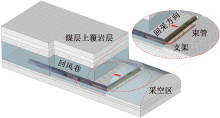
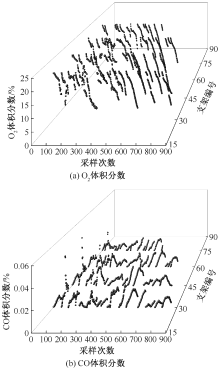
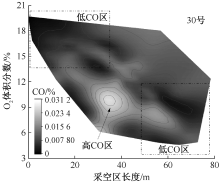
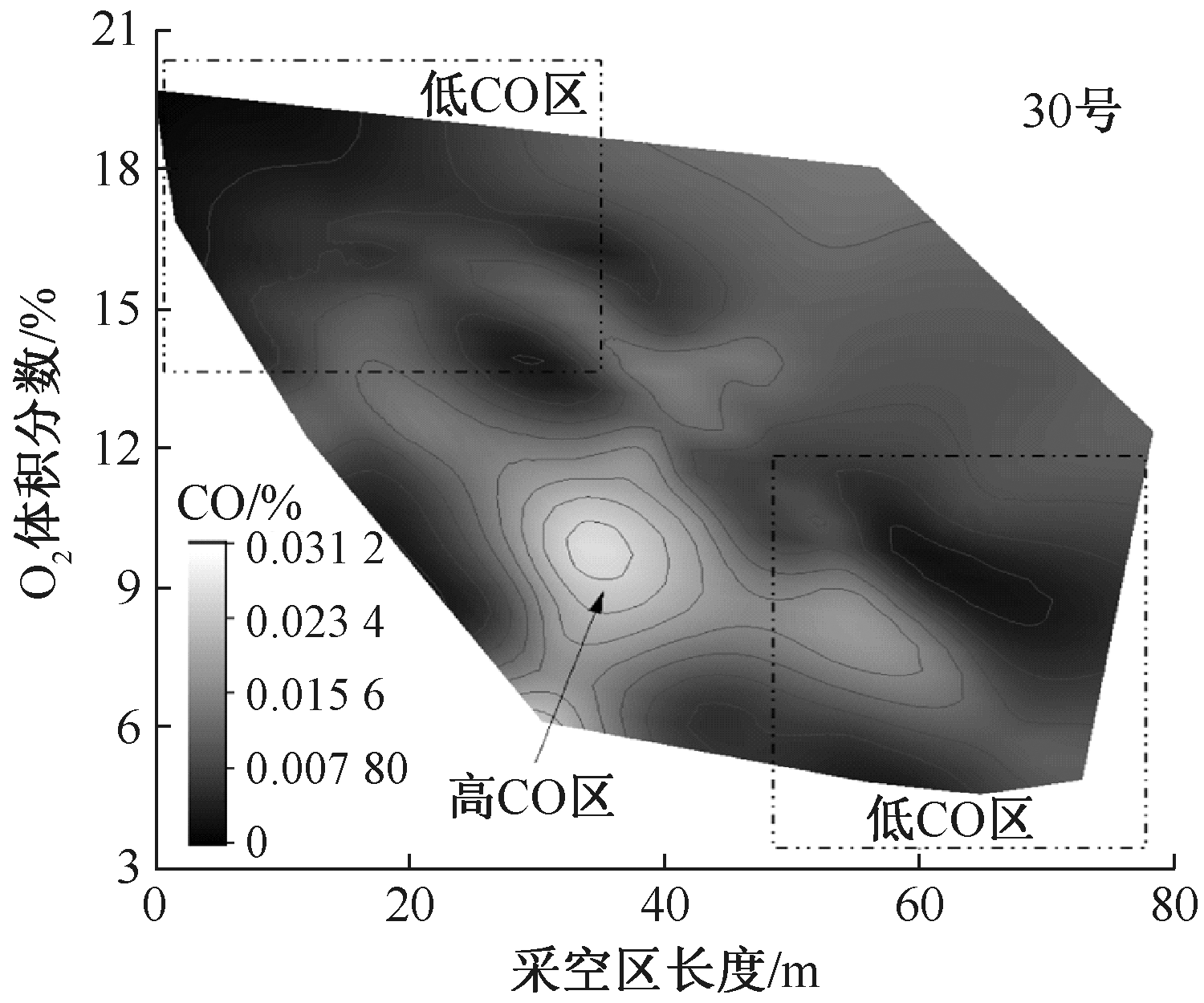
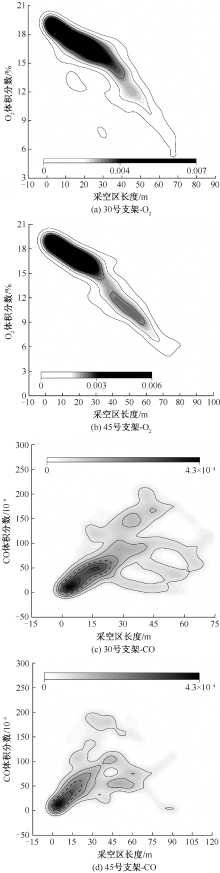
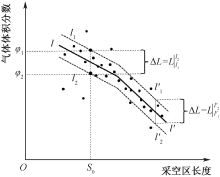
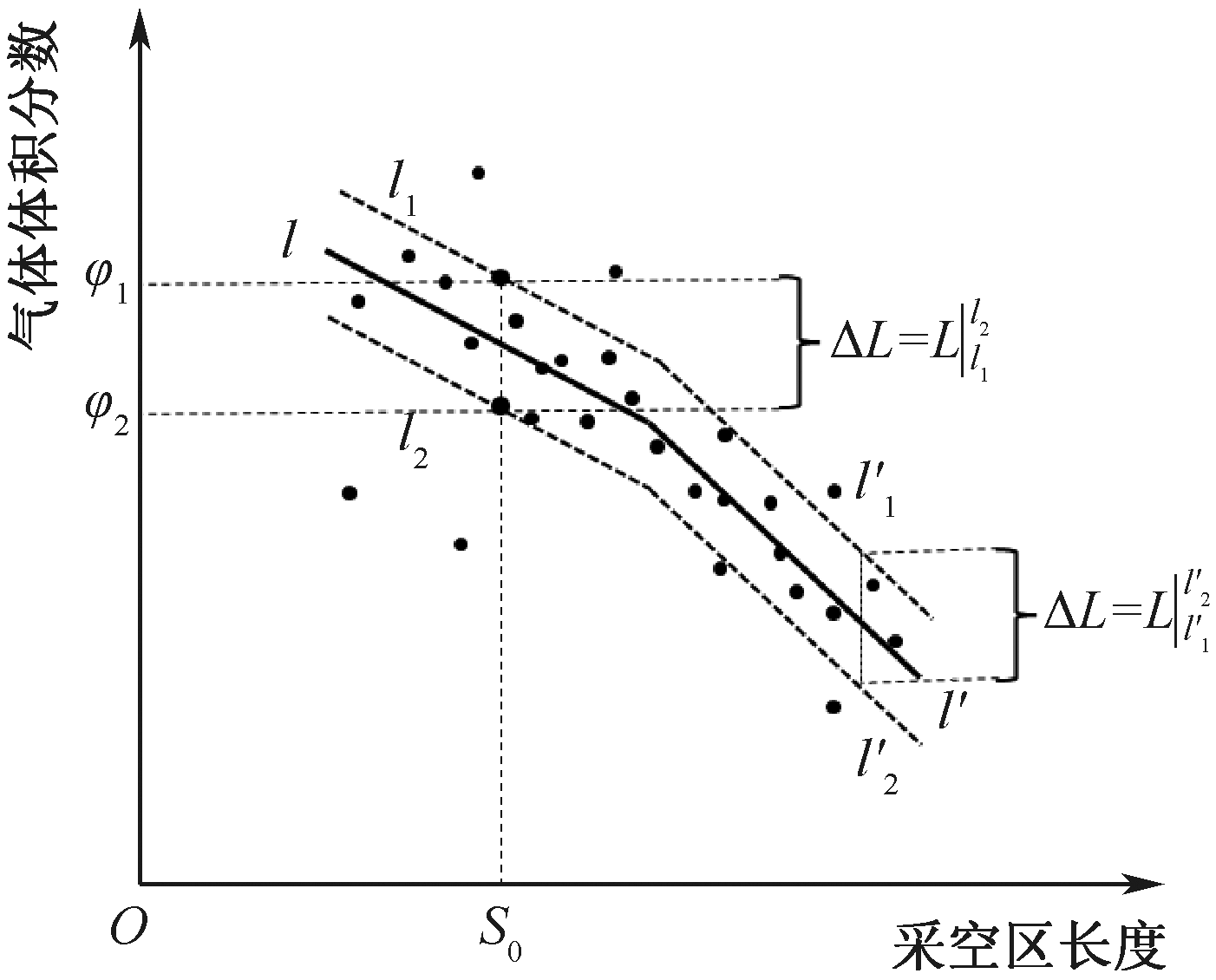
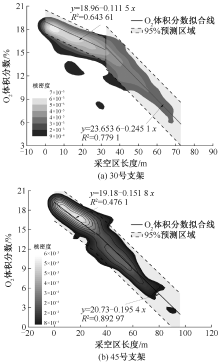
| [1] |
ZHU Hongqing, WANG Jiashuo, LI Rui, et al. Experimental and quantum chemical study of synergistic inhibitor based on physicochemical interaction in the prevention of coal spontaneous combustion[J]. Fuel, 2025,392: DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2025.134839.
|
| [2] |
肖旸, 张二川, 尹岚, 等. 地下煤火灾害机理及热动力演化与热能利用研究进展[J]. 煤矿安全, 2024, 55(11):1-18.
|
|
XIAO Yang, ZHANG Erchuan, YIN Lan, et al. Research progress of underground coal fire disaster mechanism, thermodynamic evolution and thermal energy utilization[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2024, 55(11): 1-18.
|
| [3] |
张巨峰, 施式亮, 鲁义, 等. 矿井瓦斯与煤自燃共生灾害:耦合关系、致灾机制、防控技术[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(10):149-155.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.10.021
|
|
ZHANG Jufeng, SHI Shiliang, LU Yi, et al. Symbiotic disasters of mine gas and coal spontaneous combustion: coupling relationship, disaster mechanism, prevention and control technology[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(10): 149-155.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2020.10.021
|
| [4] |
张家林, 杨帆, 张望, 等. 深部资源开采创新成效分析与思考[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2024, 41(3):450-461.
|
|
ZHANG Jialin, YANG Fan, ZHANG Wang, et al. Innovation effectiveness analysis and technology management reflection of deep resource exploitation[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2024, 41(3): 450-461.
|
| [5] |
董宪伟, 崔静, 董轩萌, 等. 不同氧体积分数影响预氧化煤自燃特性研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2025, 21(7):62-69.
|
|
DONG Xianwei, CUI Jing, DONG Xuanmeng, et al. Effect of different oxygen volume fractions on spontaneous combustion characteristics of pre-oxidized coal[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2025, 21(7): 62-69.
|
| [6] |
信亚男. 高抽巷抽采条件下采空区瓦斯与煤自燃耦合灾害的研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2019.
|
|
XIN Ya'nan. Study on coupling disasters of gas and coal spontaneous combustion in goaf under the condition of high drainage roadway[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2019.
|
| [7] |
YAN Qingqiong, LU Yi, WANG Qiao, et al. Research progress and development trend of coal spontaneous combustion prevention technology[J]. Combustion Science and Technology, 2025, 197: DOI: 10.1080/00102202.2024.2331752.
|
| [8] |
郭军, 刘华, 金彦, 等. 地下煤自燃隐蔽火源探测方法综述及新技术展望[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(8):111-119.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.08.0296
|
|
GUO Jun, LIU Hua, JIN Yan, et al. Summary of underground hidden coal spontaneous combustion fire source detection methods and prospect of new technologies[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(8): 111-119.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.08.0296
|
| [9] |
王德明. 煤矿热动力灾害及特性[J]. 煤炭学报, 2018, 43(1):137-142.
|
|
WANG Deming. Thermodynamic disaster in coal mine and its characteristics[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(1): 137-142.
|
| [10] |
秦波涛, 仲晓星, 王德明, 等. 煤自燃过程特性及防治技术研究进展[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2021, 49(1):66-99.
|
|
QIN Botao, ZHONG Xiaoxing, WANG Deming, et al. Research progress of coal spontaneous combustion process characteristics and prevention technology[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(1): 66-99.
|
| [11] |
任万兴, 郭庆, 石晶泰, 等. 基于标志气体统计学特征的煤自燃预警指标构建[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(6):1747-1758.
|
|
REN Wanxing, GUO Qing, SHI Jingtai, et al. Construction of early warning indicators for coal spontaneous combustion based on statistical characteristics of index gases[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(6): 1747-1758.
|
| [12] |
LEI Changkui, DENG Jun, CAO Kai, et al. A comparison of random forest and support vector machine approaches to predict coal spontaneous combustion in gob[J]. Fuel, 2018: DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.11.006.
|
| [13] |
邓军, 李青蔚, 肖旸, 等. 原煤和氧化煤的低温氧化特性[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2018, 38(1):1-7.
|
|
DENG Jun, LI Qingwei, XIAO Yang, et al. Characteristics of low-temperature oxidation of raw and oxidized coals[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2018, 38(1): 1-7.
|
| [14] |
LIANG Yuntao, YANG Yalan, GUO Sida, et al. Combustion mechanism and control approaches of underground coal fires: a review[J]. International Journal of Coal Science & Technology, 2023, 10: DOI: 10.1007/S40789-023-00581-W.
|
| [15] |
GUO Qing, REN Wanxing, LU Wei. New classification method of coal spontaneous combustion three zones in the goaf based on non-parametric kernel density estimation[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2023, 30: DOI: 10.1007/S11356-022-22528-5.
|
| [16] |
李增华, 苗国栋. 煤自燃大分子量气态产物生成规律研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2023, 52(6):1119-1128.
|
|
LI Zenghua, MIAO Guodong. Study of the emission law of higher-molecular-weight gases during coal spontaneous combustion[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2023, 52(6): 1119-1128.
|
| [17] |
李金虎, 黄珏洁, 陆伟, 等. 煤中高活性含碳固体自由基与煤自燃反应性的相关关系[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2024, 52(12):127-142.
|
|
LI Jinhu, HUANG Juejie, LU Wei, et al. Correlation between highly active carbon-containing solid free radicals and spontaneous combustion reactivity of coal[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2024, 52(12): 127-142.
|
| [18] |
梁运涛, 王伟, 王刚, 等. 《煤矿防灭火细则》编制原则及要点解读[J]. 煤矿安全, 2022, 53(5):230-235.
|
|
LIANG Yuntao, WANG Wei, WANG Gang, et al. Compilation principle and key points interpretation of Coal Mine Fire Prevention and Control Rules[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(5): 230-235.
|
| [19] |
曹凯, 杨海宇, 李长红, 等. 基于最适带宽的核密度估计源搜索方法[J]. 计算机仿真, 2024, 41(3):441-447.
|
|
CAO Kai, YANG Haiyu, LI Changhong, et al. Source search method for kernel density estimation based on optimal bandwidth[J]. Computer Simulation, 2024, 41(03): 441-447.
|
| [20] |
牛文铁, 才福友, 付景静. 基于自适应带宽核密度估计的载荷外推方法研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2021, 52(1):375-384.
|
|
NIU Wentie, CAI Fuyou, FU Jingjing. Load extrapolation method based on adaptive bandwidth kernel density estimation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2021, 52(1): 375-384.
|