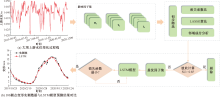
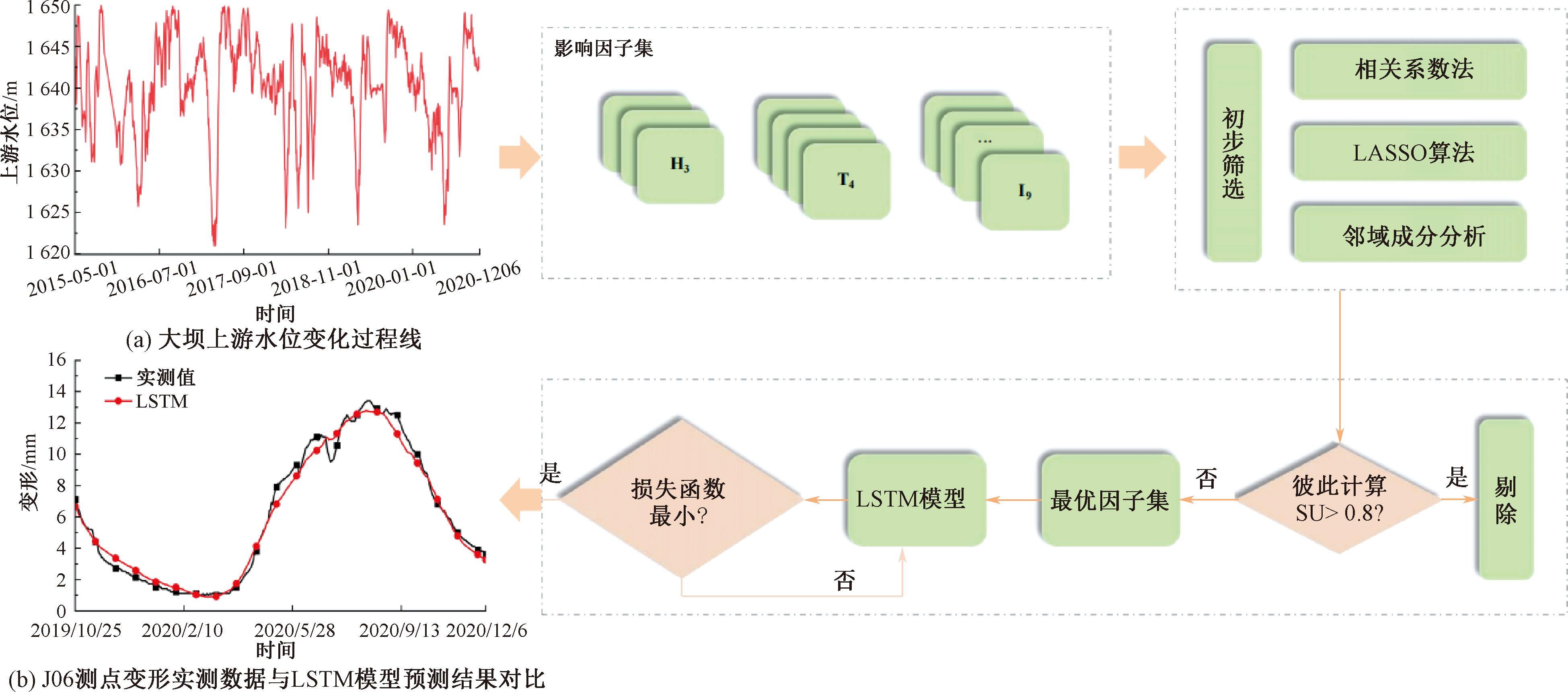
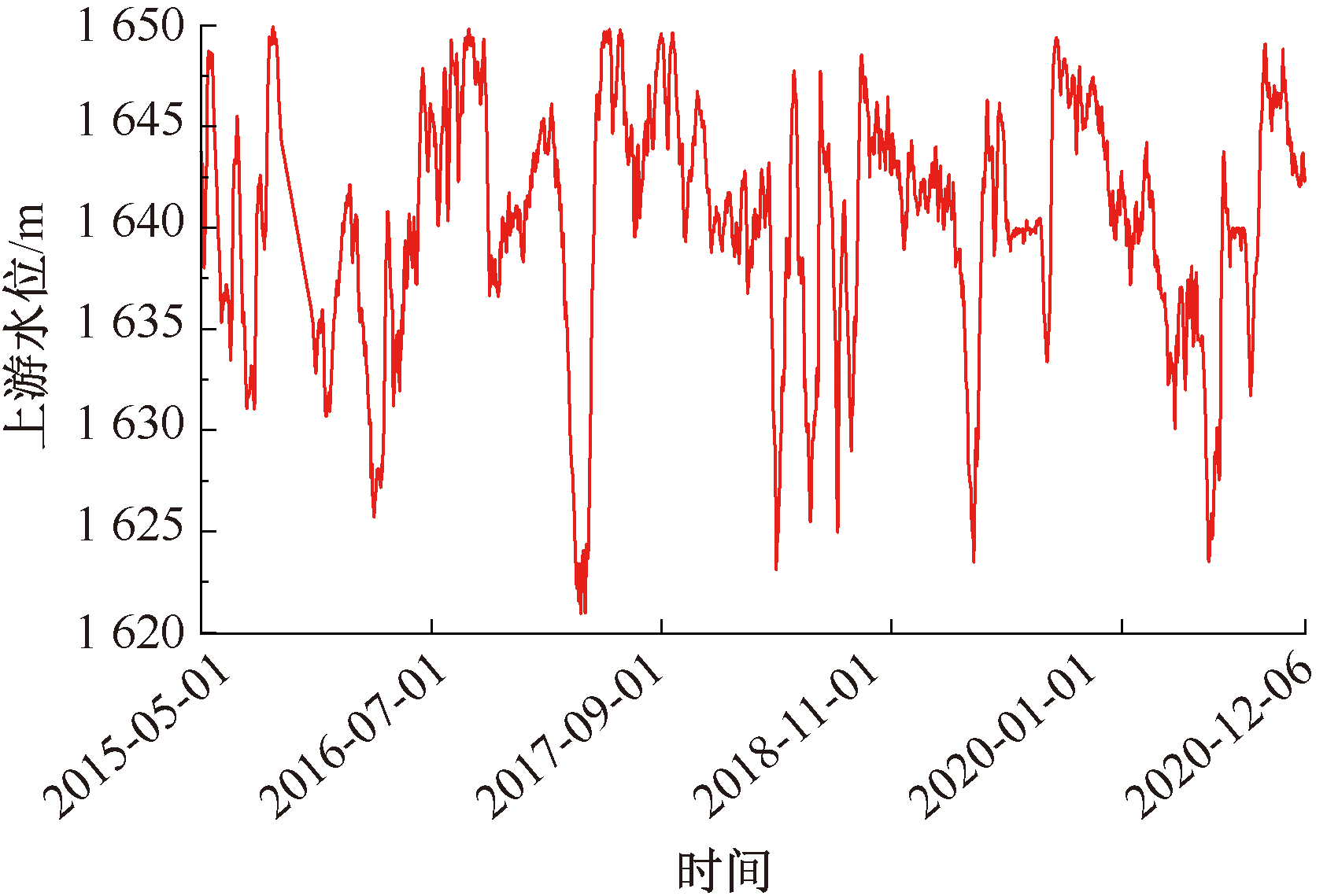
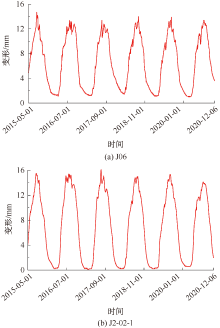
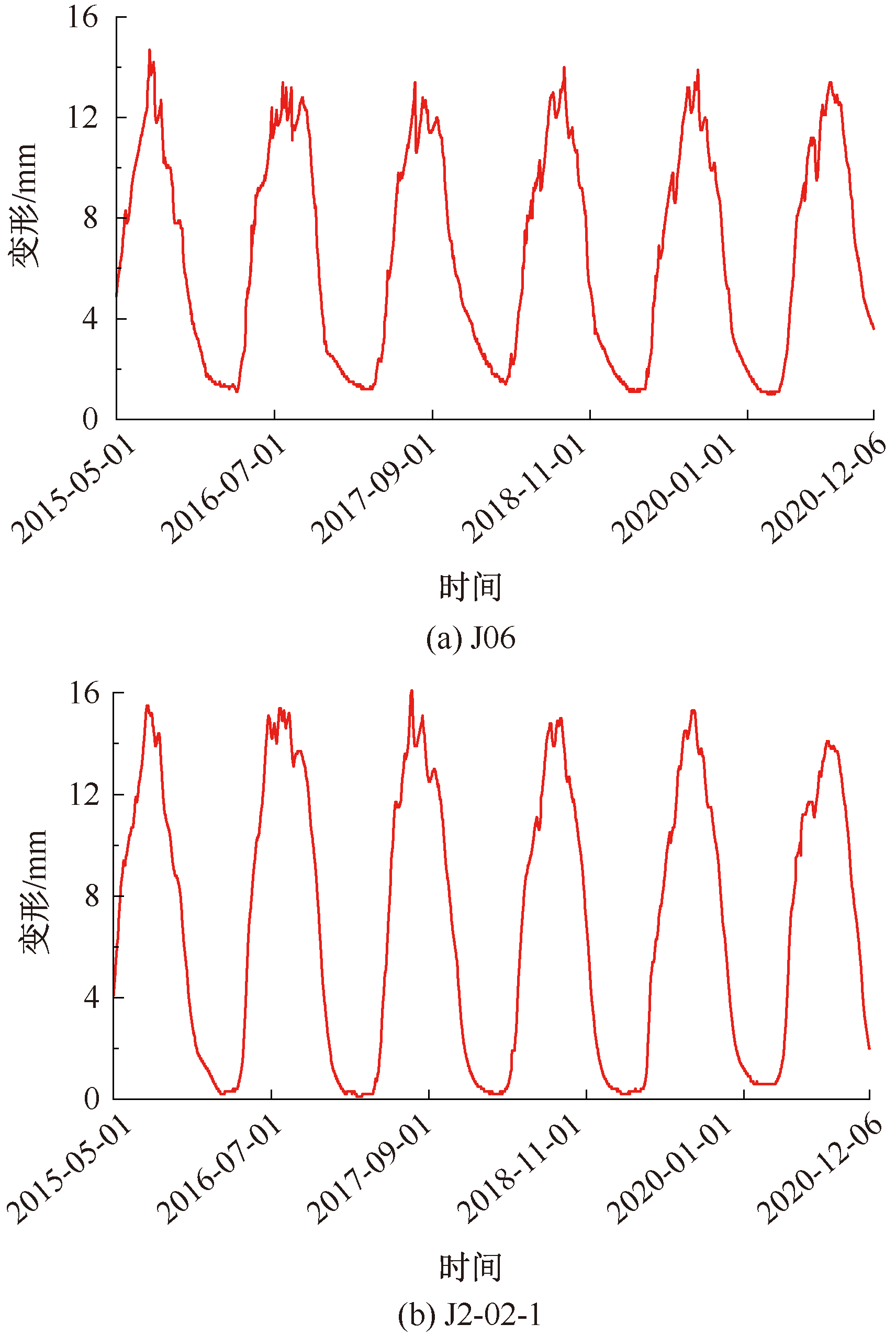
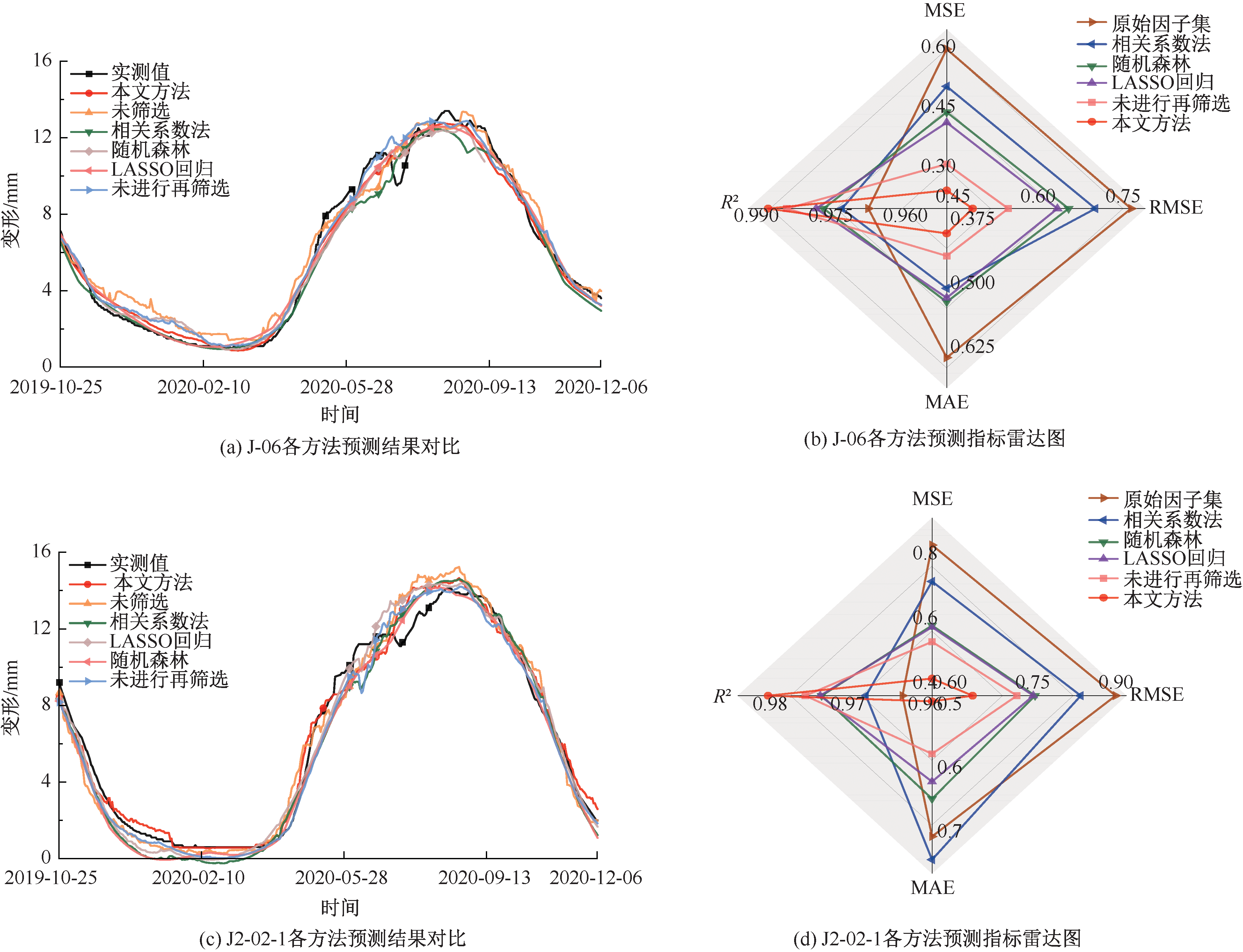
| [1] |
吴中如. 水工建筑物安全监控理论及其应用[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2003:1.
|
| [2] |
周仁练, 苏怀智, 韩彰, 等. 混凝土坝变形的长期预测模型与应用[J]. 水力发电学报, 2021, 40(9):122-131.
|
|
ZHOU Renlian, SU Huaizhi, HAN Zhang, et al. Long-term deformation prediction model of concrete dams and its application[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2021, 40(9): 122-131.
|
| [3] |
WILLM G, BEAUJOINT N. Les mÉthodes de surveillance des barrages au service de la production hydraulique d'ElectricitÉ de France, problèmes anciens et solutions nouvelles[C]. IXth International Congress on Large Dams, 1967: 529-550.
|
| [4] |
GAMSE S, OBERGUGGENBERGER M. Assessment of long-term coordinate time series using hydrostatic-season-time model for rock-fill embankment dam[J]. Structural Control and Health Monitoring, 2017, 24(1): DOI: 10.1002/stc.1859.
|
| [5] |
KARLUPIA N, ABROL P. Wrapper-based optimized feature selection using nature-inspired algorithms[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2023, 35(17): 12 675-12 689.
doi: 10.1007/s00521-023-08383-6
|
| [6] |
赵佳蕊, 王玲芝, 李晨阳. 基于LEA-LSTM的光伏发电功率短期预测方法[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22(11):34-42.
|
|
ZHAO Jiarui, WANG Lingzhi, LI Chenyang. A short-term prediction method of photovoltaic power generation based on LEA-LSTM[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22(11):34-42.
|
| [7] |
罗璐, 李志, 张启灵. 大坝变形预测的最优因子长短期记忆网络模型[J]. 水力发电学报, 2023, 42(2):24-35.
|
|
LUO Lu, LI Zhi, ZHANG Qiling. Optimal factor set based long short-term memory network model for prediction of dam deformation[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2023, 42(2):24-35.
|
| [8] |
郑好, 李登华, 丁勇. 基于集成因子优选算法的面板堆石坝变形预测模型[J]. 排灌机械工程学报, 2025, 43(2):178-186.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8530.23.0262
|
|
ZHENG Hao, LI Denghua, DING Yong. Deformation prediction model of panel rockfill dam based on integrated factor optimization algorithm[J]. Journal of Drainage and Irrigation Machinery Engineering, 2025, 43(2): 178-186.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8530.23.0262
|
| [9] |
SU Yan, WENG Kailiang, LIN Chuan, et al. Dam deformation interpretation and prediction based on a long short-term memory model coupled with an attention mechanism[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(14): DOI: 10.3390/app11146625.
|
| [10] |
蒙伟, 何川, 陈子全, 等. 岭回归在岩体初始地应力场反演中的应用[J]. 岩土力学, 2021, 42(4):1156-1169.
|
|
MENG Wei, HE Chuan, CHEN Ziquan, et al. Application of ridge regression in the inversion analysis of the initial geo-stress field of rock masses[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(4):1156-1169.
|
| [11] |
袁冬阳, 顾冲时, 顾昊. 严寒地区混凝土重力坝变形行为分析与预测模型[J]. 水利学报, 2022, 53(6):733-746.
|
|
YUAN Dongyang, GU Chongshi, GU Hao. Displacement behavior analysis and prediction model of concrete gravity dams in cold region[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2022, 53(6):733-746.
|
| [12] |
徐韧, 苏怀智, 杨立夫. 基于GP-XGBoost的大坝变形预测模型[J]. 水利水电科技进展, 2021, 41 (5): 41-46,70.
|
|
XU Ren, SU Huaizhi, YANG Lifu. Dam deformation prediction model based on GP-XGBoost[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 2021, 41 (5): 41-46,70.
|
| [13] |
LIU Mingkai, WEN Zhiping, SU Huaizhi. Deformation prediction based on denoising techniques and ensemble learning algorithms for concrete dams[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2024, 238:DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.122022.
|
| [14] |
何裕坤, 晁阳, 李同春, 等. 基于SBO-LSTM的大坝变形预测模型[J]. 水利水电技术:中英文, 2024, 55 (增1): 78-86.
|
|
HE Yukun, CHAO Yang, LI Tongchun, et al. Dam deformation prediction model based on SBO-LSTM[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2024, 55(S1): 78-86.
|
| [15] |
吉丽萍, 黄景涛, 李一凡, 等. 一种基于多信息融合的风电功率预测特征选择方法[J]. 兰州理工大学学报, 2024, 50 (5): 94-100.
|
|
JI Liping, HUANG Jingtao, LI Yifan, et al. A wind power prediction feature selection method based on multi-information fusion[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University of Technology, 2024, 50 (5): 94-100.
|
| [16] |
XIONG Rui, SUN Yue, WANG Chenxu, et al. A data-driven method for extracting aging features to accurately predict the battery health[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2023, 57: 460-470.
doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2023.02.034
|
| [17] |
高浩田, 李东喜, 陈泽华, 等. 基于交互式多特征融合算法的药物靶标预测[J]. 太原理工大学学报, 2024, 55(4): 751-758.
|
|
GAO Haotian, LI Dongxi, CHEN Zehua, et al. Prediction of drug-target interactions based on interactive multi-feature fusion algorithm[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 2024, 55(4): 751-758.
|
| [18] |
王晓楠, 苏文浩, 董灵波. 应用特征选择和机器学习方法建立兴安落叶松单木树龄预测模型[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2024, 52 (11): 64-71,82.
|
|
WANG Xiaonan, SU Wenhao, DONG Lingbo. Establishing a prediction model for the age of Larix gmelinii individual tree using feature selection and machine learning methods[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2024, 52(11): 64-71, 82.
|
| [19] |
毛杰, 陈宓舟, 许磊, 等. 基于双重选择LASSO模型的我国股市定价因子边际有效性研究[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2024, 44 (9): 2993-3008.
doi: 10.12011/SETP2023-0831
|
|
MAO Jie, CHEN Mizhou, XU Lei, et al. Research on the marginal effectiveness of Chinese stock markets'pricing factors: application of double-selection LASSO model[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2024, 44 (9): 2993-3008.
|
| [20] |
刘天翼, 艾星星, 张九丹. 基于MLR-DE-LSTM的大坝变形串联组合预测模型[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2025(2):207-212.
|
|
LIU Tianyi, AI Xingxing, ZHANG Jiudan. Dam deformation serial combined prediction model based on MLR-DE-LSTM[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2025(2):207-212.
|
| [21] |
史云峰, 韩晓明, 王利红, 等. 基于特征选择和机器学习的锂电池寿命早期预测[J]. 现代电子技术, 2024, 47 (22): 90-98.
|
|
SHI Yunfeng, HAN Xiaoming, WANG Lihong, et al. Lithium battery life early prediction based on feature selection and machine learning[J]. Modern Electronics Technique, 2024, 47 (22): 90-98.
|
| [22] |
YU Lei, LIU Huan. Feature selection for high-dimensional data: a fast correlation-based filter solution[C]. Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-03),2003: 856-863.
|