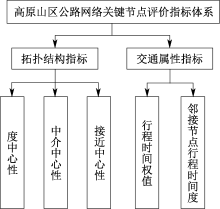
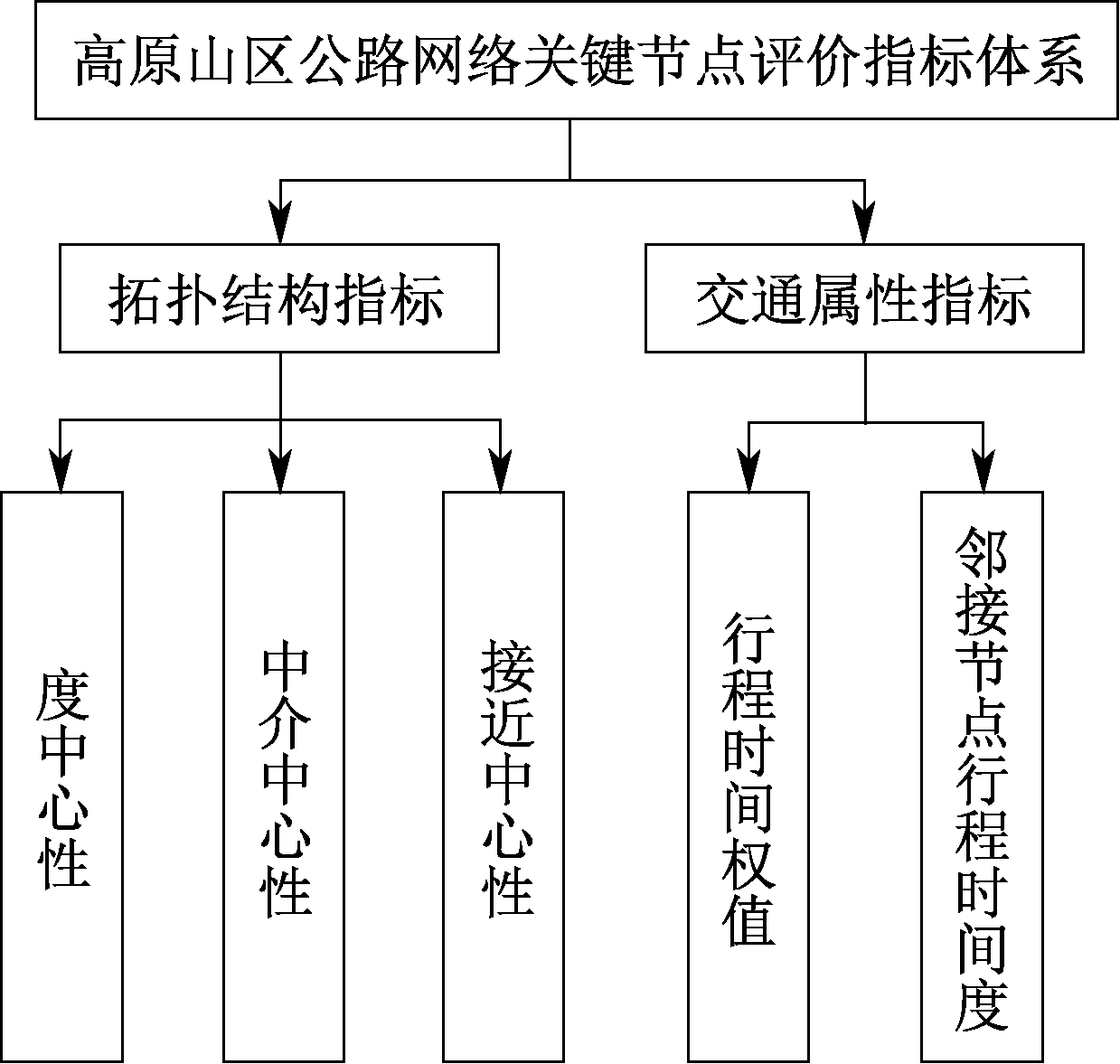
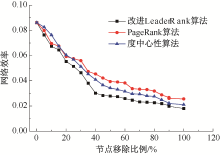
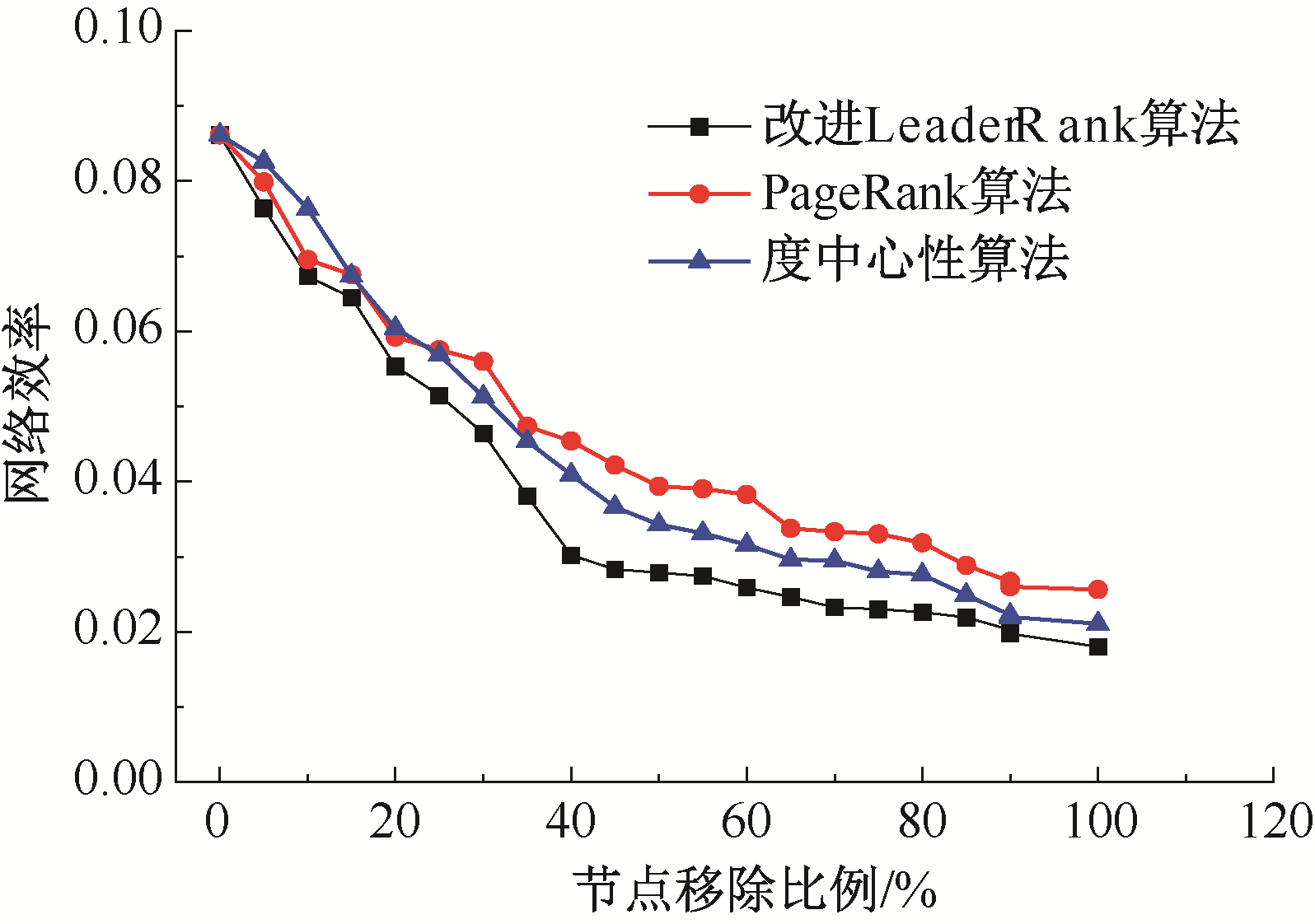
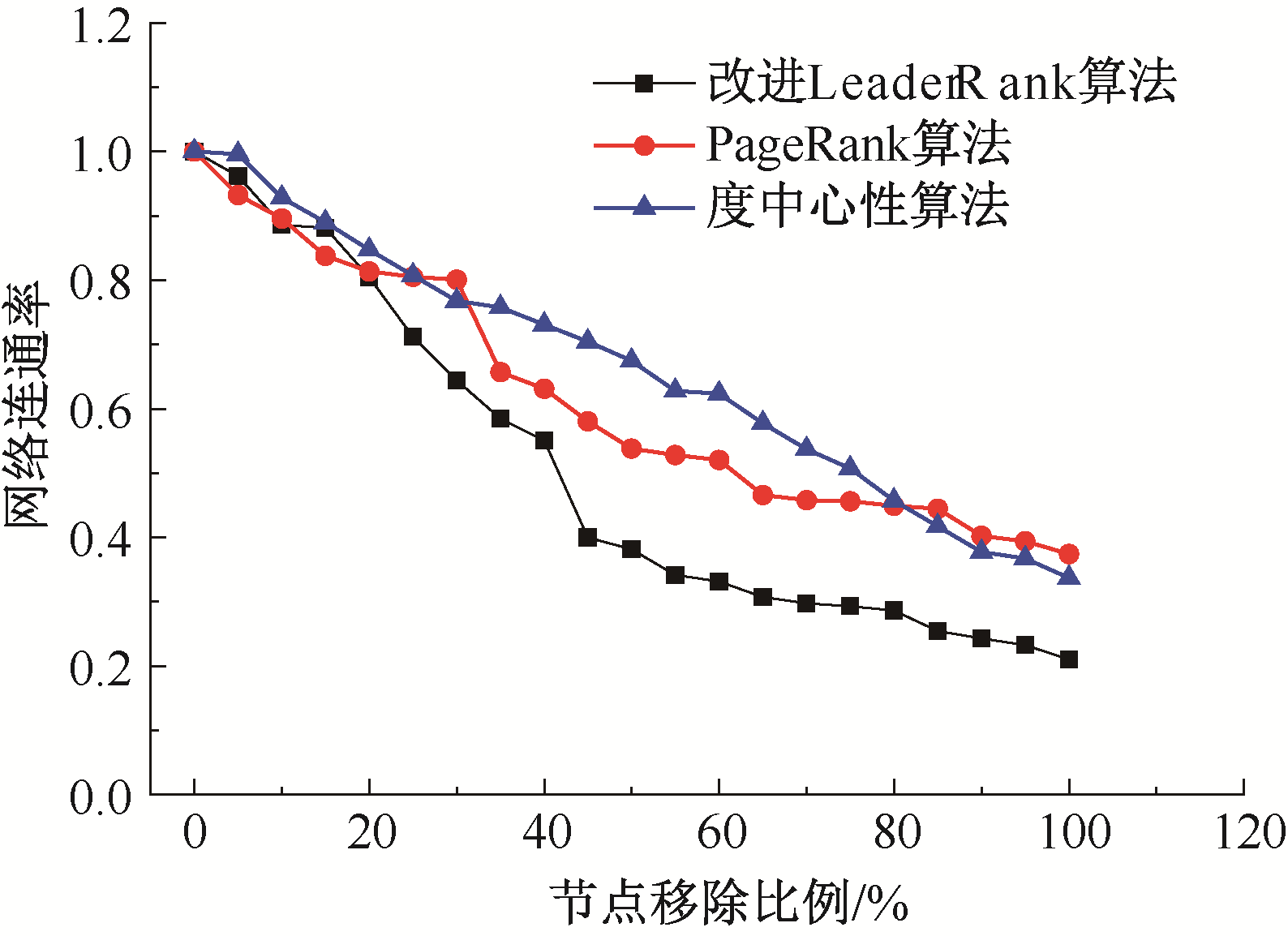
| [1] |
刘瑞, 叶堃晖, 张正丰. 复杂网络视角下我国高速公路演变特征研究[J]. 项目管理技术, 2020, 18(10): 26-33.
|
|
LIU Rui, YE Kunhui, ZHANG Zhengfeng. Research on the evolution characteristics of China's highways from the perspective of complex networks[J]. Project Management Technology, 2023, 18(10): 26-33.
|
| [2] |
崔杨, 曾俊伟, 钱勇生, 等. 基于复杂网络的西部地区公路网可靠性研究[J]. 公路工程, 2018, 43(3): 46-51.
|
|
CUI Yang, ZENG Junwei, QIAN Yongsheng, et al. Reliability research of highway network in northwest China based on complex network theory[J]. Highway Engineering, 2018, 43(3): 46-51.
|
| [3] |
代洪娜, 李炜. 考虑流量加权的高速公路网脆弱性研究[J]. 公路, 2019, 64(5): 181-187.
|
|
DAI Hongna, LI Wei. Study of expressway network vulnerability considering on traffic flow[J]. Highway, 2019, 64(5): 181-187.
|
| [4] |
林培群, 刘子豪, 闫明月. 基于多元加权中心特征的高速公路网韧性研究[J]. 重庆交通大学学报:自然科学版, 2023, 42(10): 122-131.
|
|
LIN Peiqun, LIU Zihao, YAN Mingyue. Resilience of highway network based on multiple weighted center characteristics[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University :Natural Science, 2023, 42(10):122-131.
|
| [5] |
吴丽娜, 吕岩峰, 慈玉生. 省域高速公路网络连通可靠性:黑龙江省案例分析[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2018, 18(增1): 134-140.
|
|
WU Li'na, LYU Yanfeng, CI Yusheng. Connectivity Reliability for provincial freeway network: a case study in Heilongjiang, China[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2018, 18(S1): 134-140.
|
| [6] |
AKBARZADEH M, MEMARMONTAZERIN S, DERRIBLE S, et al. The role of travel demand and network centrality on the connectivity and resilience of an urban street system[J]. Transportation, 2019, 46(5): 1127-1141.
|
| [7] |
王灵丽, 黄敏, 高亮. 基于聚类算法的交通网络节点重要性评价方法研究[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2020, 38(2): 80-88.
|
|
WANG Lingli, HUANG Min, GAO Liang. Methods of importance evaluation of traffic network node based on clustering algorithms[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2020, 38(2): 80-88.
|
| [8] |
张贵兰. 基于节点综合重要度的城市道路交通网络相继拥堵疏散路径规划[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2022.
|
|
ZHANG Guilan. Cascading failure evacuation path planning of urban road traffic network based on comprehensive importance of nodes[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2022.
|
| [9] |
冯慧芳, 柏凤山, 徐有基. 基于轨迹大数据的城市交通感知和路网关键节点识别[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2018, 18(3): 42-47, 54.
|
|
FENG Huifang, BAI Fengshan, XU Youji. Urban traffic perception and critical node ide.pngication of road network based on trajectory big data[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2018, 18(3): 42-47,54.
|
| [10] |
李卓, 何瑞春, 李文霞. 考虑时空动态特征的高速铁路网络鲁棒性评估[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2024, 34(4): 111-120.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.04.0648
|
|
LI Zhuo, HE Ruichun, LI Wenxia. Robustness evaluation for high-speed railway network with spatiotemporal dynamic characteristics[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2024, 34(4): 111-120.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2024.04.0648
|
| [11] |
徐云帆. 基于复杂网络理论的公路网脆弱性识别方法研究[D]. 济南: 山东交通学院, 2023.
|
|
XU Yunfan. The ide.pngication method research of road network's vulnerability based on complex network theory[D]. Ji'nan: Shandong Jiaotong University, 2023.
|
| [12] |
李倩, 张飞涟. 模糊可拓工程优选模型的城市轨道交通路网方案评价方法[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2009, 30(6): 126-131.
|
|
LI Qian, ZHANG Feilian. Evaluation methodology of urban mass transit network project option using the fuzzy expandable engineering optimization model[J]. China Railway Science, 2009, 30(6): 126-131.
|
| [13] |
朱克毓, 董庆兴, 梁昌勇, 等. 一类三角模糊层次分析法的无效性分析[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2015, 35(8): 2104-2112.
doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(2015)8-2104
|
|
ZHU Keyu, DONG Qingxing, LIANG Changyong, et al. The analysis of the invalidity of one kind triangular fuzzy AHP[J]. Systems Engineering-Theoryj & Practice, 2015, 35(8): 2104-2112.
|
| [14] |
魏业文, 吴希韬, 聂俊波, 等. 基于博弈论-改进TOPSIS 的电能质量综合评价[J]. 电子测量技术, 2021, 44(16): 50-56.
|
|
WEI Yewen, WU Xitao, NIE Junbo, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of power quality based on BWM-CRITIC-TOPSIS method[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2021, 44(16): 50-56.
|
| [15] |
王铁旦, 穆毅强, 彭定洪. HAZOP风险评级的变权犹豫模糊方法[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(5): 61-67.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.05.1335
|
|
WANG Tiedan, MU Yiqiang, PENG Dinghong. Hesitant fuzzy method with variable weight for HAZOP risk sorting[J]. China Safety Seience Journal, 2022, 32(5): 61-67.
|
| [16] |
魏震波, 鞠啟, 易刚春, 等. 基于改进LeaderRank算法的电网连锁故障关键线路辨识方法[J]. 高电压技术, 2021, 47(12): 4265-4273.
|
|
WEI Zhenbo, JU Qi, YI Gangchun, et al. Ide.pngication of critical lines of power grid cascading failures based on modified LeaderRank algorithm[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2021, 47(12): 4265-4273.
|