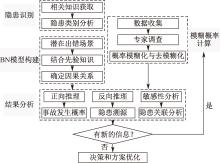
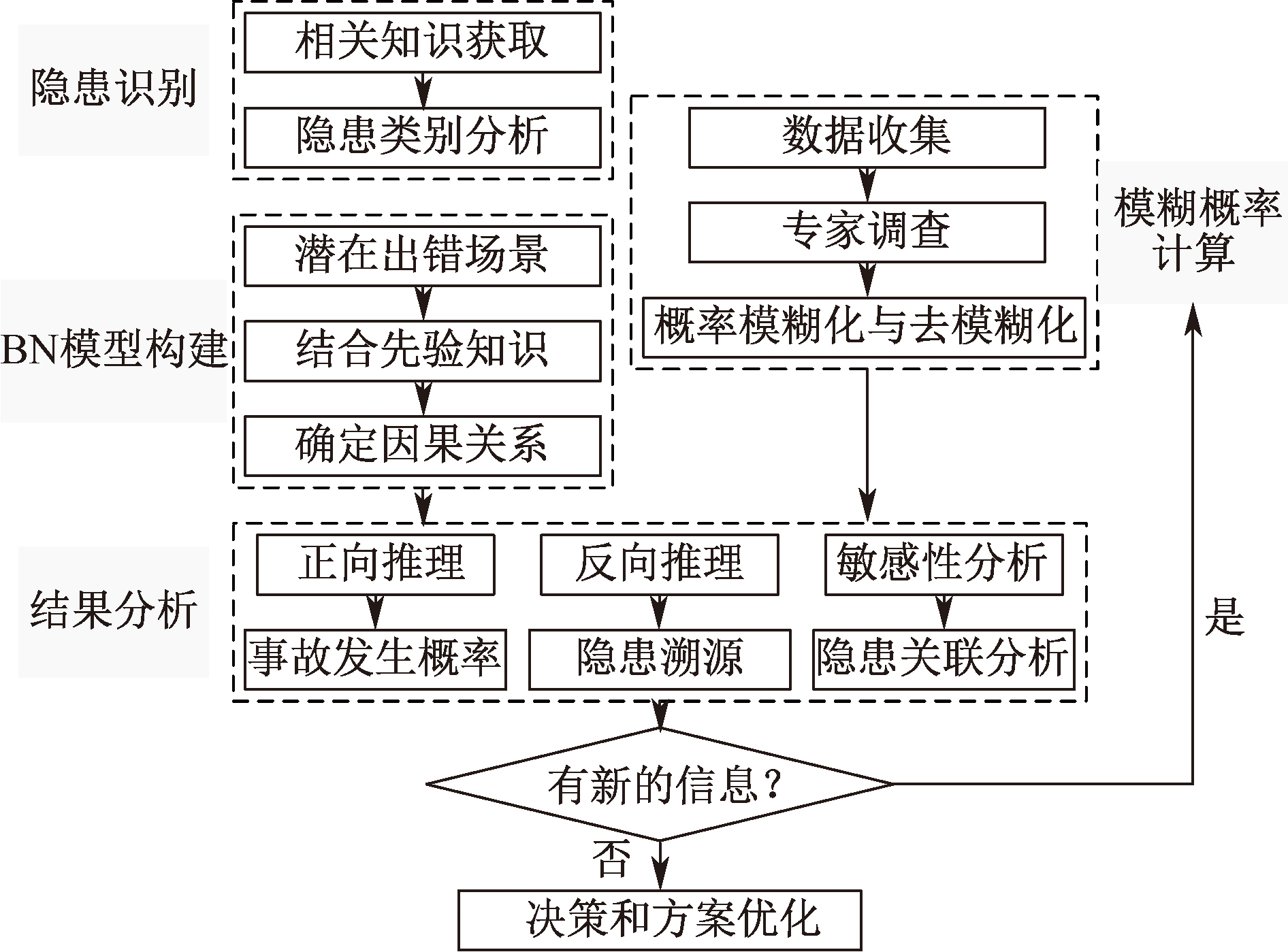
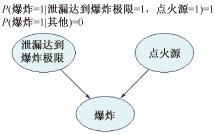
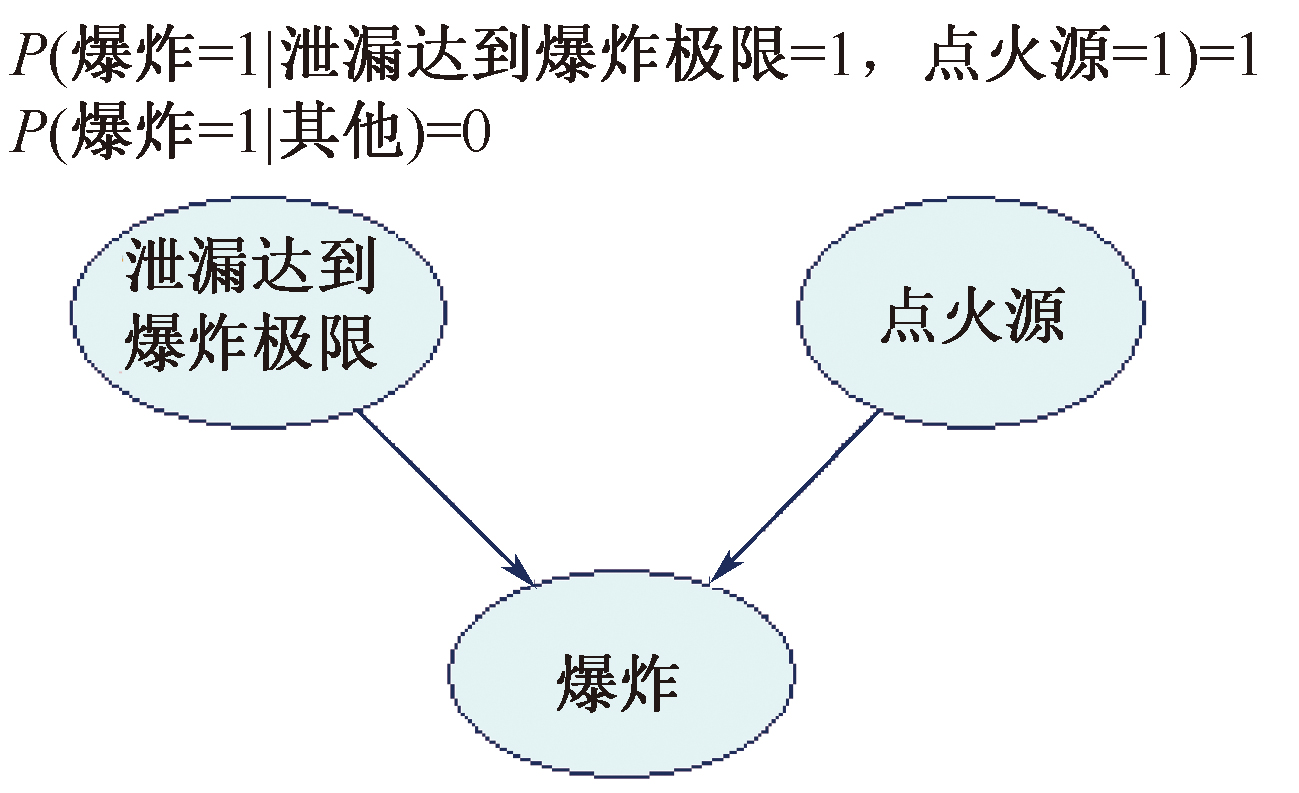
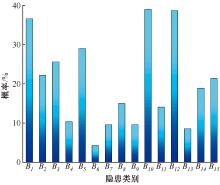
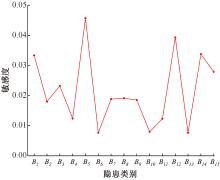
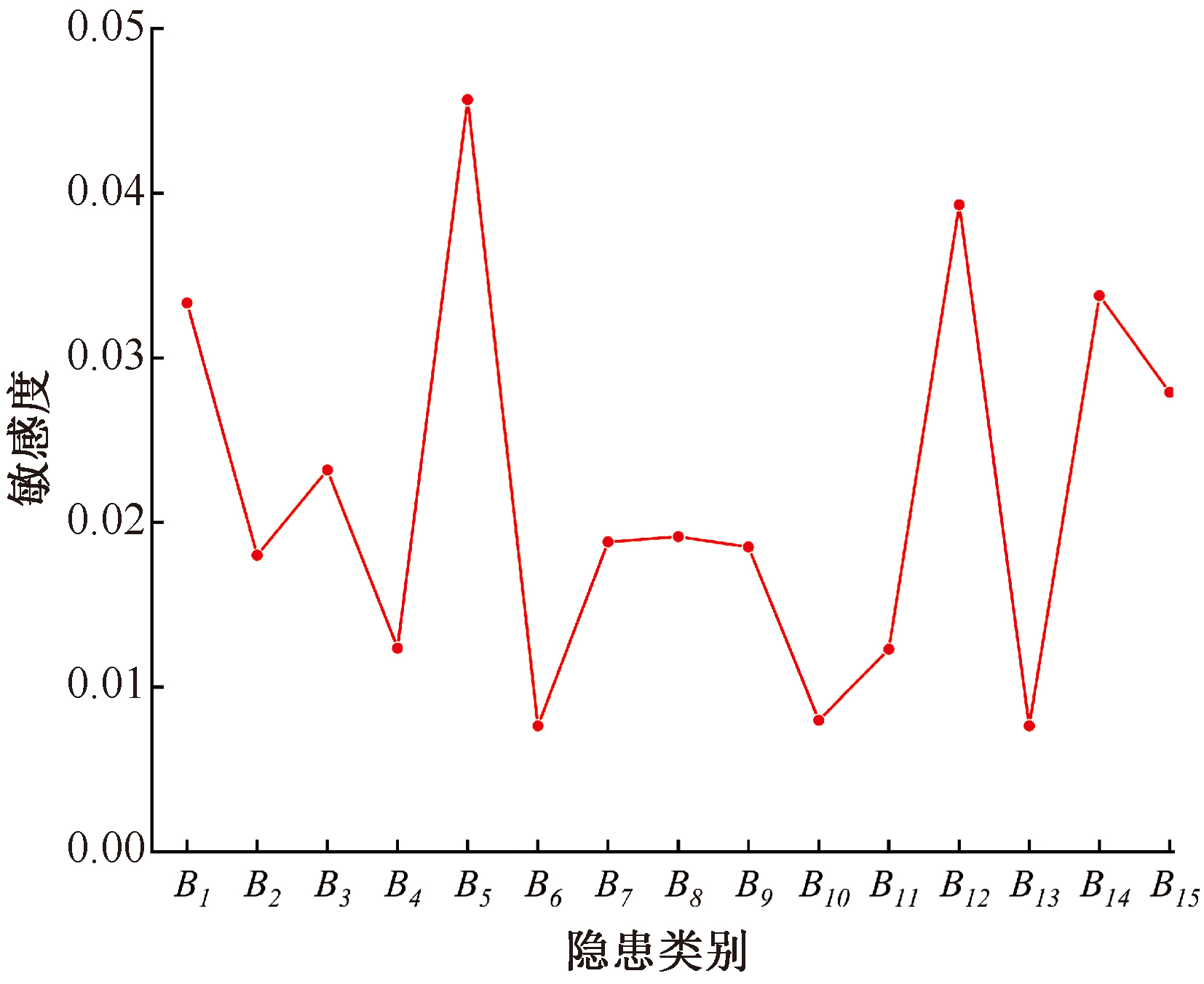
| [1] |
张圣柱, 王旭, 魏利军, 等. 2016—2020年全国化工和危险化学品事故分析研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2021, 17(10):119-126.
|
|
ZHANG Shengzhu, WANG Xu, WEI Lijun, et al. Analysis and research on chemical and hazardous chemicals accidents in China during 2016-2020[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2021, 17(10):119-126.
|
| [2] |
裴甲坤, 王飞跃, 郭换换, 等. 基于改进尖点突变模型的化工事故致因分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(7):20-25.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.07.004
|
|
PEI Jiakun, WANG Feiyue, GUO Huanhuan, et al. Cause analysis of chemical accidents based on improved cusp catastrophe model[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(7):20-25.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.07.004
|
| [3] |
刘庆龙, 曲秋影, 赵东风, 等. 基于多源异构数据融合的化工安全风险动态量化评估方法[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(3):1769-1777.
doi: 10.11949/0438-1157.20200749
|
|
LIU Qinglong, QU Qiuying, ZHAO Dongfeng, et al. Dynamic quantitative assessment method of chemical safety risk based on multi-source heterogeneous data fusion[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(3):1769-1777.
|
| [4] |
周荣义, 林金玉, 刘勇. 危险货物道路运输风险评估的集对模型及应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(1):173-179.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.01.029
|
|
ZHOU Rongyi, LIN Jinyu, LIU Yong. A risk assessment model for hazmat road transportation based on set pair analysis and its application[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(1):173-179.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.01.029
|
| [5] |
WU Chao, HUANG Lang. A new accident causation model based on information flow and its application in Tianjin port fire and explosion accident[J]. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2019, 182:73-85.
|
| [6] |
陈伟珂, 张欣. 危化品储运火灾爆炸事故多因素耦合动力学关系[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27(6):49-54.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.06.009
|
|
CHEN Weike, ZHANG Xin. Dynamic relationship between multi coupling risk factors of hazardous chemical storage and transportation fire and explosion accidents[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27(6):49-54.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.06.009
|
| [7] |
JIANG Wei, HAN Wei. Analysis of "2·28" KEEPER chemical industries hazardous chemical explosion accident based on FTA and HFACS[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2018, 15(10):DOI: 10.3390/ijerph15102151.
|
| [8] |
付净, 聂方超, 刘虹, 等. 基于FTA-24Model的化工事故原因分析[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2019, 26(6):159-165.
|
|
FU Jing, NIE Fangchao, LIU Hong, et al. Cause analysis of chemical accidents based on FTA-24Model[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2019, 26(6):159-165.
|
| [9] |
鲁义, 伍江乐, 邵淑珍, 等. 基于贝叶斯网络的危化品道路运输事故推理模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(3):174-182.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.03.024
|
|
LU Yi, WU Jiangle, SHAO Shuzhen, et al. Prediction model for road transport accidents of hazardous chemicals based on Bayesian network[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(3):174-182.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.03.024
|
| [10] |
宋英华, 刘子奇, 刘丹, 等. 基于模糊贝叶斯网络的化工园区火灾爆炸事故情景推演[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2022, 29(3):86-93.
|
|
SONG Yinghua, LIU Ziqi, LIU Dan, et al. Scenario deduction of fire and explosion accidents in chemical industry parks based on fuzzy Bayesian network[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2022, 29(3):86-93.
|
| [11] |
李丽, 周荣义, 王凌睿, 等. 基于后悔理论的危化品公路桥梁运输风险评估[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2022, 29(2):71-77.
|
|
LI Li, ZHOU Rongyi, WANG Lingrui, et al. Risk assessment of road bridge transportation of hazardous chemicals based on regret theory[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2022, 29(2):71-77.
|
| [12] |
胡志芳, 覃盼. 基于贝叶斯网络的三峡通航安全风险评估[J]. 水道港口, 2022, 43(4):555-560.
|
|
HU Zhifang, QIN Pan. Navigation safety risk assessment of the Three Gorges based on Bayesian networks[J]. Journal of Waterway and Harbor, 2022, 43(4):555-560.
|
| [13] |
朱敬聪, 朱晓光, 关磊. 基于贝叶斯网络的化工企业人员应急疏散研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2021, 21(2):739-745.
|
|
ZHU Jingcong, ZHU Xiaoguang, GUAN Lei. On the emergency evacuation of the personnel in the chemical enterprises based on the Bayesian network[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2021, 21(2):739-745.
|
| [14] |
李敏, 林志军, 鲁义, 等. 基于模糊贝叶斯网络的煤矿瓦斯爆炸风险评估[J]. 煤炭学报, 2023, 48(增2):626-637.
|
|
LI Min, LIN Zhijun, LU Yi, et al. Risk assessment of gas explosion in coal mines based on fuzzy Bayesian network[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2023, 48(S2):626-637.
|
| [15] |
易玉枚, 廖可兵, 易灿南. 基于BN的模糊系统事故风险管理辅助分析[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2015, 22(3):105-110.
|
|
YI Yumei, LIAO Kebing, YI Cannan. Study on the assistant analysis for accident risk management based on fuzzy system and BN[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2015, 22(3):105-110.
|