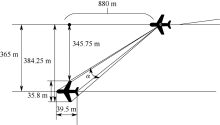
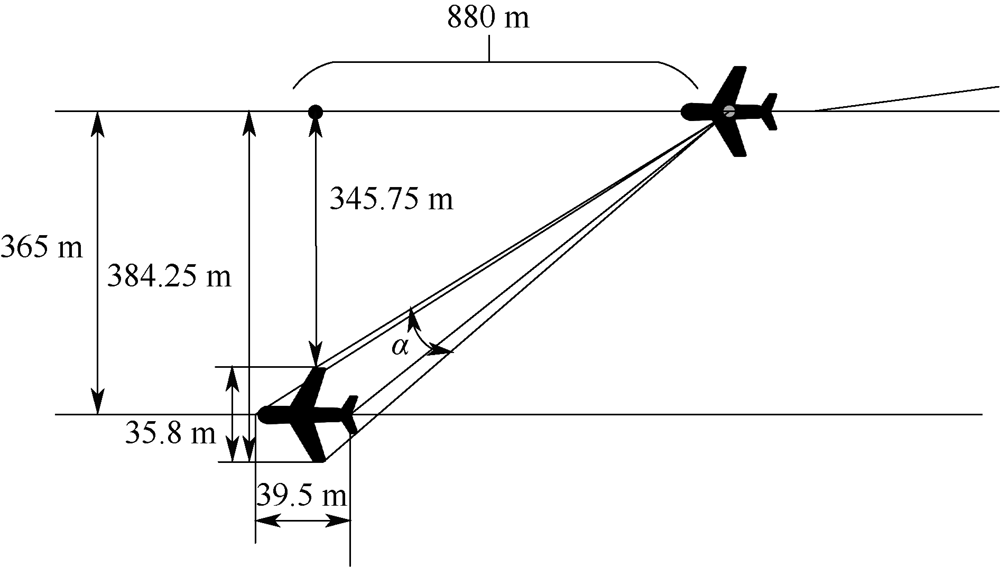
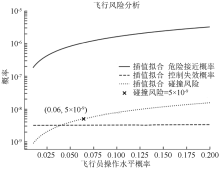
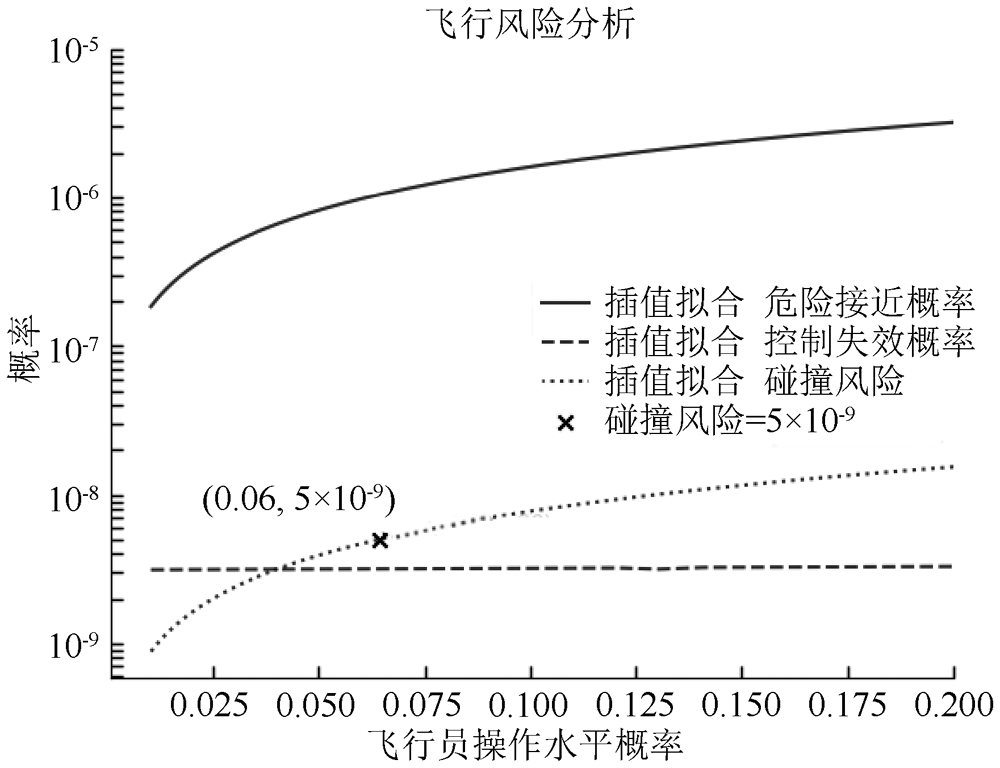
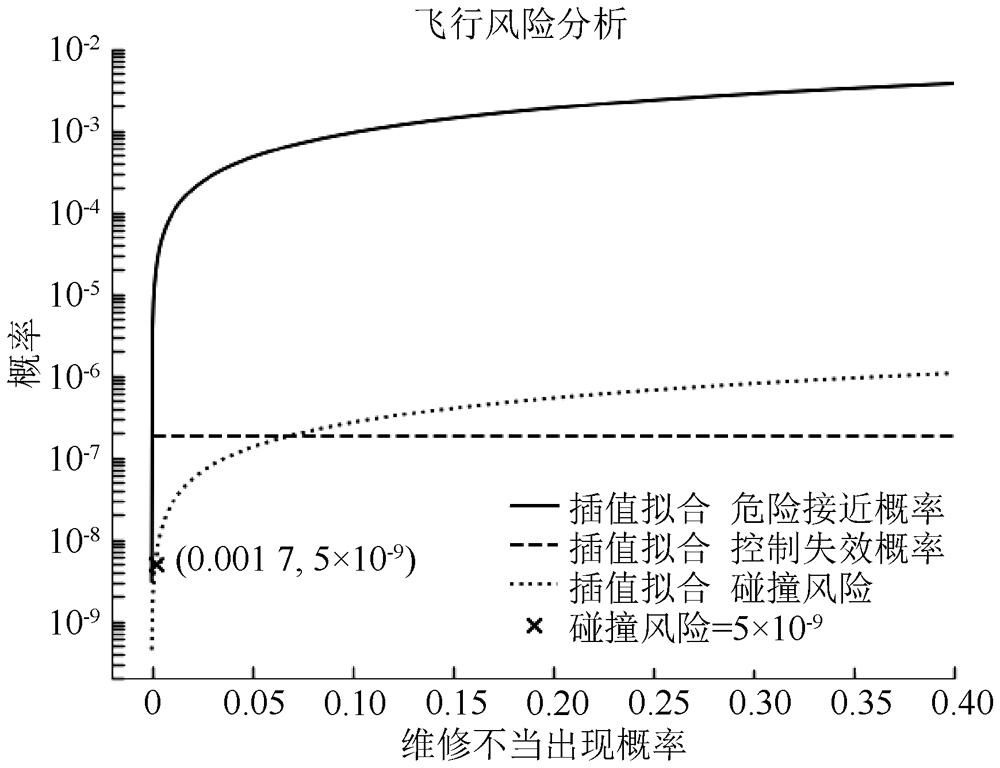
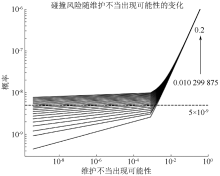
| [1] |
ALLER M C, SCANLON C H. Proceedings of the NASA workshop on flight deck centered parallel runway approaches in instrument meteorological conditions[R]. NASA, 1996.
|
| [2] |
HAMMER J. Study of the geometry of a dependent approach procedure to closely spaced parallel runways[C]. 18th Digital Avionics Systems Conference, 1999:DOI: 10.1109/DASC.1999.863731.
|
| [3] |
HAMMER J. Case study of paired approach procedure to closely spaced parallel runways[J]. Air Traffic Control Quarterly, 2000, 8(3):223-252.
|
| [4] |
EFTEKARI R R, HAHHER J B, HAVENS D A, et al. Feasibility analyses for paired approach procedures for closely spaced parallel runways[C]. Integrated Communications, Navigation and Surveillance Conference (ICNS), 2011: DOI: 10.1109/ICNSURV.2011.5935291.
|
| [5] |
LANDRY S J, LYNAM A. Safe zone for closely spaced parallel approaches[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2011, 34(2):608-613.
|
| [6] |
KING B T, KUCHAR J K. Evaluation of collision alerting system requirements for paired approach[C]. Proceedings of the 19th Digital Avionics Systems Conference, 2000:DOI: 10.1109/DASC.2000.886910.
|
| [7] |
GUERREIRO N M, NEITZKE K W, JOHNSON S C, et al. Characterizing a wake-free safe zone for the simplified aircraft-based paired approach concept[C]. AIAA Atmospheric and Space Environments Conference, 2010:76-81.
|
| [8] |
GUERREIRO N M, NEITZKE K W. Simulated wake characteristics data for closely spaced parallel runway operations analysis[C]. AIAA Aviation Technology, Integration, & Operations, 2012:DOI: 10.2514/6.2012-5560.
|
| [9] |
MADDEN M M. Analytical assessment of simultaneous parallel approach feasibility from total system error[C]. 14th AIAA Aviation Technology, Integration, and Operations Conference, 2014:DOI: 10.2514/6.2014-3153.
|
| [10] |
MCKISSICK B. Wake encounter analysis for a closely spaced parallel runway paired approach simulation[C]. 9th AIAA Aviation Technology, Integration, and Operations Conference (ATIO), 2009:DOI: 10.2514/6.2009-6943.
|
| [11] |
PRIESS S. Analysis of an ADS-B in method for calculating the interval management paired approach collision safety limit[C]. 2017 IEEE/AIAA 36th Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), 2017:1-8.
|
| [12] |
MADDEN M M. Kinematic modeling of separation compression for paired approaches to closely-spaced parallel runways[C]. AIAA Aviation Technology, Integration, & Operations Conference. 2014:DOI: 10.2514/6.2014-3150.
|
| [13] |
GEYER M, SOARES M, BARNES S, et al. RNAV (GPS) total system error models for use in wake encounter risk analysis of dependent paired approaches to closely-spaced parallel runways[R]. JOHN A. Volpe National Transportation Systems Center (US), 2014.
|
| [14] |
胡明华, 田勇, 李凯, 等. 机场近距平行跑道进近方法研究[J]. 交通运输工程与信息学报, 2003, 1(1):64-69.
|
|
HU Minghua, TIAN Yong, LI Kai, et al. Study of approach procedure to closely spaced parallel runways[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information, 2003, 1(1):64-69.
|
| [15] |
孙佳, 田勇, 万莉莉, 等. 相关进近模式的近距平行跑道尾流危险区域分析[J]. 飞行力学, 2013, 31(3):281-284,288.
|
|
SUN Jia, TIAN Yong, WAN Lili, et al. Vortex hazardous region analysis of closely spaced parallel runways based on the relevant parallel approach mode[J]. Flight Dynamics, 2013, 31(3):281-284,288.
|
| [16] |
田勇, 孙佳, 万莉莉, 等. 近距平行跑道间隔确定方法[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2013, 13(1):70-76.
|
|
TIAN Yong, SUN Jia, WAN Lili, et al. Separation determining method of closely spaced parallel runways[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2013, 13(1):70-76.
|
| [17] |
何昕, 张凤飞, 宋斐. 基于机动避让程序的配对进近安全前界计算[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2019, 19(2):425-430.
|
|
HE Xin, ZHANG Fengfei, SONG Fei. Calculation of the safety front boundary of the paired approach procedure based on the evasive maneuvers[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2019, 19(2):425-430.
|
| [18] |
蒋豪, 侯宇杰, 陈亚青, 等. 基于蒙特卡洛算法的配对进近安全前界计算[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2020, 20(5):1795-1802.
|
|
JIANG Hao, HOU Yujie, CHEN Yaqing, et al. Calculation of the collision-safe boundary of the paired approach procedure based on the Monte Carlo algorithm[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2020, 20(5):1795-1802.
|
| [19] |
韩丹, 蒋豪, 陈亚青. 微分对策理论在配对进近防撞安全间隔研究中的应用[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2022, 22(5):2617-2623.
|
|
HAN Dan, JIANG Hao, CHEN Yaqing. Application of differential game in collision safety limit for paired approach[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2022, 22(5):2617-2623.
|
| [20] |
卢飞, 赵二丽, 梁献匀. 定位误差影响下的配对进近纵向碰撞风险研究[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2023, 41(4):24-32.
|
|
LU Fei, ZHAO Erli, LIANG Xianyun. A study on longitudinal collision risk of airplanes during paired approach under the influence of positioning error[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2023, 41(4):24-32.
|
| [21] |
郑浩然, 谢春生, 卢飞. 基于改进EVENT模型的配对进近碰撞风险研究[J]. 综合运输, 2021, 43(12):84-90.
|
|
ZHENG Haoran, XIE Chunsheng, LU Fei. Research on collision risk of paired approach based on improved EVENT model[J]. China Transportation Review, 2021, 43(12):84-90.
|
| [22] |
何昕, 马义龙. 基于计算流体力学的配对进近尾流安全间隔研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(5):77-83.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.05.2075
|
|
HE Xin, MA Yilong. Study on wake safety intervals of PA based on CFD[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(5):77-83.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.05.2075
|
| [23] |
卢飞, 陈昊南. 模糊PID控制下的CSPRs配对进近纵向碰撞风险[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(11):97-104.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.11.0895
|
|
LU Fei, CHEN Haonan. Longitudinal collision risk of CSPRs paired approach under fuzzy PID control[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(11):97-104.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.11.0895
|
| [24] |
张兆宁, 陈子辰, 卢飞. 配对进近侧向位置误差QAR参数关联性分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(8):47-52.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.08.007
|
|
ZHANG Zhaoning, CHEN Zichen, LU Fei. Correlation analysis of QAR parameters for paired approach lateral position error[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(8):47-52.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.08.007
|
| [25] |
LU Fei, SUN Ruishan, CHEN Huiyu, et al. Research on vertical overlap of the paired approach based on QAR[J]. IEEE Access, 2022,10:94 568-94 582.
|
| [26] |
卢飞, 滕景杰, 吴俊, 等. 尾流影响下的CSPRs配对进近侧向碰撞风险分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(2):99-105.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.02.016
|
|
LU Fei, TENG Jingjie, WU Jun, et al. Later collision risk of CSPRs paired approach under wake impact[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(2):99-105.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.02.016
|
| [27] |
卢飞, 滕景杰, 吴俊, 等. 尾涡流场影响下的CSPRs配对进近侧向碰撞动力学分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(4):21-27.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.04.004
|
|
LU Fei, TENG Jingjie, WU Jun, et al. Later collision dynamics of CSPRs paired approach under influence of wake vortex field[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(4):21-27.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.04.004
|
| [28] |
冯思捷. 基于Fuzzy Bayesian的学习和推理方法在邮件系统中的应用[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017.
|
|
FENG Sijie. The application of learning and reasoning method based on Fuzzy Bayesian in mail system[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2017.
|
| [29] |
张兆宁, 梁玉文, 高俊英, 等. 自由飞行下基于事件树的碰撞风险评估模型[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2015, 15(2):304-308.
|
|
ZHANG Zhaoning, LIANG Yuwen, GAO Junying, et al. Assessment model of collision risk based on event tree in free flight[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2015, 15(2):304-308.
|