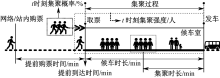
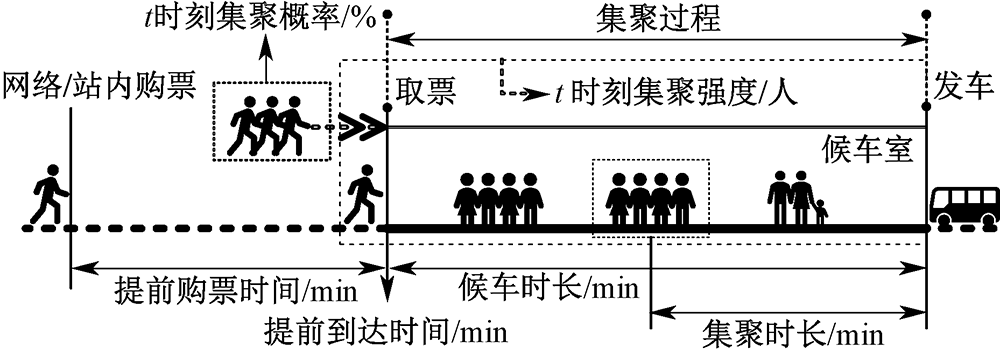
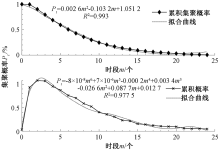
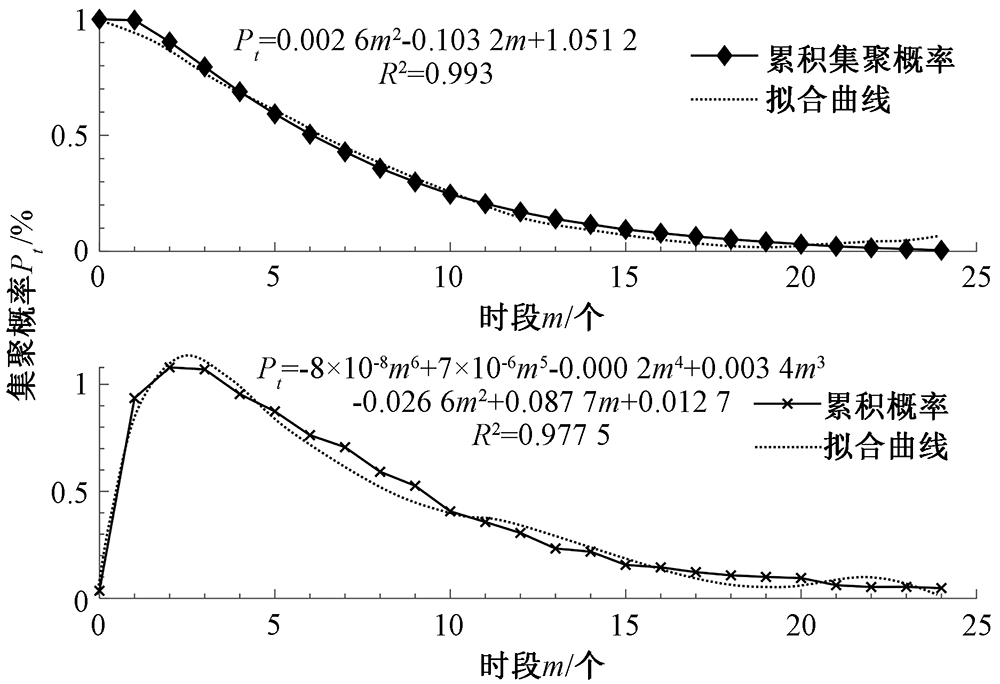
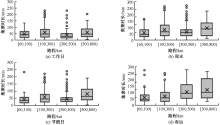
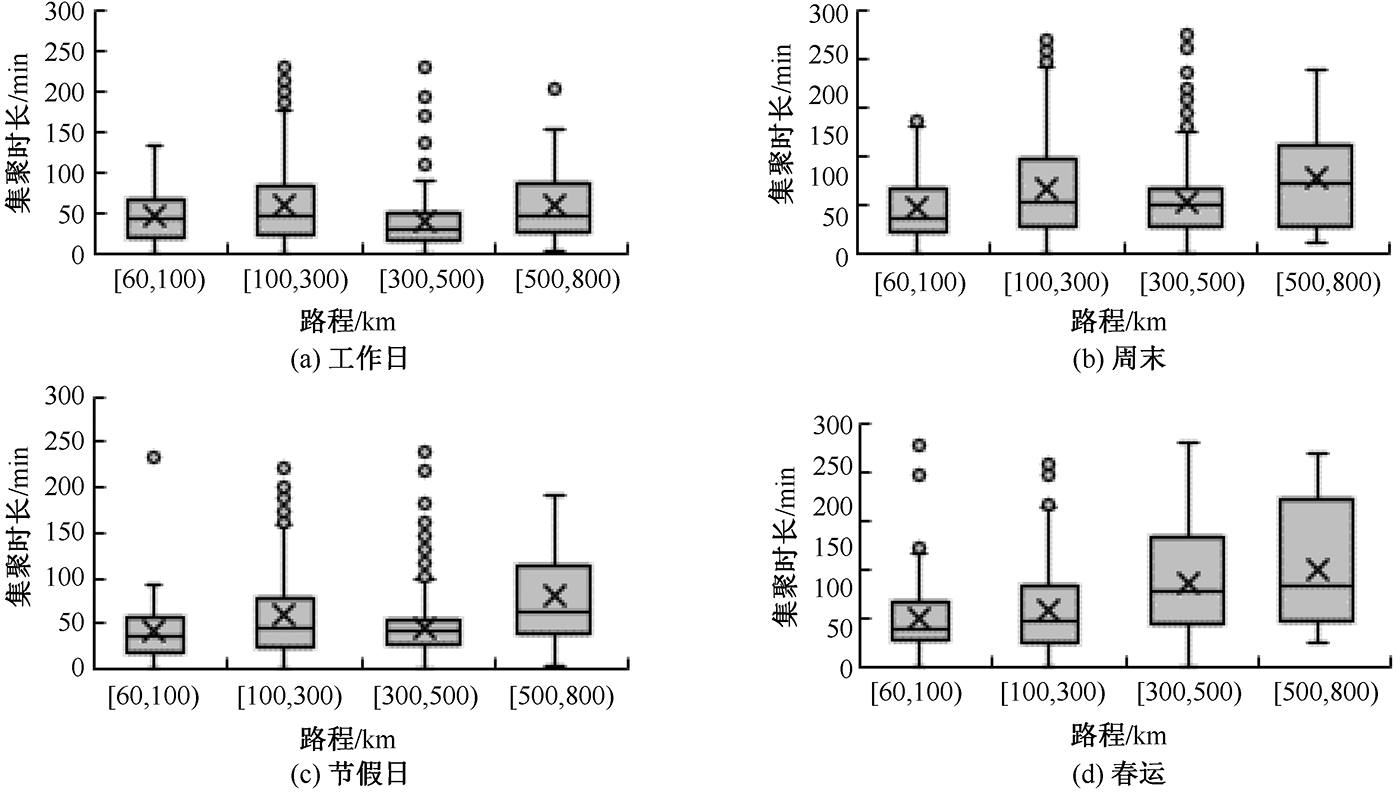
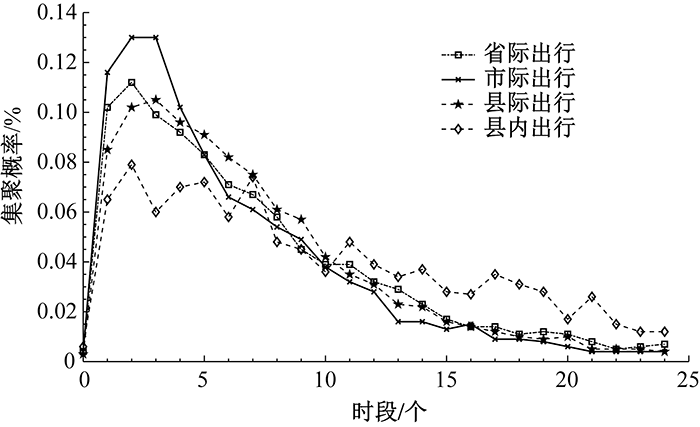
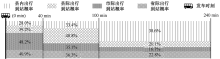
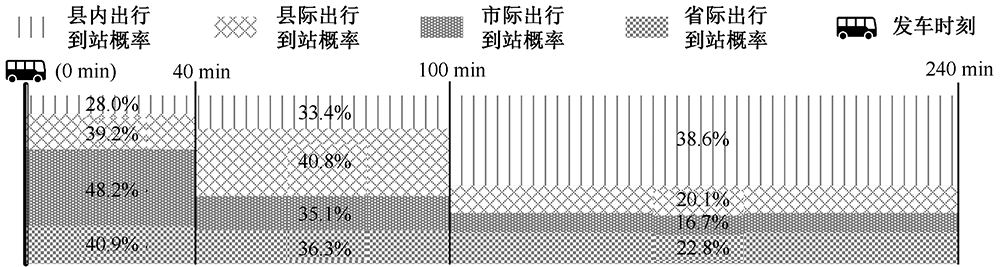
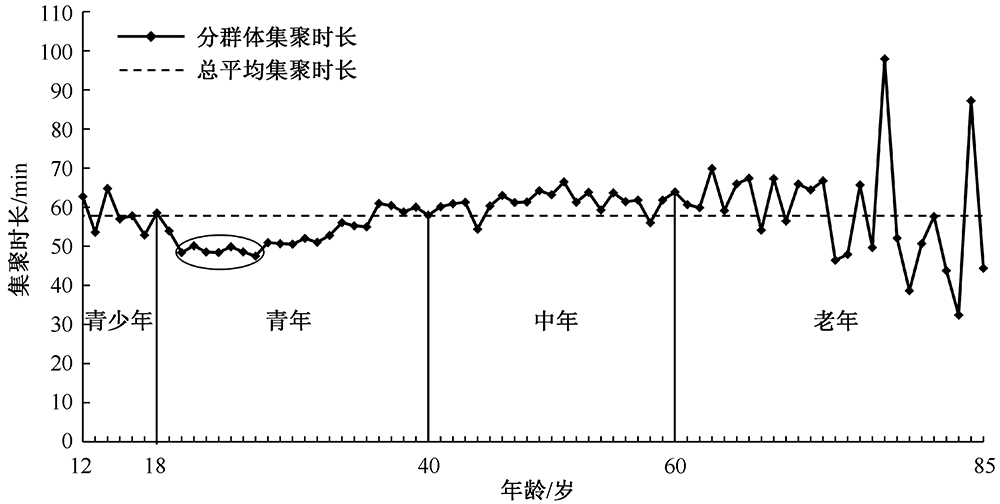
| [1] |
覃频频, 陆凯平, 黄大明, 等. 利用模糊集理论评价公路客运站安全管理工作[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2006, 16(5):31-36.
|
|
QIN Pinpin, LU Kaiping, HUANG Daming, et al. Assessment of highway bus station by fuzzy set theory[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2006, 16(5):31-36.
|
| [2] |
ODD I, ØYVIND S. Waiting time and the role and value of information in scheduled transport[J]. Research in Transportation Economics, 2008, 23(1):41-52.
doi: 10.1016/j.retrec.2008.10.005
|
| [3] |
MARCO L, ULRICH W, ANDREW N. Passenger arrival rates at public transport stations[C]. CD-ROM. Proceedings of the 86th Annual Meeting of the Transportation Research Board, 2007:1-12.
|
| [4] |
王菲, 孙全欣, 毛保华, 等. 基于时刻表协调的同台换乘聚集人数计算模型[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2013, 13(3):163-169.
|
|
WANG Fei, SUN Quanxin, MAO Baohua, et al. Calculation model for passenger assembling on one-platform-transfer station based on timetable coordination[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2013, 13(3):163-169.
|
| [5] |
刘启钢, 朱克非, 杜旭升. 大型客运站最高聚集人数仿真计算方法研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2011, 33(8):1-6.
|
|
LIU Qigang, ZHU Kefei, DU Xusheng. Research on calculation method of the maximum number of gathering passengers in large stations[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2011, 33(8):1-6.
|
| [6] |
王爱丽, 董宝田, 高春霞. 铁路客运站旅客聚集分布仿真模型与算法研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2013, 13(1):142-148.
|
|
WANG Aili, DONG Baotian, GAO Chunxia. Assembling model and algorithm of railway passengers distribution[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2013, 13(1):142-148.
|
| [7] |
杨晓光, 安健, 刘好德, 等. 公交运行服务质量评价指标体系探讨[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2010, 10(4):13-21.
|
|
YANG Xiaoguang, AN Jian, LIU Haode, et al. Evaluation architecture discussion of route-level transit service quality[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2010, 10(4):13-21.
|
| [8] |
吕慎, 田锋, 莫一魁. 轨道交通枢纽地铁换乘接运公交乘客平均候车时间研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2014, 31(12):92-97.
|
|
LYU Shen, TIAN Feng, MO Yikui. Average waiting time of passengers transferring from subway to feeder bus at rail transit hub[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2014, 31(12):92-97.
|
| [9] |
戢晓峰, 连晨希. 公路城际出行链模式划分及其形成机制[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2017, 17(6):13-19,39.
|
|
JI Xiaofeng, LIAN Chenxi. Intercity highway trip chain model and its formation mechanism[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2017, 17(6):13-19,39.
|
| [10] |
戢晓峰, 李德林. 基于潜在类别的公路旅客群体细分模型[J]. 公路交通科技, 2019, 36(10):152-158.
|
|
JI Xiaofeng, LI Delin. A model for segmentation of highway passenger groups based on latent class[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2019, 36(10):152-158.
|
| [11] |
李军, 贾顺平. 道路客运提前购票行为模型[J]. 公路交通科技, 2019, 36(10):144-151.
|
|
LI Jun, JIA Shunping. A model for advance ticketing behaviors of road passenger transport[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2019, 36(10):144-151.
|
| [12] |
吴仲文. 客运专线客运站候车大厅规模研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2010.
|
|
WU Zhongwen. Study on waiting hall scale of passenger dedicated line station[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2010.
|
| [13] |
张瑞博. 铁路客运站候车能力分析及计算方法研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2011.
|
|
ZHANG Ruibo. Analysis and calculation method of waiting capacity at railway passenger stations[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2011.
|
| [14] |
刘晓芳, 吝涛, 郑千惠, 等. 城市街巷型公共空间人群聚集安全风险量化评估[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2016, 26(12):134-139.
|
|
LIU Xiaofang, LIN Tao, ZHENG Qianhui, et al. Quantitative risk assessment of crowd safety in urban public space in street form[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2016, 26(12):134-139.
|