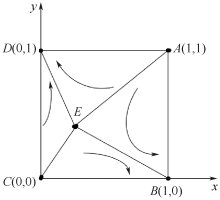
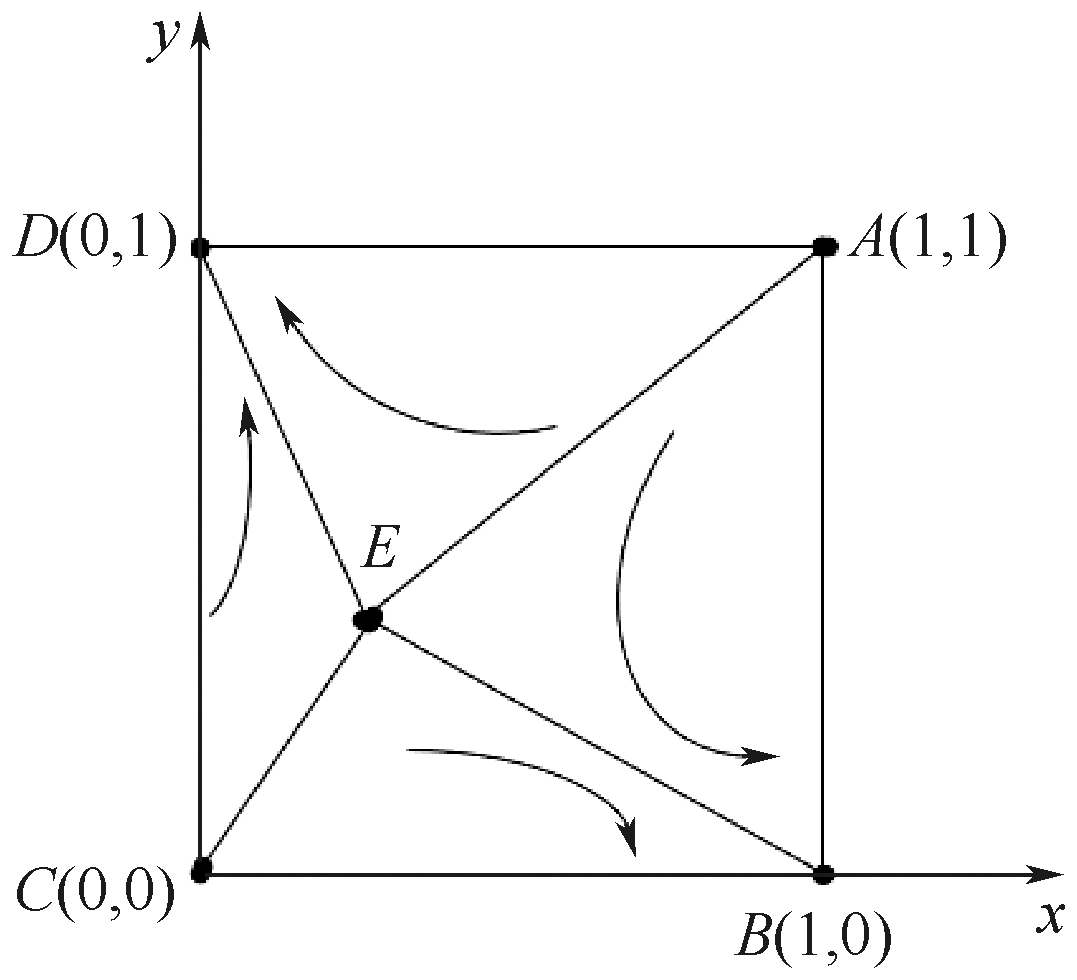
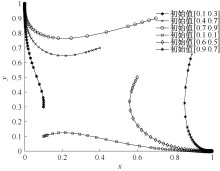
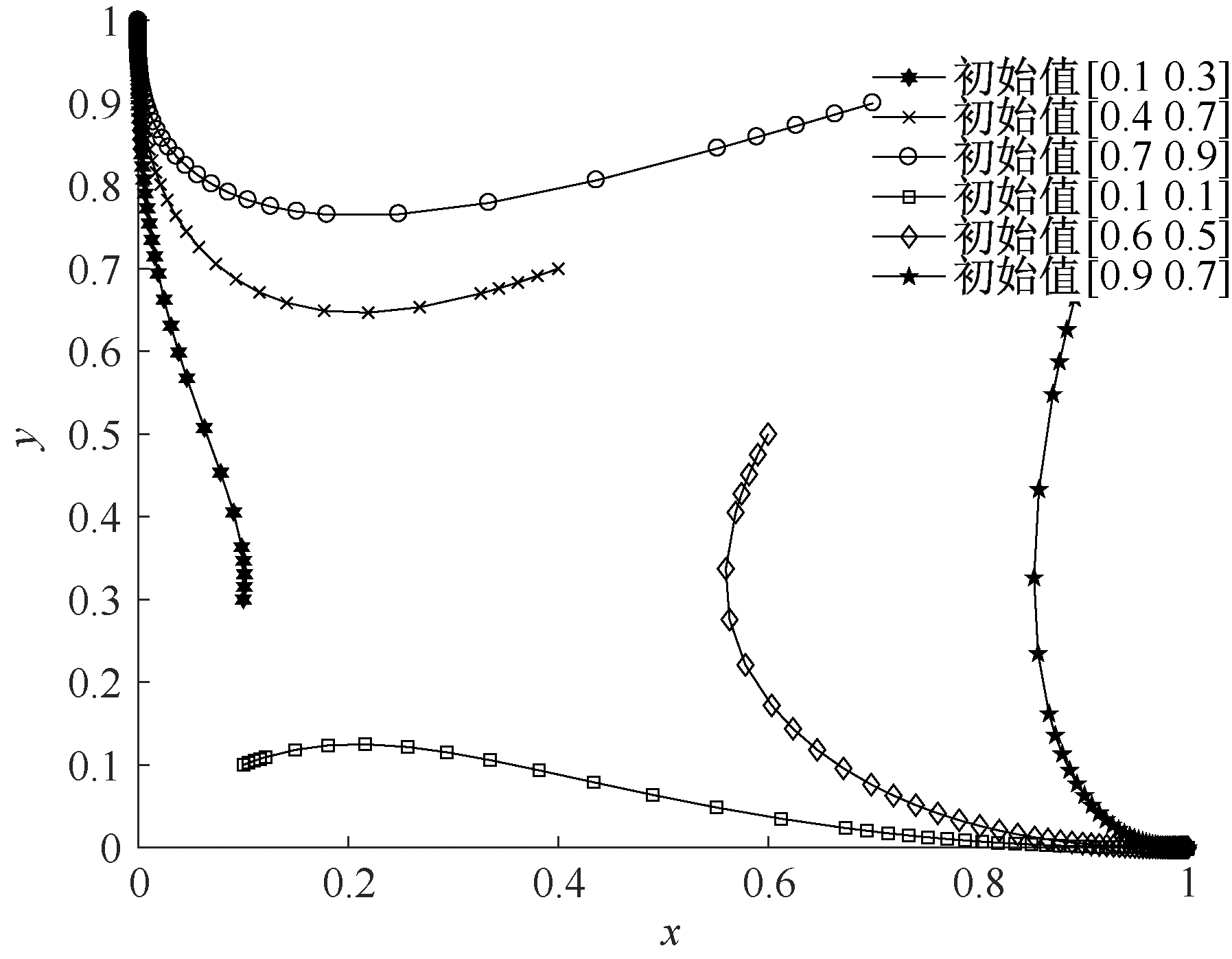
| [1] |
黄利华, 王亚飞, 马英楠, 等. 地铁站突发事件下乘客疏散行为认知特性研究[J]. 武汉理工大学学报:信息与管理工程版, 2021, 43(2):99-105.
|
|
HUANG Lihua, WANG Yafei, MA Yingnan, et al. Research on the cognitive characteristics of passengers' evacuation behavior in subway station emergency[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology: Information & Management Engineering, 2021, 43(2):99-105.
|
| [2] |
郑倩倩. 论城市公共安全风险评估机制的构建:基于上海外滩踩踏事件的分析[J]. 学理论, 2015(25):66-68.
|
|
ZHENG Qianqian. Construction of mechanism of risk assessment on urban public safety: based on the analysis of the stampede at Shanghai's bund area[J]. Theory Research, 2015(25):66-68.
|
| [3] |
孔令争, 张蕊, 杨明航, 等. 地铁车站通道行人超越行为改进社会力模型[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2022, 22(9):3722-3726.
|
|
KONG Lingzheng, ZHANG Rui, YANG Minghang, et al. Improved social force model of pedestrian overtaking behavior in subway station corridors[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2022, 22(9):3722-3726.
|
| [4] |
邢国新, 赵海龙, 任丹彤. 地铁车站安全疏散模型综述[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2023, 23(7):2417-2427.
|
|
XING Guoxin, ZHAO Hailong, REN Dantong. Synthetic analysis of safe evacuation models for subway stations[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2023, 23(7):2417-2427.
|
| [5] |
LO S M, HUANG H C, WANG P, et al. A game theory based exit selection model for evacuation[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2006, 41(5):364-369.
doi: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2006.02.003
|
| [6] |
GUO Yan, SONG Yan, CHEN Weiling. . Evolutionary game of emergency evacuation after an earthquake at a university: how to promote orderly evacuation[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9:2516-2534.
doi: 10.1109/Access.6287639
|
| [7] |
GUAN Junbiao, WANG Kaihua. Towards pedestrian room evacuation with a spatial game[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2019, 347:492-501.
doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2018.11.003
|
| [8] |
MA Yaping, LIU Xiaoying, HUO Feizhou, et al. Analysis of cooperation behaviors and crowd dynamics during pedestrian evacuation with group existence[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(9):1-19.
doi: 10.3390/su14010001
|
| [9] |
刘根旺, 周颖, 张磊, 等. 基于博弈论的人员疏散演化研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2020, 56(8):49-54.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1905-0175
|
|
LIU Genwang, ZHOU Ying, ZHANG Lei, et al. Research on pedestrian evacuation evolution based on game theory[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2020, 56(8):49-54.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1905-0175
|
| [10] |
FUKUI M, ISHIBASHI Y. Self-organized phase transitions in cellular automaton models for pedestrians[J]. Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 1999, 68 (8):2861-2863.
doi: 10.1143/JPSJ.68.2861
|
| [11] |
FUKUI M, ISHIBASHI Y. Jamming transition in cellular automaton models for pedestrians on passageway[J]. Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 1999, 68 (11):3738-3739.
doi: 10.1143/JPSJ.68.3738
|
| [12] |
YUE Hao, GUAN Hongzhi, ZHANG Juan, et al. Study on bi-direction pedestrian flow using cellular automata simulation[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2010, 389(3):527-539.
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2009.09.035
|
| [13] |
SUN Yi. Simulations of bi-direction pedestrian flow using kinetic Monte Carlo methods[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2019, 524:519-531.
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2019.04.081
|
| [14] |
YANAGISAWA D. Coordination game in bidirectional flow[J]. Collective Dynamics, 2016: DOI: 10.17815/CD.2016.8.
|
| [15] |
陈迅, 赖纯见. 区域房地产市场四方有限理性博弈研究[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2016, 36(4):857-874.
doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(2016)04-0857-18
|
|
CHEN Xun, LAI Chunjian. Research on the game of 4-player with bounded rationality in regional real estate market[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2016, 36(4):857-874.
|
| [16] |
ZHENG Xiaoping, CHENG Yuan. Conflict game in evacuation process: a study combining Cellular Automata model[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2011, 390(6):1042-1050.
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2010.12.007
|
| [17] |
SHI Dongmei, WANG Binghong. Evacuation of pedestrians from a single room by using snowdrift game theories[J]. Physical Review E, Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 2013, 87(2): DOI: 10.1103/physreve.87.022802.
|
| [18] |
FRIEDMAN D. Evolutionary game in economics[J]. Econometrica, 1991, 59(3):637-666.
doi: 10.2307/2938222
|
| [19] |
徐瑞华, 罗帆. 机场净空区无人机扰航监管演化博弈研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(5):25-30.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.05.005
|
|
XU Ruihua, LUO Fan. Evolutionary game research of supervision on unmanned aerial vehicle interference with flights in airfield clearance area[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(5):25-30.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.05.005
|
| [20] |
曹策俊, 朱彦青, 张帆顺, 等. 考虑信任的公私合作监管演化博弈分析:以新冠病毒医疗垃圾管理为例[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(7):38-47.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.07.006
|
|
CAO Cejun, ZHU Yanqing, ZHANG Fanshun, et al. Evolutionary game analysis of public-private cooperative supervision considering trust: taking medical waste management[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(7):38-47.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.07.006
|