EB/OL]. [2022-09-04]. http://www.bjnews.com.cn/news/2020/02/05/684729.
|
| [14] |
FRIEDMAN D. Evolutionary game in economics[J]. Econometrica, 1991, 59(3):637-666.
doi: 10.2307/2938222
|
| [15] |
疫情肆虐全球,看看各国那些被哄抢的产品有哪些[EB/OL].[2022-09-04]. https://www.cifnews.com/article/61794.
|