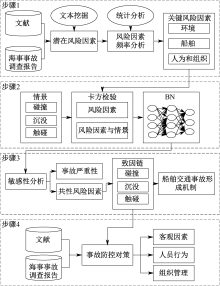
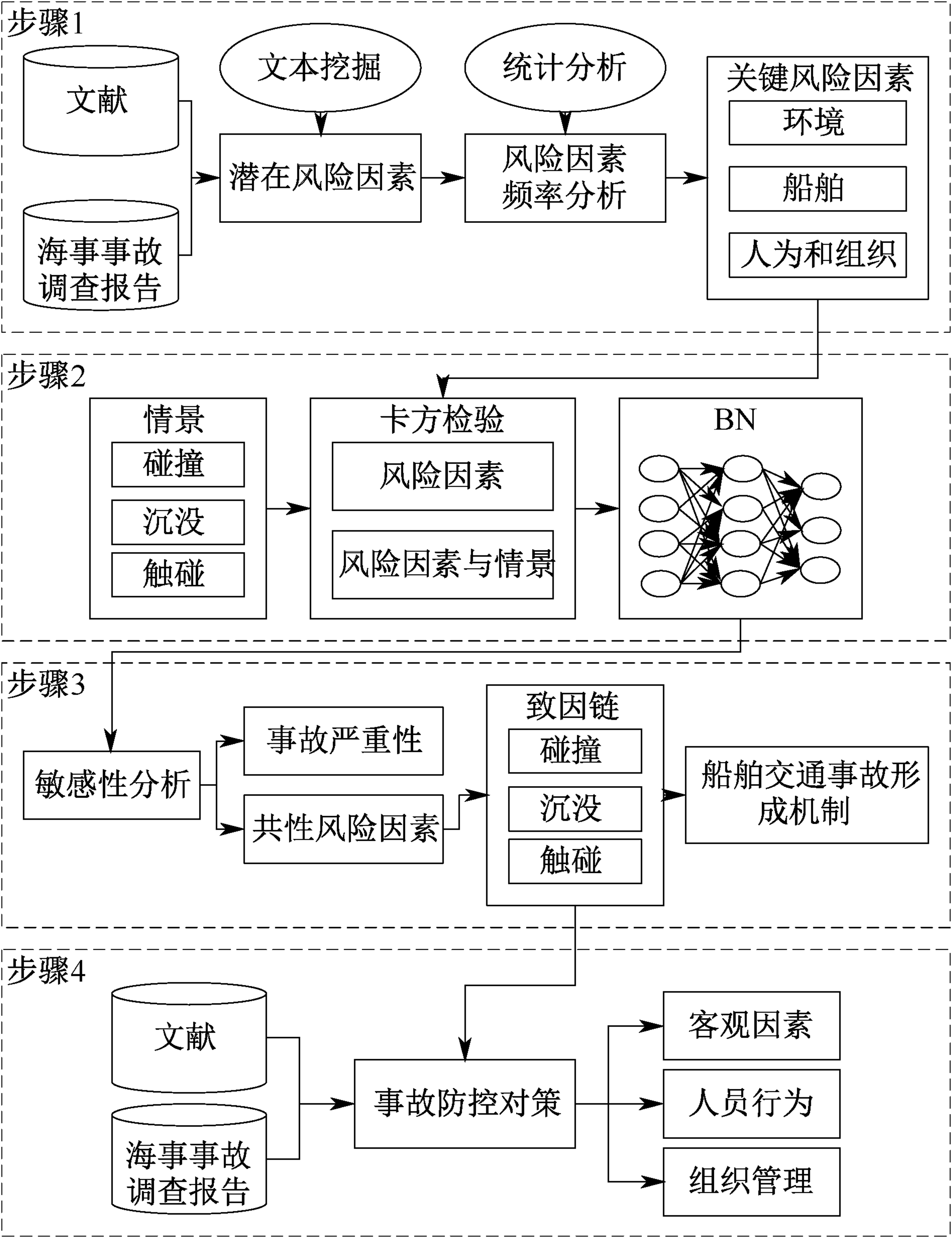
| [1] |
WU Bing, TIAN Huibin, YAN Xinping, et al. A probabilistic consequence estimation model for collision accidents in the downstream of Yangtze River using Bayesian networks[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part O: Journal of Risk and Reliability, 2020, 234(2): 422-436.
doi: 10.1177/1748006X19825706
|
| [2] |
YAN Xinping, WAN Chengpeng, ZHANG Di, et al. Safety management of waterway congestions under dynamic risk conditions: a case study of the Yangtze River[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2017, 59: 115-128.
doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2017.05.053
|
| [3] |
ZHANG Di, YAN Xinping, YANG Zaili, et al. An accident data-based approach for congestion risk assessment of inland waterways: a Yangtze River case[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part O: Journal of Risk and Reliability, 2014, 228(2): 176-188.
doi: 10.1177/1748006X13508107
|
| [4] |
陈伟炯, 卢忆宁, 张善杰, 等. 跨海大桥船桥碰撞模糊Bow-tie风险评估方法[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(1):87-92.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.01.015
|
|
CHEN Weijiong, LU Yining, ZHANG Shanjie, et al. A method for assessing risk of ship sea-bridge collision based on fuzzy-Bow-tie[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(1):87-92.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.01.015
|
| [5] |
KUM S, SAHIN B. A root cause analysis for Arctic Marine accidents from 1993 to 2011[J]. Safety Science, 2015, 74: 206-220.
doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2014.12.010
|
| [6] |
ZHANG Mingyang, ZHANG Di, GOERLANDT F, et al. Use of HFACS and fault tree model for collision risk factors analysis of icebreaker assistance in ice-covered waters[J]. Safety Science, 2019, 111: 128-143.
doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2018.07.002
|
| [7] |
WANG Likun, WANG Jinhui, SHI Mingyang, et al. Critical risk factors in ship fire accidents[J]. Maritime Policy & Management, 2021, 48(6): 895-913.
|
| [8] |
TRUCCO P, CAGNO E, RUGGERI F, et al. A Bayesian belief network modelling of organizational factors in risk analysis: a case study in maritime transportation[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2008, 93(6): 845-856.
doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2007.03.035
|
| [9] |
WANG Likun, YANG Zaili. Bayesian network modelling and analysis of accident severity in waterborne transportation: a case study in China[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2018, 180: 277-289.
doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2018.07.021
|
| [10] |
陈克嘉, 毛喆, 吴兵, 等. 基于互信息的长江船舶碰撞险情等级预测方法[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(11):168-175.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.11.027
|
|
CHEN Kejia, MAO Zhe, WU Bing, et al. Mutual information based prediction of level of collision incident in Yangtze river[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(11):168-175.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2018.11.027
|
| [11] |
司东森, 张英俊, 郎坤. 基于改进BN的集装箱船舶碰撞事故致因分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(10):31-37.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.10.006
|
|
SI Dongsen, ZHANG Yingjun, LANG Kun. Causation analysis of container ship collision accidents based on improved BN[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(10):31-37.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.10.006
|
| [12] |
WENG Jinxian, LIAO Shiguan, WU Bing, et al. Exploring effects of ship traffic characteristics and environmental conditions on ship collision frequency[J]. Maritime Policy & Management, 2020, 47(4): 523-543.
|
| [13] |
中华人民共和国交通运输部. 水上交通事故统计办法[L].2014-09-30.
|
| [14] |
ZHAO Xiaoyuan, YUAN Haiwen, YU Qing. Autonomous vessels in the Yangtze river: a study on the maritime accidents using data-driven Bayesian networks[J]. Sustainability, 2021, 13(17): DOI: 10.3390/su13179985.
doi: 10.3390/su13179985
|
| [15] |
国际海事组织. 1972年国际海上避碰规则[L]. 1972-10-20.
|
|
International Maritime Organization. International convention on the rules of collision avoidance by sea in 1972[L]. 1972-10-20.
|