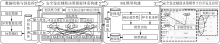
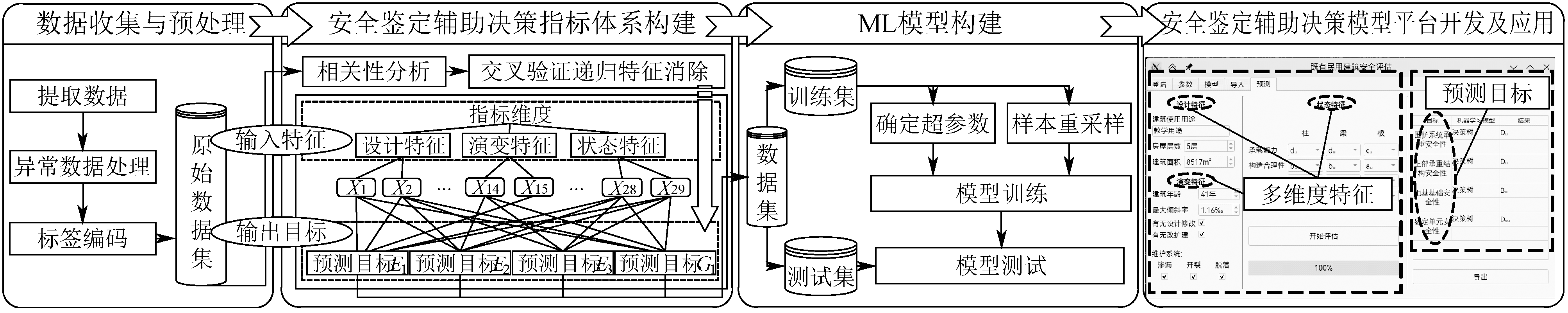
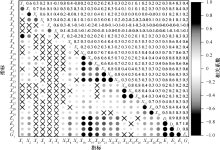
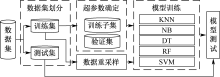
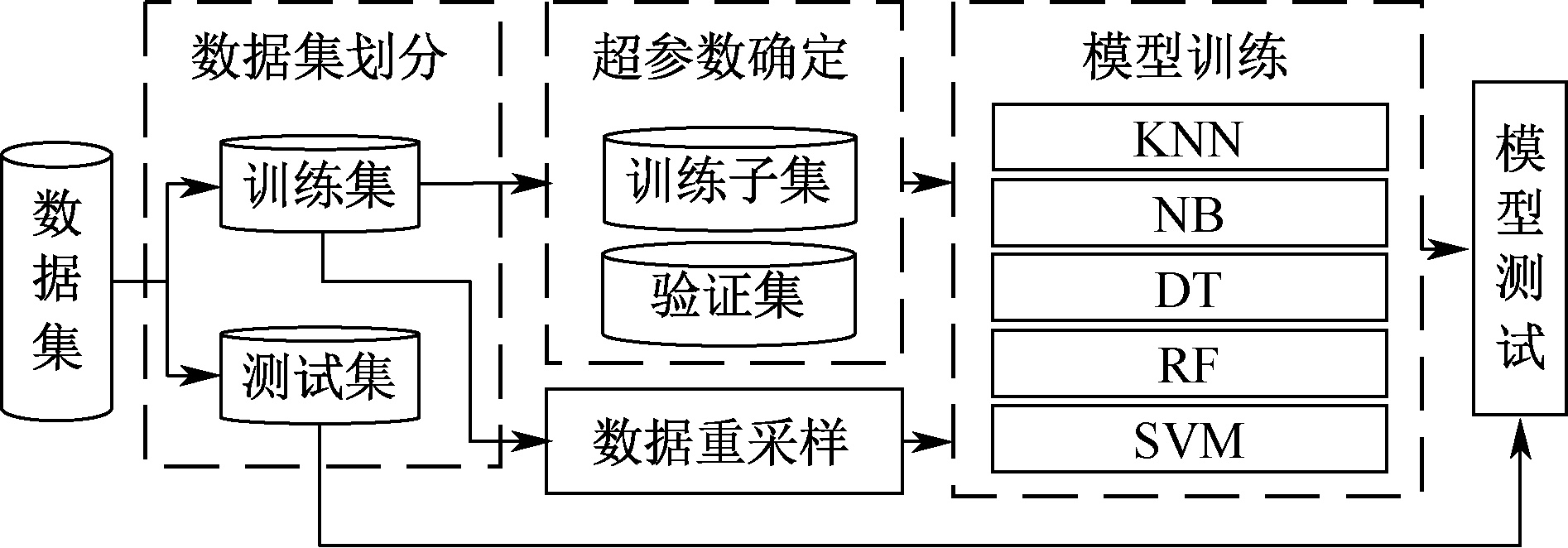
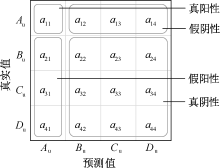
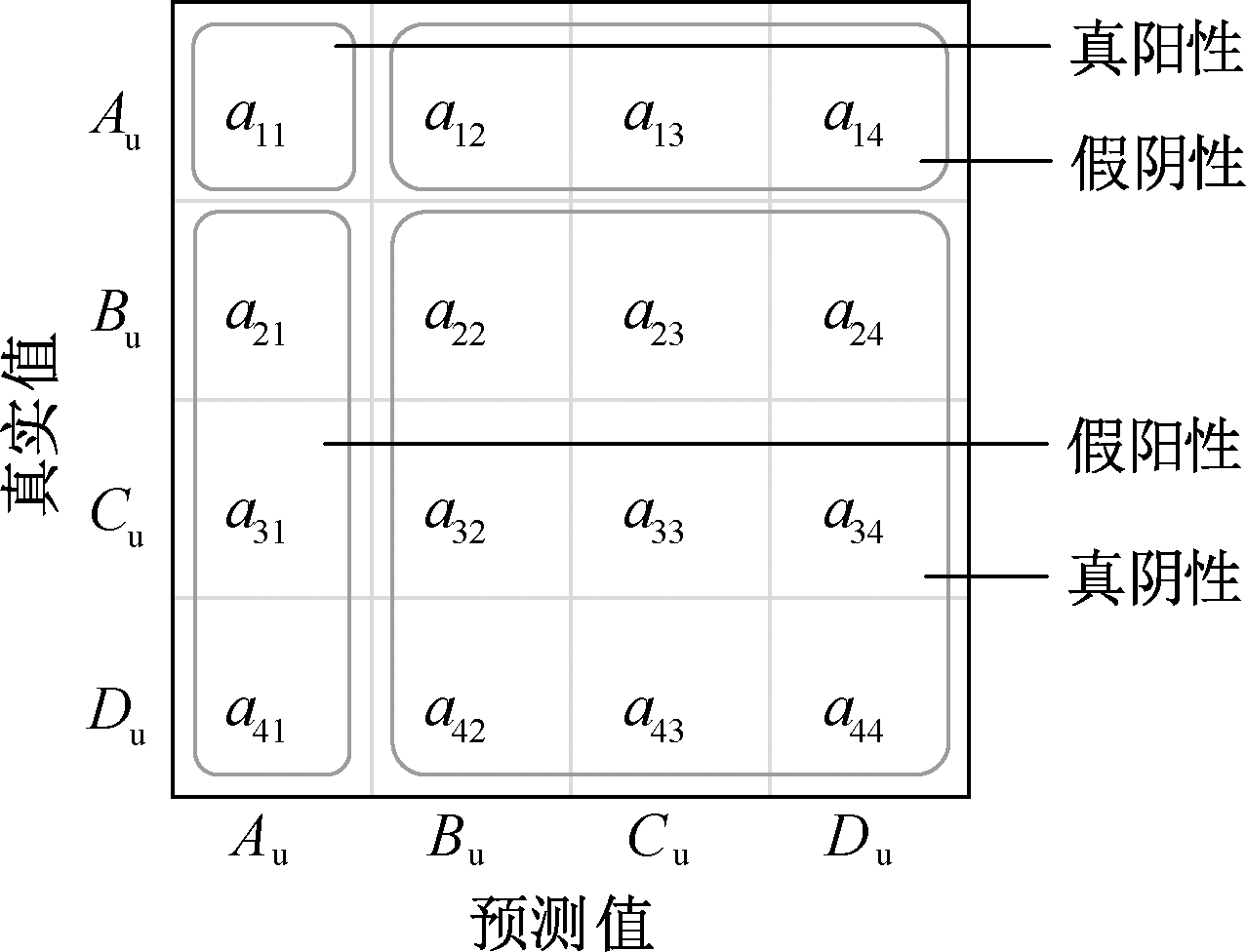
| [1] |
中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 住房城乡建设部关于全面开展城市体检工作的指导意见[EB/OL]. (2023-11-29). https://www.gov.cn/lianbo/bumen/202312/content_6918797.htm.
|
| [2] |
张鑫, 李安起, 赵考重. 建筑结构鉴定与加固改造技术的进展[J]. 工程力学, 2011, 28(1):1-11,25.
|
|
ZHANG Xin, LI Anqi, ZHAO Kaozhong. Advances in assessment and retrofitting of building structures[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2011, 28(1):1-11,25.
|
| [3] |
李俊杰, 葛德, 孙文. 基于结构健康监测系统的某办公建筑运营期结构响应分析[J]. 建筑结构, 2023, 53(21):107-111.
|
|
LI Junjie, GE De, SUN Wen. Structural response analysis of an office building during operation based on structural health monitoring system[J]. Building Structure, 2023, 53(21):107-111.
|
| [4] |
蒋维乐, 姚坤, 林启敬, 等. 结构健康监测系统在木结构古建筑中的应用[J]. 传感技术学报, 2024, 37(8):1295-1306.
|
|
JIANG Weile, YAO Kun, LIN Qijing, et al. Application of structural health monitoring system in wooden-structure ancient buildings[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2024, 37(8):1295-1306.
|
| [5] |
黄永, 鲍跃全, 李惠. 结构状态识别与评估的机器学习方法研究进展[J]. 力学进展, 2023, 53(4):774-792.
|
|
HUANG Yong, BAO Yuequan, LI Hui. Research advances in machine learning for structural state identification and condition assessment[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2023, 53(4):774-792.
|
| [6] |
周艳兵, 施钟淇, 金典琦, 等. 天空地一体化监测技术在既有建筑安全管控中的应用和展望[J]. 建筑结构, 2022, 52(增2):1893-1897.
|
|
ZHOU Yanbing, SHI Zhongqi, JIN Dianqi, et al. Application and prospect of integrated spaceborne, airborne and terrestrial monitoring technology in safety management and control of existing buildings[J]. Building Structure, 2022, 52(S2):1893-1897.
|
| [7] |
VENKATESH P, ALAPATI M. Condition assessment of existing concrete building using non-destructive testing methods for effective repair and restoration: a case study[J]. Civil Engineering Journal, 2017, 3(10):841-855.
|
| [8] |
ALAVI H, BORTOLINI R, FORCADA N. BIM-based decision support for building condition assessment[J]. Automation in Construction, 2022,135:DOI: 10.1016/j.autcon.2021.104117.
|
| [9] |
DING Zhikun, NIU Jindi, LIU Shan, et al. An approach integrating geographic information system and building information modelling to assess the building health of commercial buildings[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020,257:DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120532.
|
| [10] |
GB50292—2015, 民用建筑可靠性鉴定标准[S].
|
|
GB50292-2015, Standard for appraisal of reliability of civil buildings[S].
|
| [11] |
汪明元, 陈松庭, 陈彪, 等. 考虑数据预处理和特征选择的静力触探参数研究[J]. 浙江工业大学学报, 2025, 53(1):15-21.
|
|
WANG Mingyuan, CHEN Songting, CHEN Biao, et al. Study on parameters of cone penetration test considering data pre-processing and feature selection[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University of Technology, 2025, 53(1):15-21.
|
| [12] |
段在鹏, 李帆, 郭进, 等. 城市易涝区房屋结构安全集成预警模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2023, 33(7):173-180.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.07.0759
|
|
DUAN Zaipeng, LI Fan, GUO Jin, et al. Integrated warning model for structural safety of buildings in urban waterlogged area[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2023, 33(7):173-180.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2023.07.0759
|
| [13] |
刘立渠, 彭立新, 赵振红, 等. 既有建筑结构安全性鉴定中分项系数的调整研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2024, 45(4):247-253.
|
|
LIU Liqu, PENG Lixin, ZHAO Zhenhong, et al. Research on adjusting partial factors in safety appraisal of existing building structure[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2024, 45(4):247-253.
|
| [14] |
SEDGWICK P. Spearman's rank correlation coefficient[J]. British Medical Journal, 2014,349:DOI: 10.1136/bmj.g7327.
|
| [15] |
李显, 焦宇, 陈文涛, 等. 船舶修造企业火灾事故特征挖掘与致因分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(3):29-38.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.03.0368
|
|
LI Xian, JIAO Yu, CHEN Wentao, et al. Feature mining and causative analysis of fire accidents in ship repair and building enterprises[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(3):29-38.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.03.0368
|
| [16] |
HAIRANI H, WIDIYANINGTYAS T, PRASETYA D D. Addressing class imbalance of health data: a systematic literature review on modified synthetic minority oversampling technique (SMOTE) strategies[J]. JOIV: International Journal on Informatics Visualization, 2024, 8(3):1310-1318.
|
| [17] |
LI Huixia, NYIRANDAYISABYE R, DONG Qiming, et al. Crack damage prediction of asphalt pavement based on tire noise: a comparison of machine learning algorithms[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2024,414:DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.134867.
|