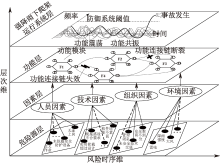
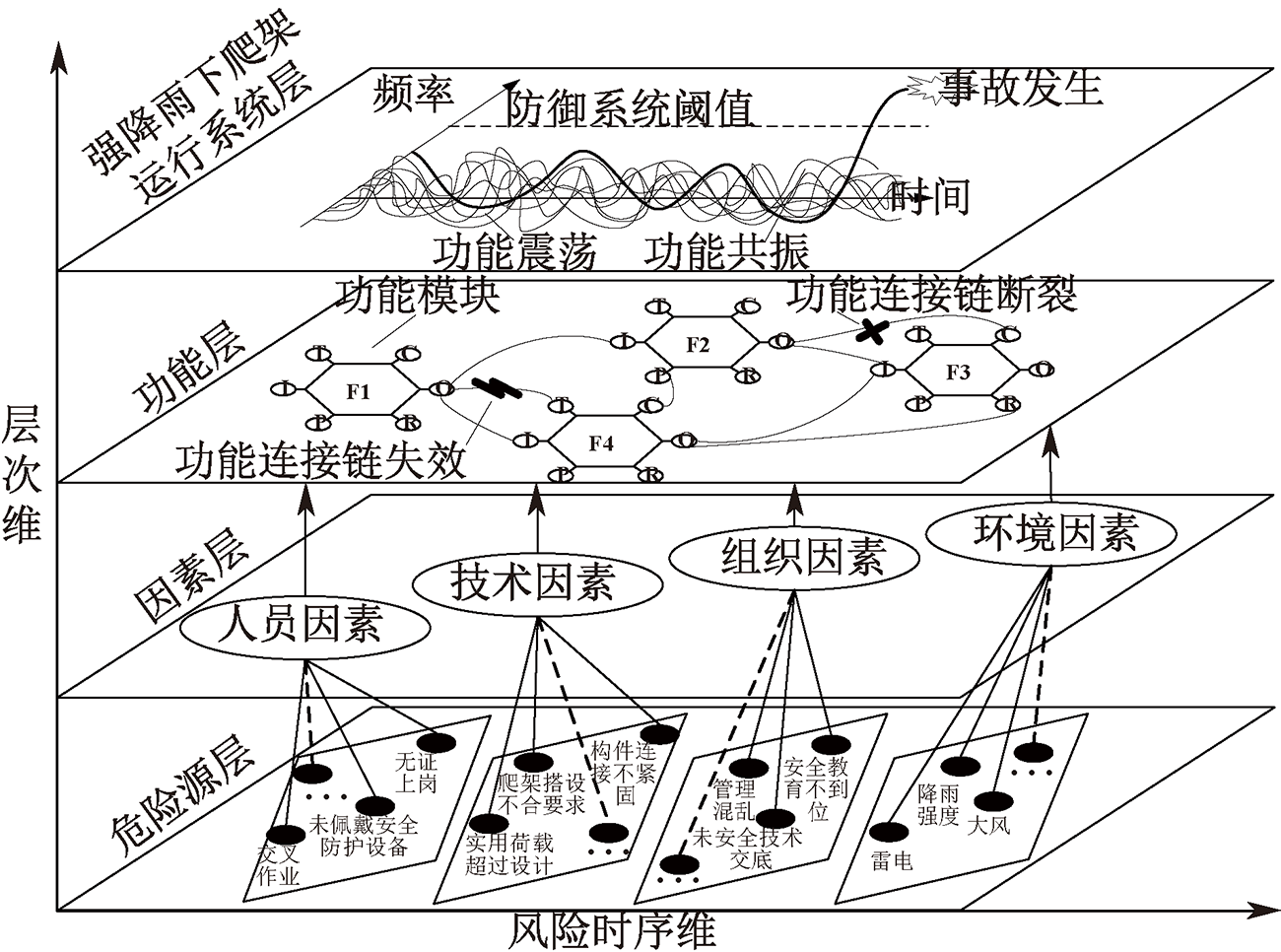
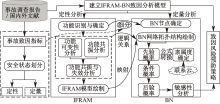
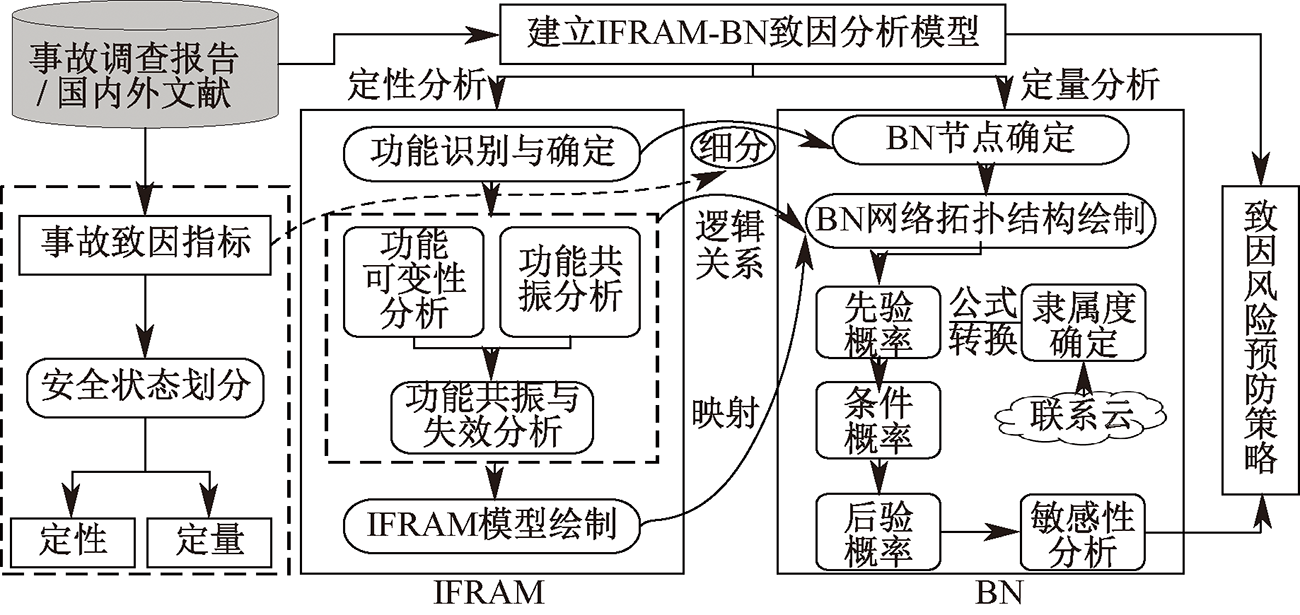
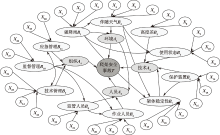
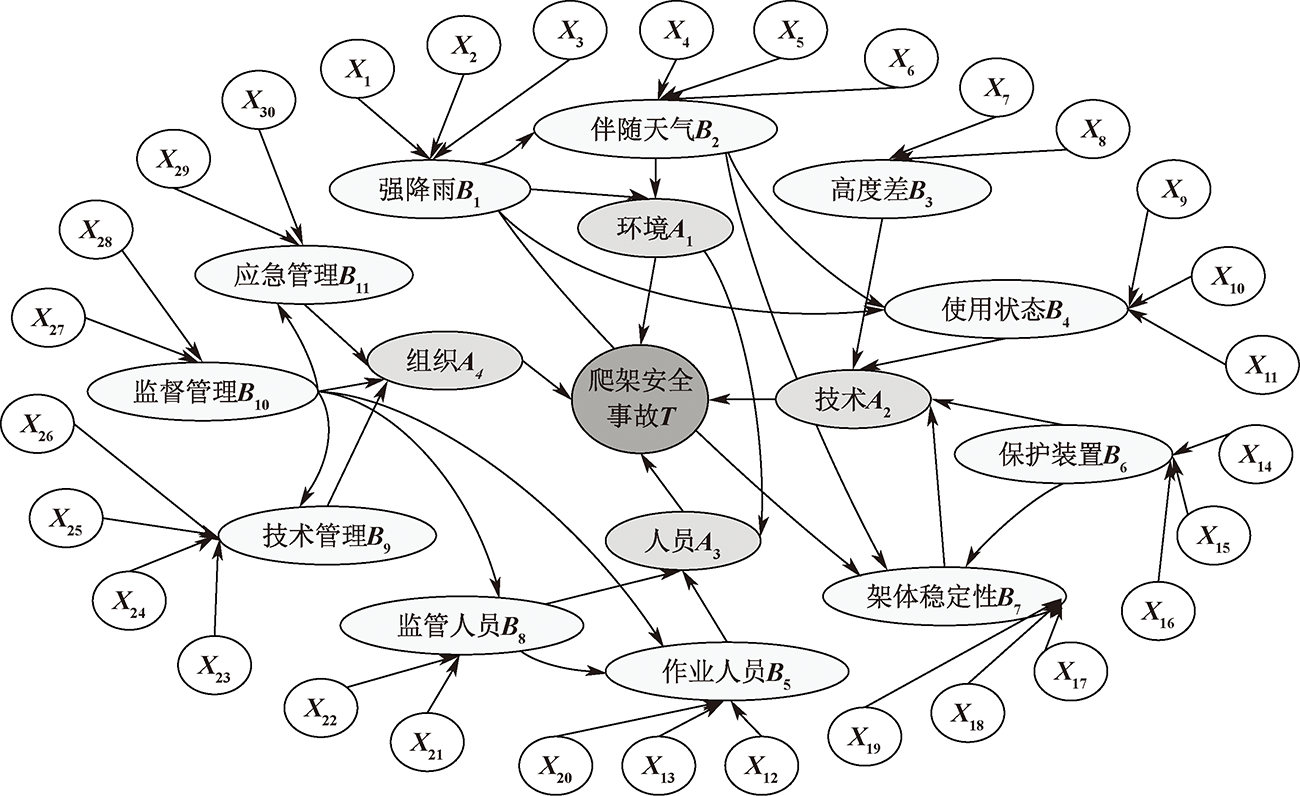
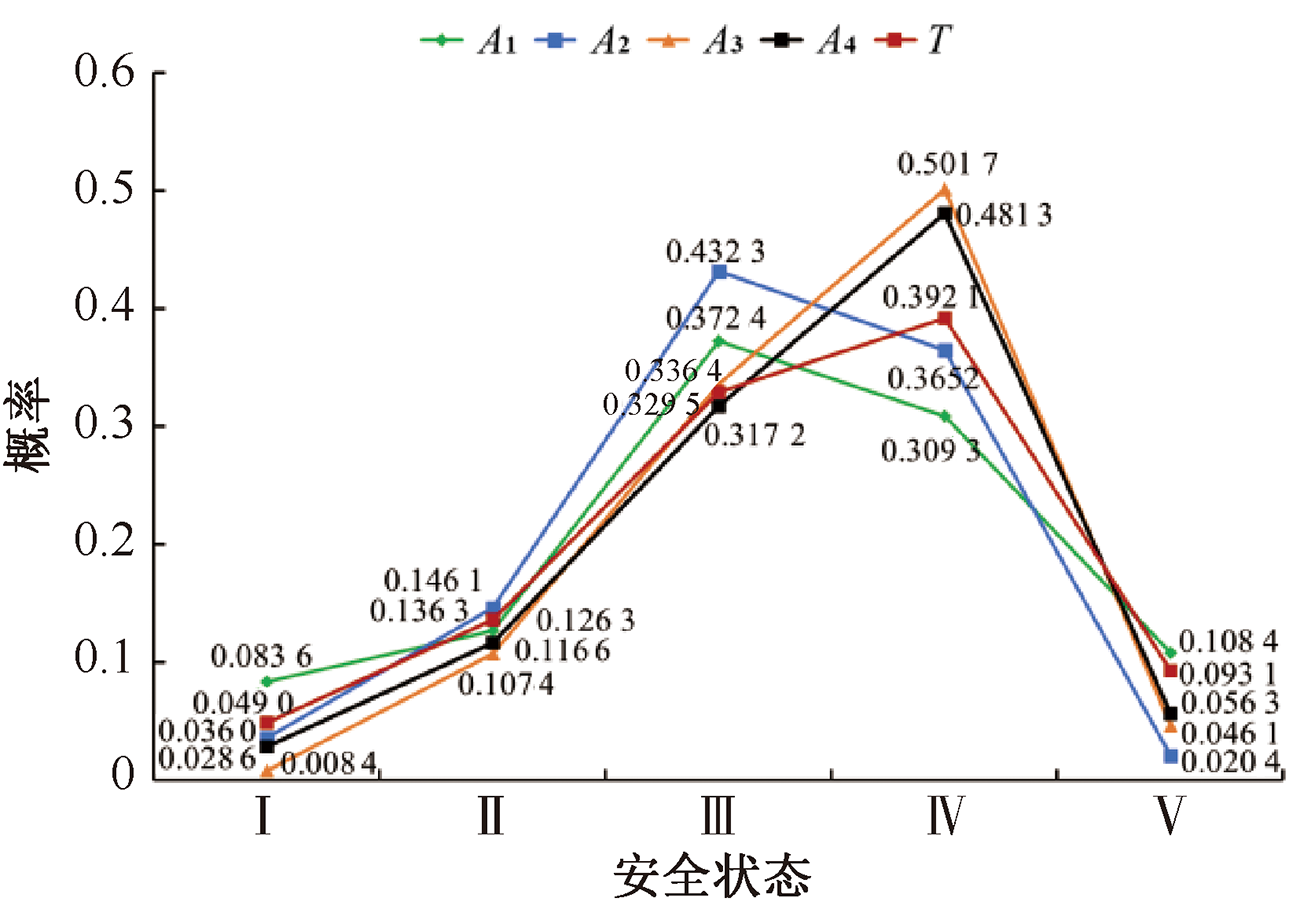
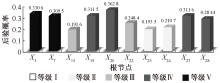
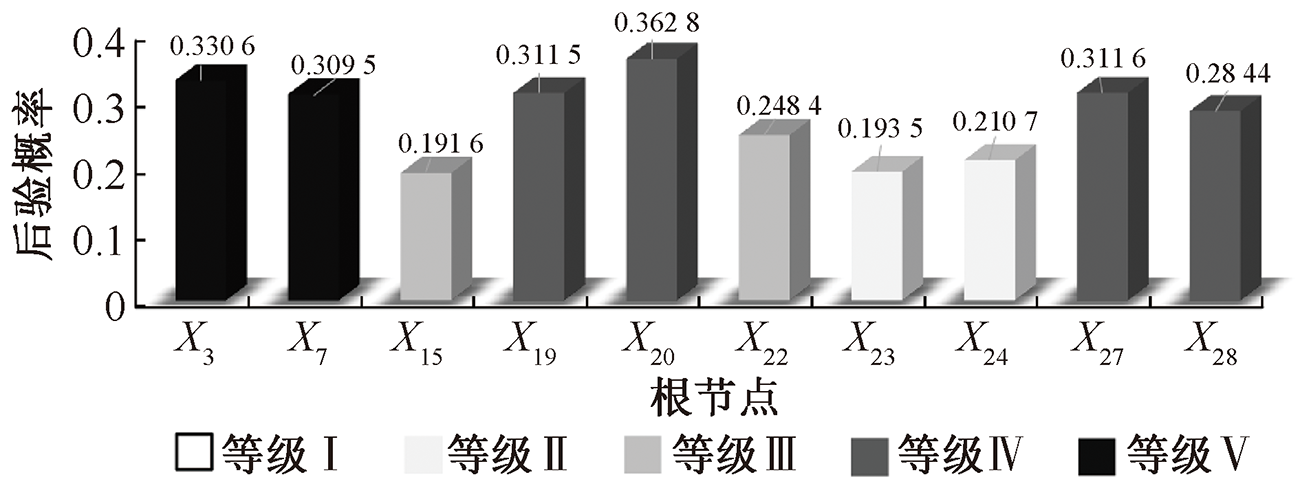
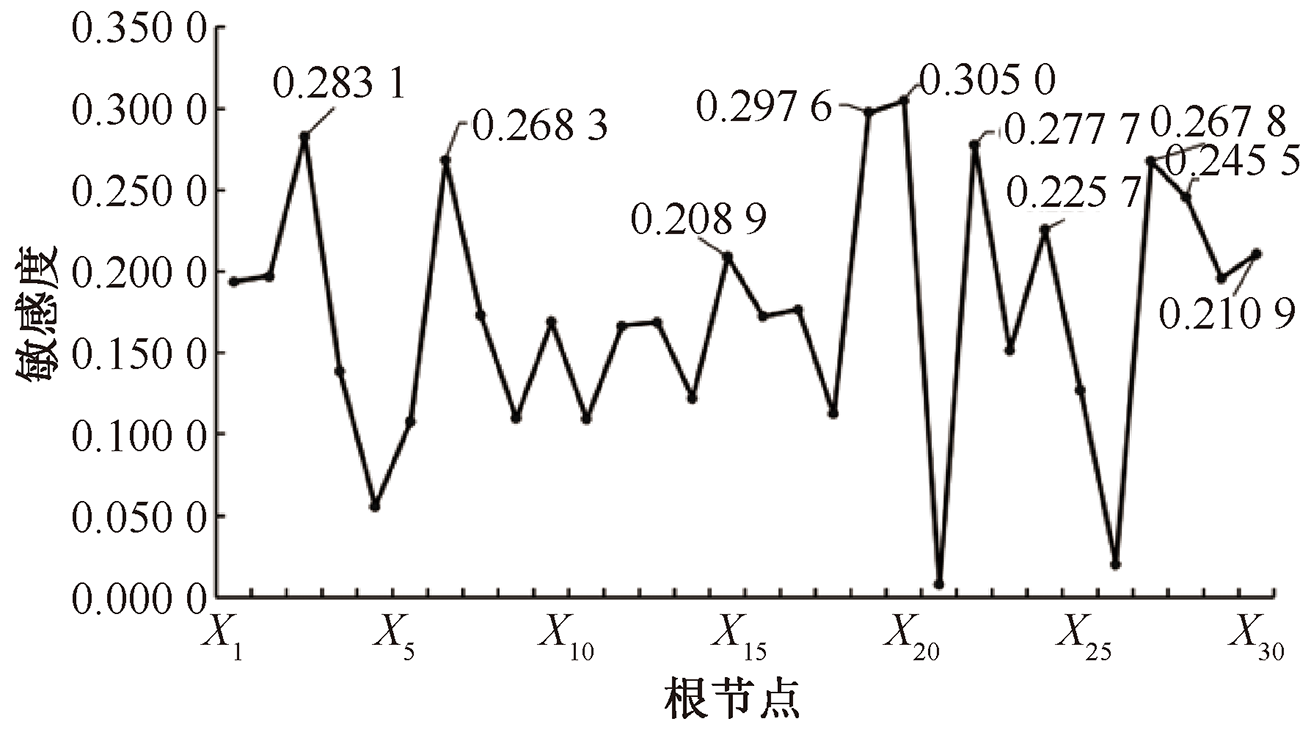
| [1] |
陈伟, 乔治, 王伟震, 等. 暴雨灾害引发施工安全事故应急处置SD模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27(6):169-174.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.06.029
|
|
CHEN Wei, QIAO Zhi, WANG Weizhen, et al. SD model for emergency disposal of construction safety accidents caused by rainstorm disasters[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27 (6): 169-174.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.06.029
|
| [2] |
裴兴旺, 赵向东, 周崇刚, 等. 基于灰色欧几里得的全钢型附着升降脚手架安全性评价[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2020, 20(2):405-415.
|
|
PEI Xingwang, ZHAO Xiangdong, ZHOU Chonggang, et al. Safety evaluation of all steel type attached lifting scaffold based on the grey euclidean weighted correlation degree theory[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2020, 20 (2): 405-415.
|
| [3] |
冯壮, 蔡东升. 基于T-S模糊故障树和BN的附着式升降脚手架倾覆和坠落事故易发性评价[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 2023, 53(2):143-151.
|
|
FENG Zhuang, CAI Dongsheng. Probability assessment of capsizing and falling accident of attached lifting scaffold based on T-S fuzzy fault tree and BN[J]. Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 2023, 53 (2): 143-151.
|
| [4] |
韦东. 基于ANSYS的附着式升降脚手架的力学分析研究及实验验证[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2021.
|
|
WEI Dong. Mechanical analysis and experimental verification of attached lifting scaffolding model based on ANSYS[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2021.
|
| [5] |
SAWICKI M, SZÓSTAK M. Quantitative assessment of the state of threat of working on construction scaffolding[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(16):DOI:10.3390/ijerph17165773.
|
| [6] |
NOWOBILSKI T, HOŁA B. Methodology based on causes of accidents for forcasting the effects of falls from scaffoldings using the construction industry in poland as an example[J]. Safety Science, 2023,157: DOI: 10.1016/J.SSCI.2022.105945.
|
| [7] |
HOLLNAGEL E. Barriers and accident prevention (hardback): routledge[J]. Ergonomics, 2004, 50(6):961-962.
|
| [8] |
王涵宇, 谭钦文. 基于FRAM的有限空间作业安全职责半定量分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(5):88-95.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.05.1382
|
|
WANG Hanyu, TAN Qinwen. Semi quantitative analysis of safety duties in confined space operations based on FRAM[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33 (5): 88-95.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.05.1382
|
| [9] |
WEIJUN L, MIN H, YIBO S, et al. A proactive operational risk identification and analysis framework based on the integration of ACAT and FRAM[J]. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2019, 186:101-109.
|
| [10] |
张人友, 崔焕焕, 张进超, 等. 基于FRAM-蒙特卡洛模拟的危化类实验安全分析和屏障管理[J]. 实验技术与管理, 2023(10):223-228.
|
|
ZHANG Renyou, CUI Huanhuan, ZHANG Jinchao, et al. Safety analysis and barrier management of hazardous chemical laboratories based on FRAM-Monte Carlo simulation[J]. Experimental Technology and Management, 2023 (10): 223-228.
|
| [11] |
尹德志, 帅斌, 黄文成, 等. Tropos-FRAM法在道路客运事故分析中的应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(8):151-157.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.08.022
|
|
YIN Dezhi, SHUAI Bin, HUANG Wencheng, et al. Application of Tropos-FRAM method in road passenger traffic accident analysis[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30 (8): 151-157.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2020.08.022
|
| [12] |
郭进平, 马卓远, 孙寅峰, 等. 基于FRAM的煤矿生产系统应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(6):73-79.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.06.1373
|
|
GUO Jinping, MA Zhuoyuan, SUN Yinfeng, et al. Application of mine production system based on FRAM[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33 (6): 73-79.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.06.1373
|
| [13] |
JOOHEE L, HYUN C. A new methodology for accident analysis with human and system interaction based on FRAM: case studies in maritime domain[J]. Safety Science, 2018, 109:57-66.
|
| [14] |
疏学明, 颜峻, 胡俊, 等. 基于Bayes网络的建筑火灾风险评估模型[J]. 清华大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 60(4):321-327.
|
|
SHU Xueming, YAN Jun, HU Jun, et al. Risk assessment model for building fires based on Bayesian network[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University:Science and Technology, 2020, 60 (4): 321-327.
|
| [15] |
|
|
LI Yue, ZHOU Zeyuan, CAI Jing. Extensible evaluation model of aircraft tire hydroplaning risk based on connection cloud[J/OL]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,1-9[2024-03-29]. https://doi.org/10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2023.0136.
|
| [16] |
陈钊, 袁航, 黄鹏宇, 等. 基于改进条件概率的贝叶斯网络隧道坍塌安全风险评价[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2023, 54(1):327-340.
|
|
CHEN Zhao, YUAN Hang, HUANG Pengyu, et al. Safety risk evaluation of tunnel collapse based on Bayesian network of improving conditional probability[J]. Journal of Central South University:Science and Technology, 2023, 54(1): 327-340.
|
| [17] |
刘剑锋. 基于物联网的附着式升降脚手架安全监控管理系统研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2017.
|
|
LIU Jianfeng. Research on safety monitoring and management system for attached self-lifting based on the internet of things[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2017.
|
| [18] |
BOŻENA H, TOMASZ N, ZUZANNA W, et al. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the causes of occupational accidents related to the use of construction scaffoldings[J]. Applied Sciences,2022,12(11):DOI: 10.3390/APP12115514. |
| [19] |
陕西省应急管理厅. 陕西省安全生产委员会办公室关于西安“9·10”重大建筑施工坍塌事故调查处理情况的通报[EB/OL].(2012-03-07). http://yjt.shaanxi.gov.cn/c/2012-03-07/559897.shtml.
|