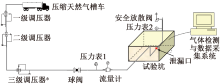
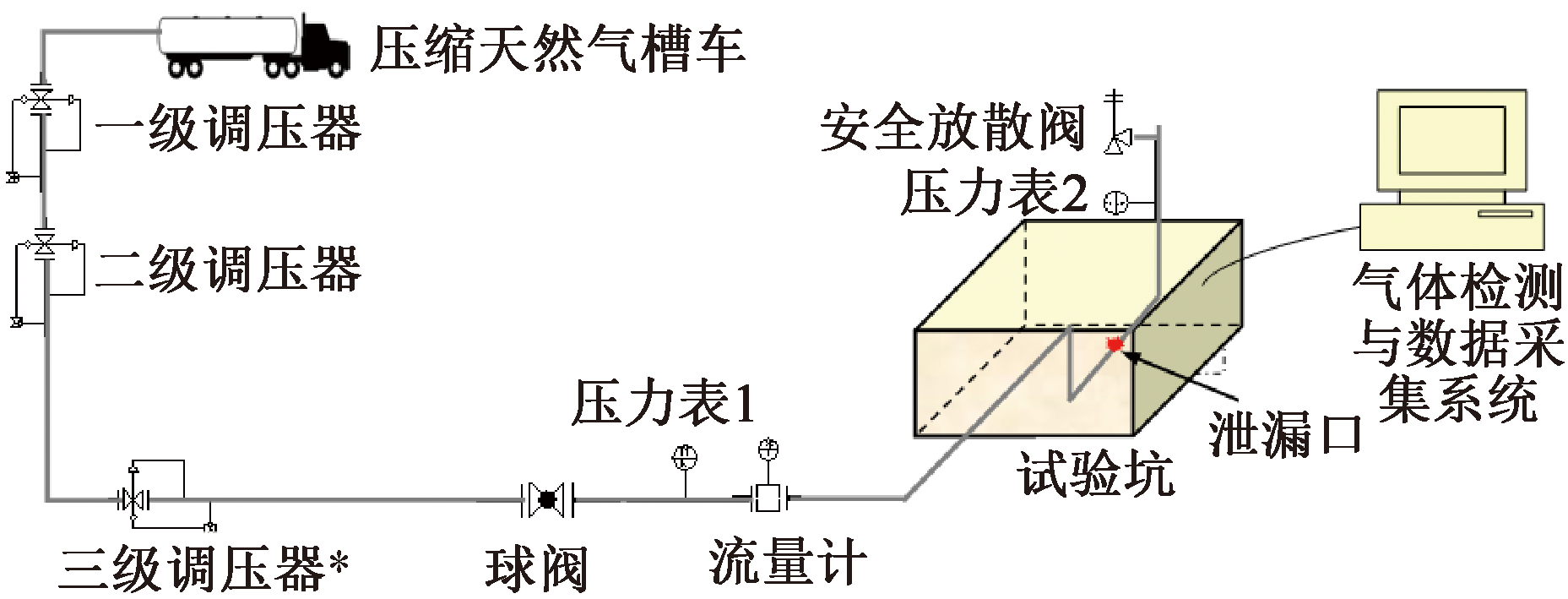
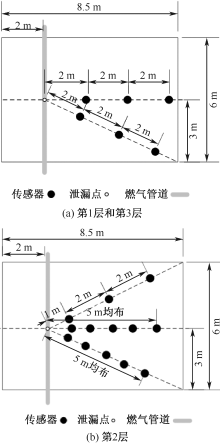
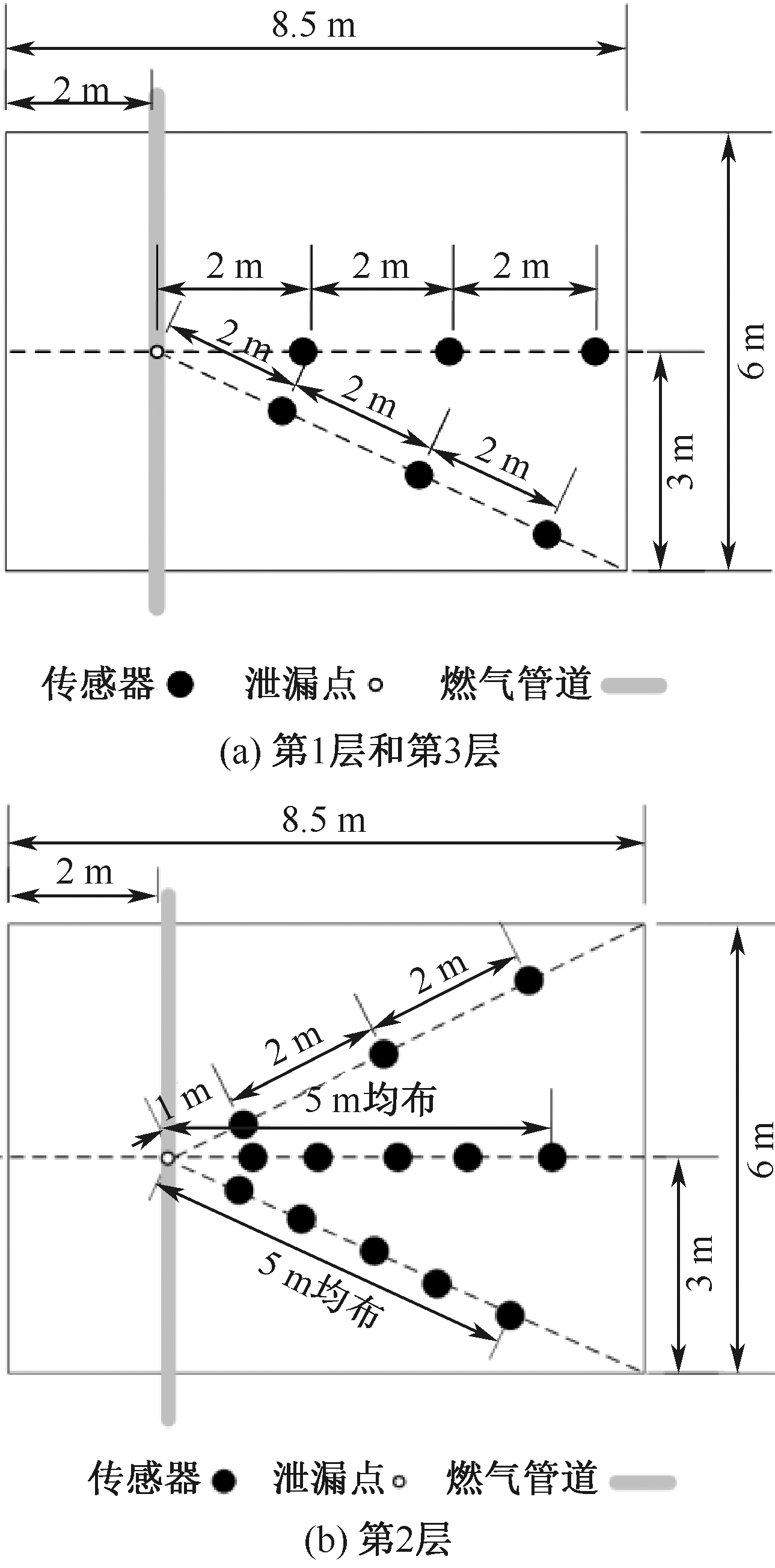
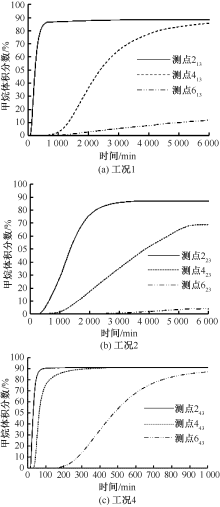
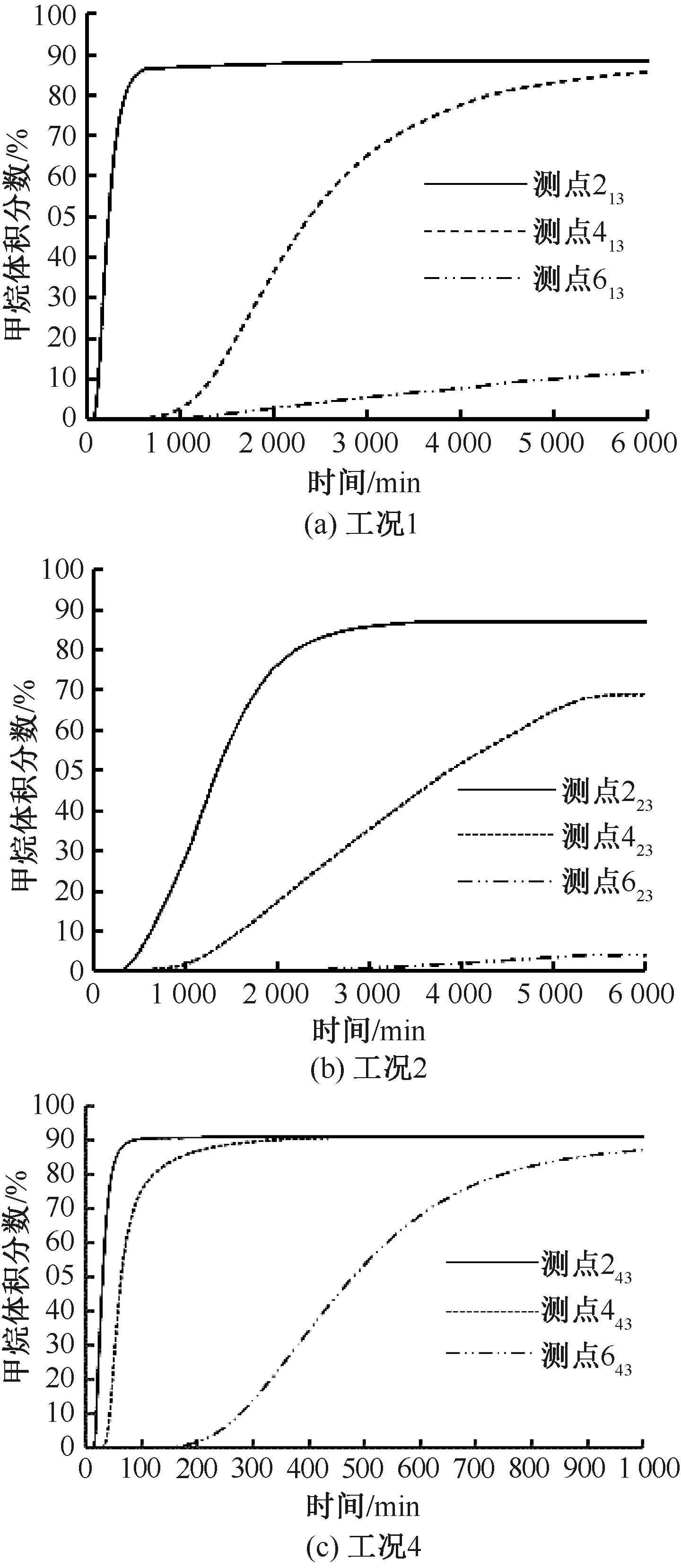
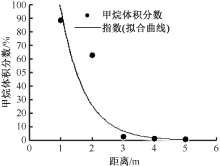
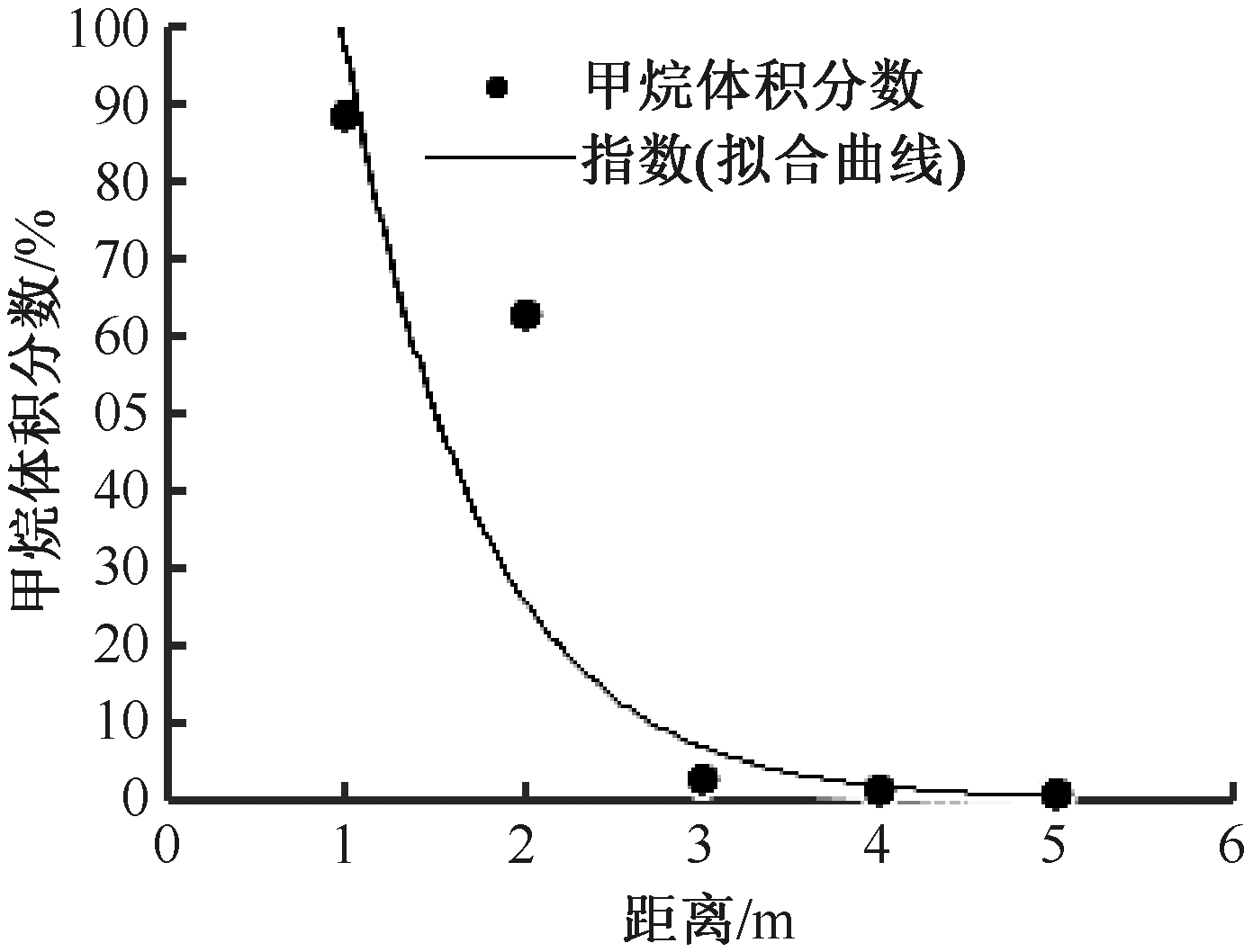
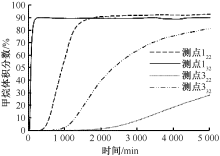
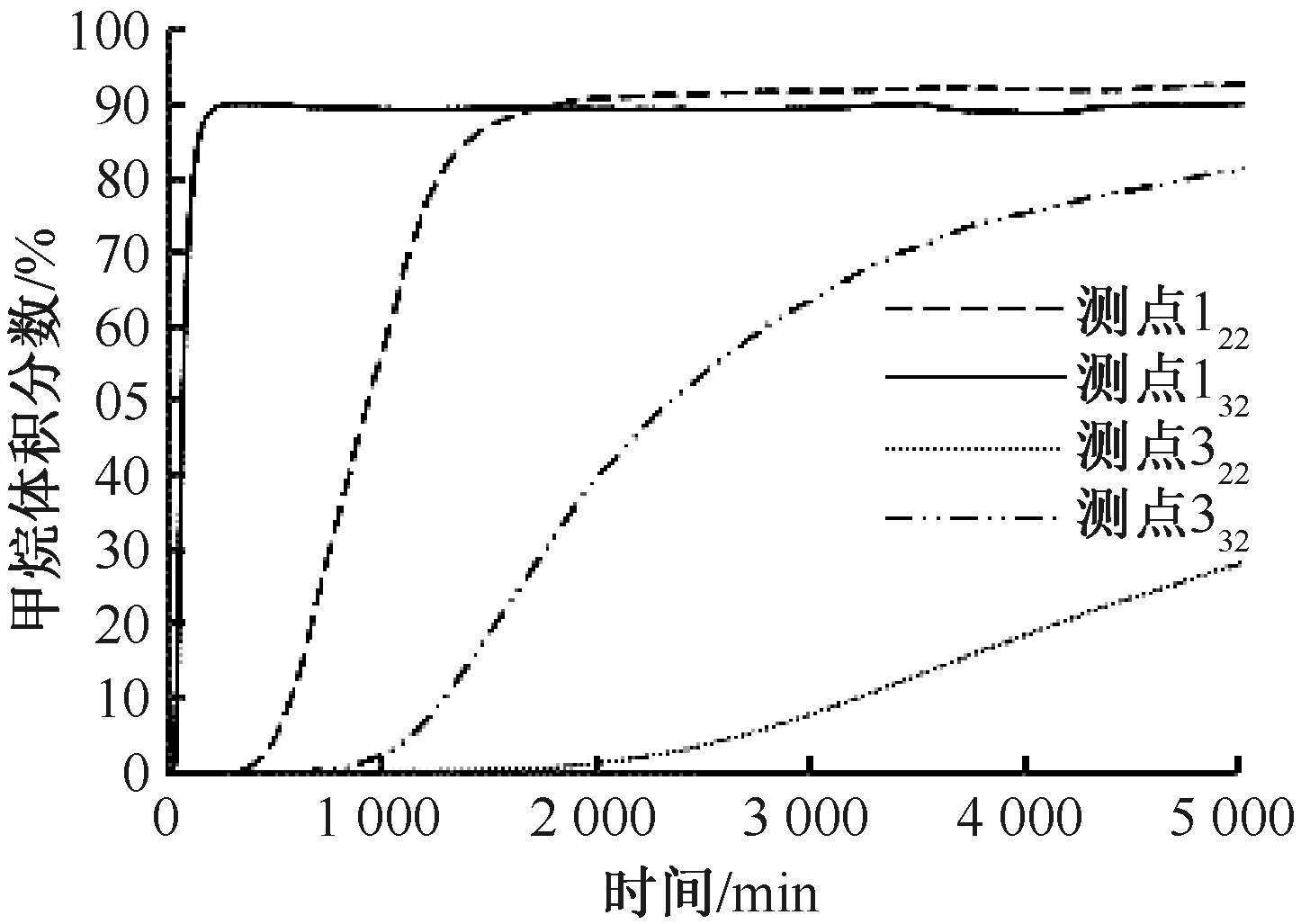
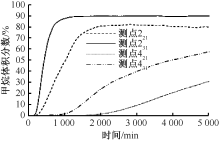
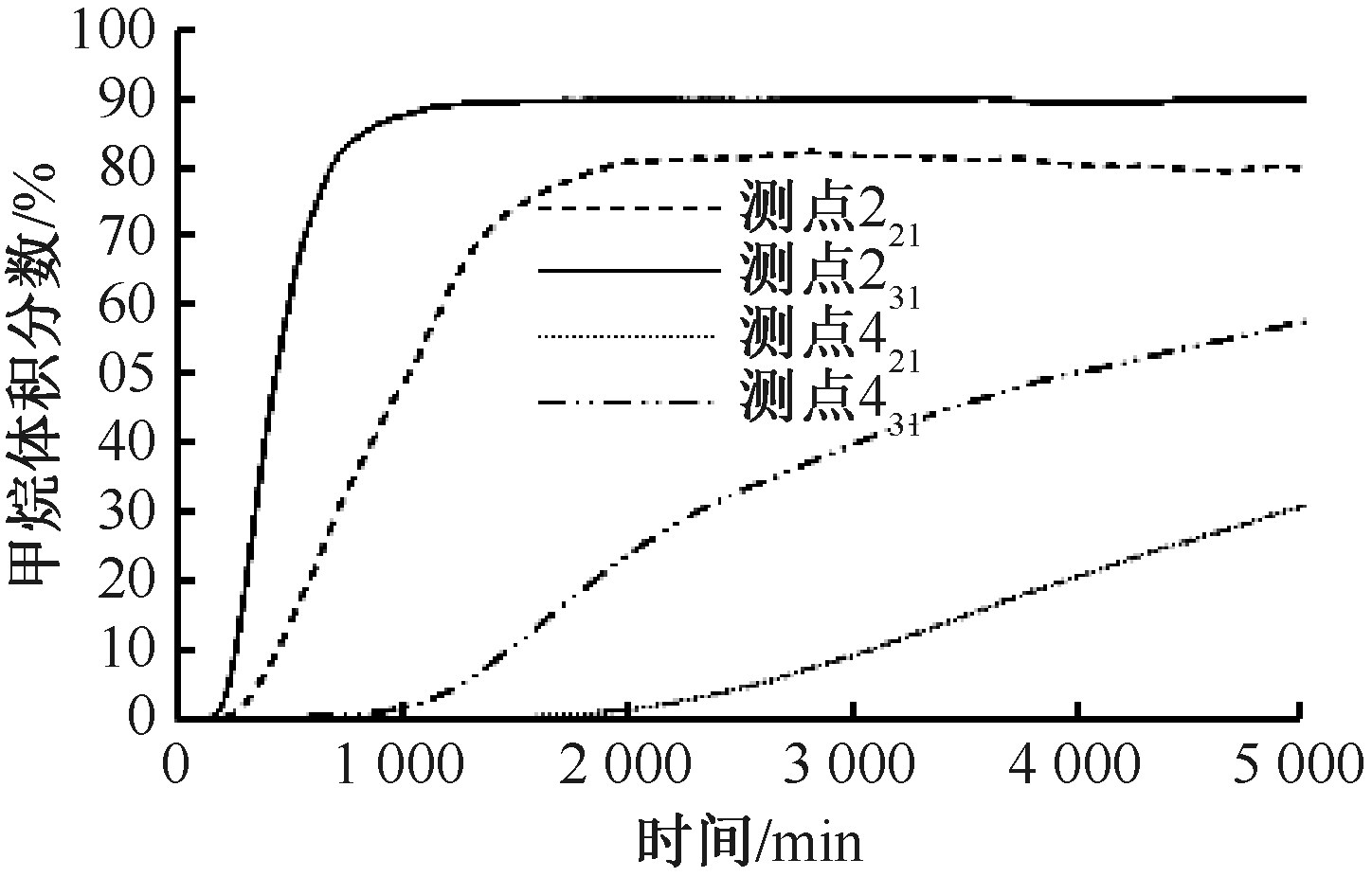
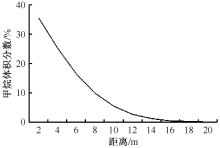
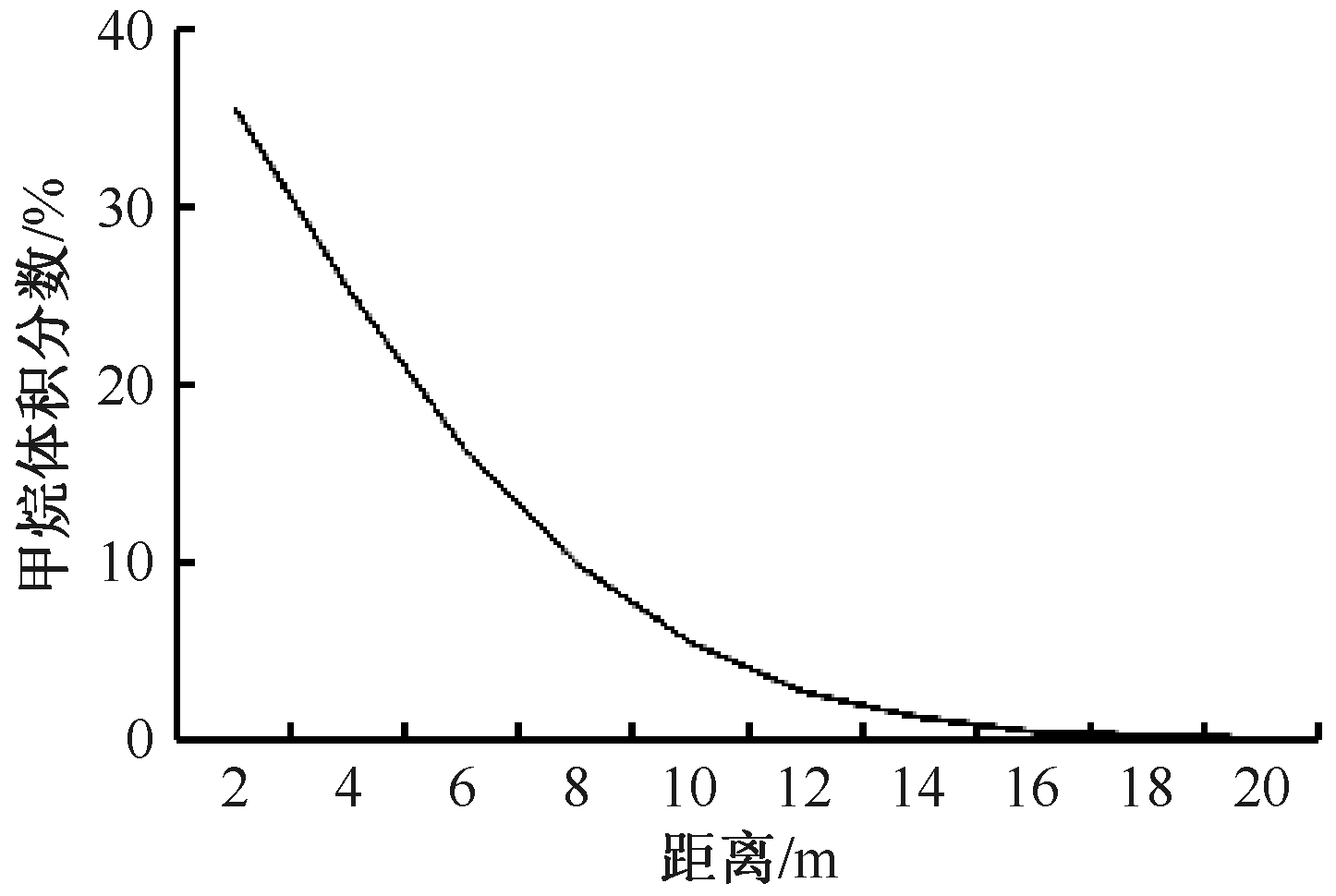
| [1] |
谢昱姝, 吴宗之, 吕良海, 等. 城市管道天然气在土壤中泄漏扩散实验研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2012, 8(4):13-17.
|
|
XIE Yushu, WU Zongzhi, LYU Lianghai, et al. Experimental research on diffusion behavior of leaked gas from underground gas pipeline[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2012, 8(4):13-17.
|
| [2] |
熊兆洪, 李振林, 宫敬, 等. 埋地管道小泄漏模型及数值求解[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(3):493-498.
doi: 10.7623/syxb201203023
|
|
XIONG Zhaohong, LI Zhenlin, GONG Jing, et al. A model for underground pipeline small leakage and its numerical solution[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(3):493-498.
doi: 10.7623/syxb201203023
|
| [3] |
张鹏, 程淑娟. 埋地天然气管道小微孔泄漏规律研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2014, 24(2):52-58.
|
|
ZHANG Peng, CHENG Shujuan. Study on small microspore leakage in buried gas pipeline[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2014, 24(2):52-58.
|
| [4] |
SHANTANU J, AMIT P, ARGHYA D, et al. Analysis of buried pipelines subjected to reverse fault motion[J]. Soil Dynamics & Earthquake Engineering, 2011, 31(7):930-940.
|
| [5] |
KIM K, ZHOU Wei, HUANG S L. Frost heave predictions of buried chilled gas pipelines with the effect of permafrost[J]. Cold Regions Science & Technology, 2008, 53(3):382-396.
|
| [6] |
王志荣, 蒋军成, 潘旭海. 模拟评价方法在劳动安全卫生预评价中的应用研究[J]. 石油与天然气化工, 2003, 32(3):181-184.
|
|
WANG Zhirong, JIANG Juncheng, PAN Xuhai. Research on the application of simulation assessment in health and safety evaluation[J]. Chemical Engineering of Oil & Gas, 2003, 32(3):181-184.
|
| [7] |
HANNA S. Britter and McQuaid (B&M) 1988 workbook nomograms for dense gas modeling applied to the Jack Rabbit II chlorine release trials[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2020:DOI: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.117539.
|
| [8] |
LIU Yanping, ZHAO Yongqiang, LIU Ming, et al. Parameterized high-precision finite element modelling method of 3D helical gears with contact zone refinement[J]. Shock and Vibration, 2019, 2019:1-17.
|
| [9] |
王向阳, 杜美萍, 汪彤, 等. 埋地燃气管道泄漏扩散过程数值模拟[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2018, 28(2):45-50.
|
|
WANG Xiangyang, DU Meiping, WANG Tong, et al. Numerical simulation of leakage of gas from buried pipeline and its diffusion process[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(2):45-50.
|
| [10] |
林晓斌. 埋地天然气管道泄漏过程天然气在土壤中扩散的数值模拟研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2014.
|
|
LIN Xiaobin. Numerical study on diffusion of the natural gas leakage from buried gas pipeline[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2014.
|
| [11] |
李云涛, 张振永, 刘玉卿, 等. 天然气管道全管径断裂事故影响范围研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(9):149-154.
|
|
LI Yuntao, ZHANG Zhenyong, LIU Yuqing, et al. Influence range of full bore rupture accidents of natural gas pipelines[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(9):149-154.
|
| [12] |
李朝阳, 马贵阳. 埋地与架空输气管道泄漏数值模拟对比分析[J]. 天然气工业, 2011, 31(7):90-93,113.
|
|
LI Chaoyang, MA Guiyang. A comparative study of numerical simulation on underground and aerial pipeline leakage at instantaneous and continuous states[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2011, 31(7):90-93,113.
|
| [13] |
王秋红, 王力文, 蒋军成, 等. 城镇地埋天然气管道泄漏诱发气云爆炸仿真[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(9):75-82.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.09.011
|
|
WANG Qiuhong, WANG Liwen, JIANG Juncheng, et al. Simulation study on gas explosion induced by gas leakage of urban buried gas pipeline[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(9):75-82.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.09.011
|
| [14] |
冯文兴, 王兆芹, 程五一. 高压输气管道小孔与大孔泄漏模型的比较分析[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2009, 16(4):108-110.
|
|
FENG Wenxing, WANG Zhaoqin, CHENG Wuyi. Analysis of the nozzle model and hole model associated with high-pressure natural gas pipeline leakage[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2009, 16(4):108-110.
|
| [15] |
冯云飞, 吴明, 闫明龙, 等. 燃气管道泄漏模型的研究进展[J]. 当代化工, 2011, 40(12):1255-1257,1260.
|
|
FENG Yunfei, WU Ming, YAN Minglong, et al. Research progress in leakage models for gas pipelines[J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry, 2011, 40(12):1255-1257,1260.
|
| [16] |
庞磊, 吕良海, 刘晨, 等. 密闭空间燃气泄漏爆炸危险区域迁移规律[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2012, 8(8):47-50.
|
|
PANG Lei, LYU Lianghai, LIU Chen, et al. Migration laws of hazardous zone for natural gas leakage explosion in enclosed spaces[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2012, 8(8):47-50.
|
| [17] |
GB 50028—2006, 城镇燃气设计规范[S].
|
|
GB 50028-2006, Cole for design of city gas engineering[S].
|
| [18] |
谢昱姝, 汪彤, 吕良海, 等. 城市管道天然气在土壤中扩散行为全尺度实验[J]. 天然气工业, 2015, 35(8):106-113.
|
|
XIE Yushu, WANG Tong, LYU Lianghai, et al. Full-scale experiment of diffusion behaviors of city pipeline gas in soils[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2015, 35(8):106-113.
|