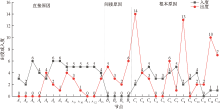
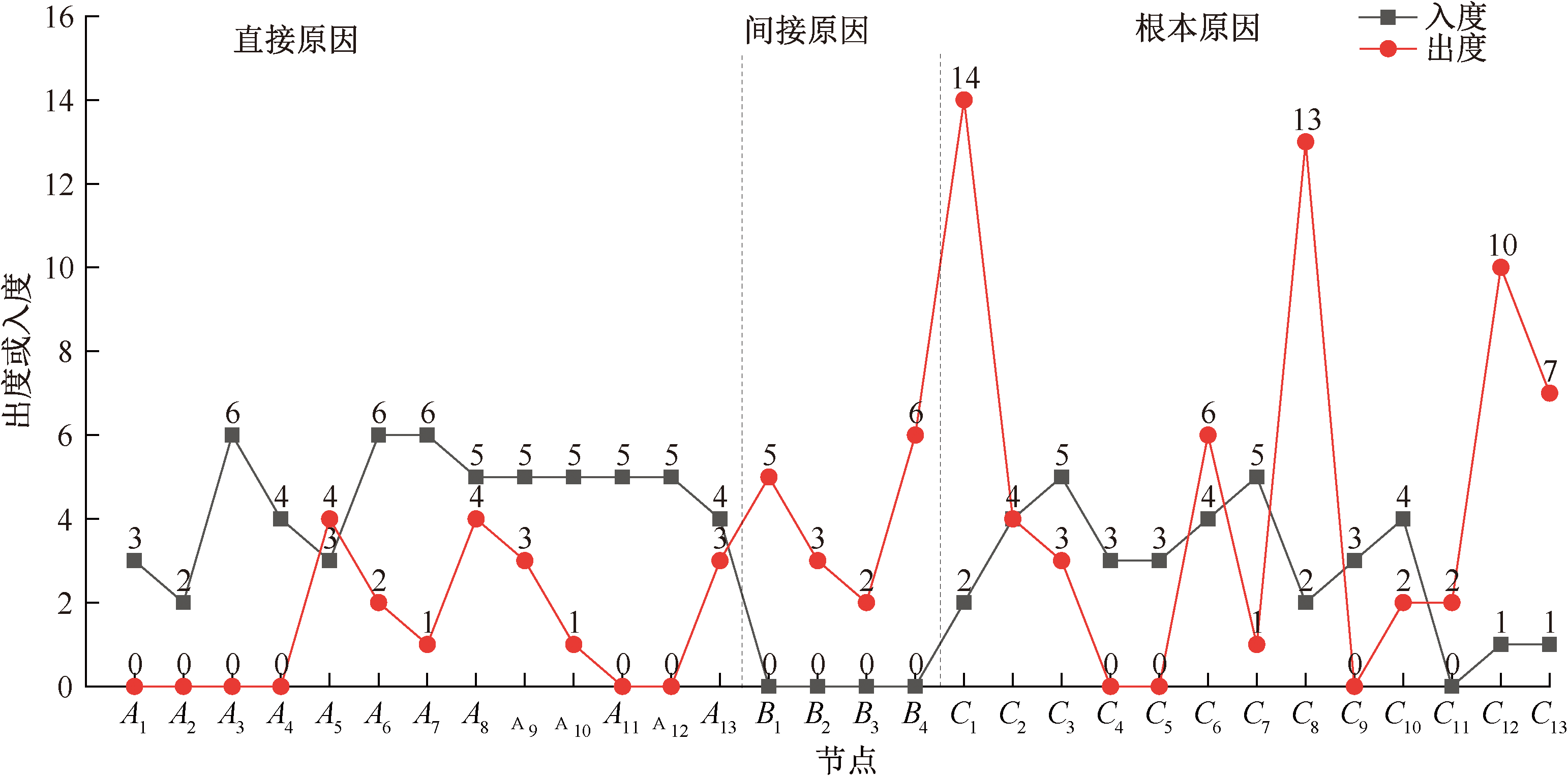
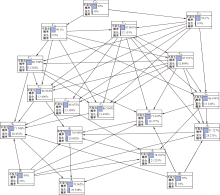
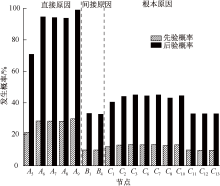
| [1] |
“1·15”盘山化工厂爆炸事故[OL]. [2023-01-15]. https://baike.baidu.com/.
|
| [2] |
“3·17”美国休斯敦油库火灾事故[OL]. [2019-03-17]. https://baike.baidu.com/.
|
| [3] |
日照市山东石大科技石化有限公司“7·16”较大着火爆炸事故调查报告[OL]. [2015-07-16]. http://www.shandong.gov.cn/index.html/.
|
| [4] |
LEVESON N. A new accident model for engineering safer systems[J]. Safety Science, 2004, 42(4): 237-270.
|
| [5] |
CEYLAN B O, KARATUĞ Ç, AKYUZ E, et al. A system theory (STAMP) based quantitative accident analysis model for complex engineering systems[J]. Safety Science, 2023, 166: DOI: 10.1016/j.ssci.2023.106232.
|
| [6] |
ALTABBAKH H, ALKAZIMI M A, MURRAY S, et al. STAMP-Holistic system safety approach or just another risk model?[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2014, 32: 109-119.
|
| [7] |
QIAO Wanguan, CHEN Xue, XIA Wenxin. STAMP-based causal analysis of the coal mine major accident: from the perspective of safety process[J]. Energy Reports, 2021, 7: 116-124.
doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2021.10.048
|
| [8] |
CHEN Jiayu, YAO Boqing, LU Qinhua, et al. A safety dynamic evaluation method for missile mission based on multi-layered safety control structure model[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2024, 241: DOI: 10.1016/j.ress.2023.109678.
|
| [9] |
EBRAHIMI H, ZAREI E, ANSARI M, et al. A system theory based accident analysis model: STAMP-fuzzy DEMATEL[J]. Safety Science, 2024, 173: DOI: org/10.1016/j.ssci.2024.106445.
|
| [10] |
孙逸林, 郑小强, 刘险峰, 等. 重大城市燃气管道泄漏爆炸事故定量分析方法研究: 以湖北十堰“6·13”事故为例[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2022, 22(6): 3312-3320.
|
|
SUN Yilin, ZHENG Xiaoqiang, LIU Xianfeng, et al. Research of quantitative analysis approach for serious leakage and explosion accident of urban gas pipeline: a case study of "6·13" accident[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2022, 22(6): 3312-3320.
|
| [11] |
吴海涛, 黎双喜. 高铁应急调度STAMP/STPA安全性分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(6): 113-120.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.06.015
|
|
WU Haitao, LI Shuangxi. High-speed railway emergency dispatching safety analysis based on STAMP/STPA[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(6): 113-120.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn 1003-3033.2021.06.015
|
| [12] |
赵挺生, 胡俊杰, 师玉栋, 等. 塔吊安装与拆卸作业安全性分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(10): 32-38.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.10.005
|
|
ZHAO Tingsheng, HU Junjie, SHI Yudong, et al. Safety analysis on tower crane installation and dismantling[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(10): 32-38.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.10.005
|
| [13] |
傅贵, 陈奕燃, 许素睿, 等. 事故致因"2-4"模型的内涵解析及第6版的研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(1): 12-19.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.01.002
|
|
FU Gui, CHEN Yiran, XU Surui, et al. Detailed explanations of 24Model and development of its 6th version[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(1): 12-19.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.01.002
|
| [14] |
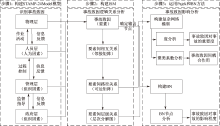
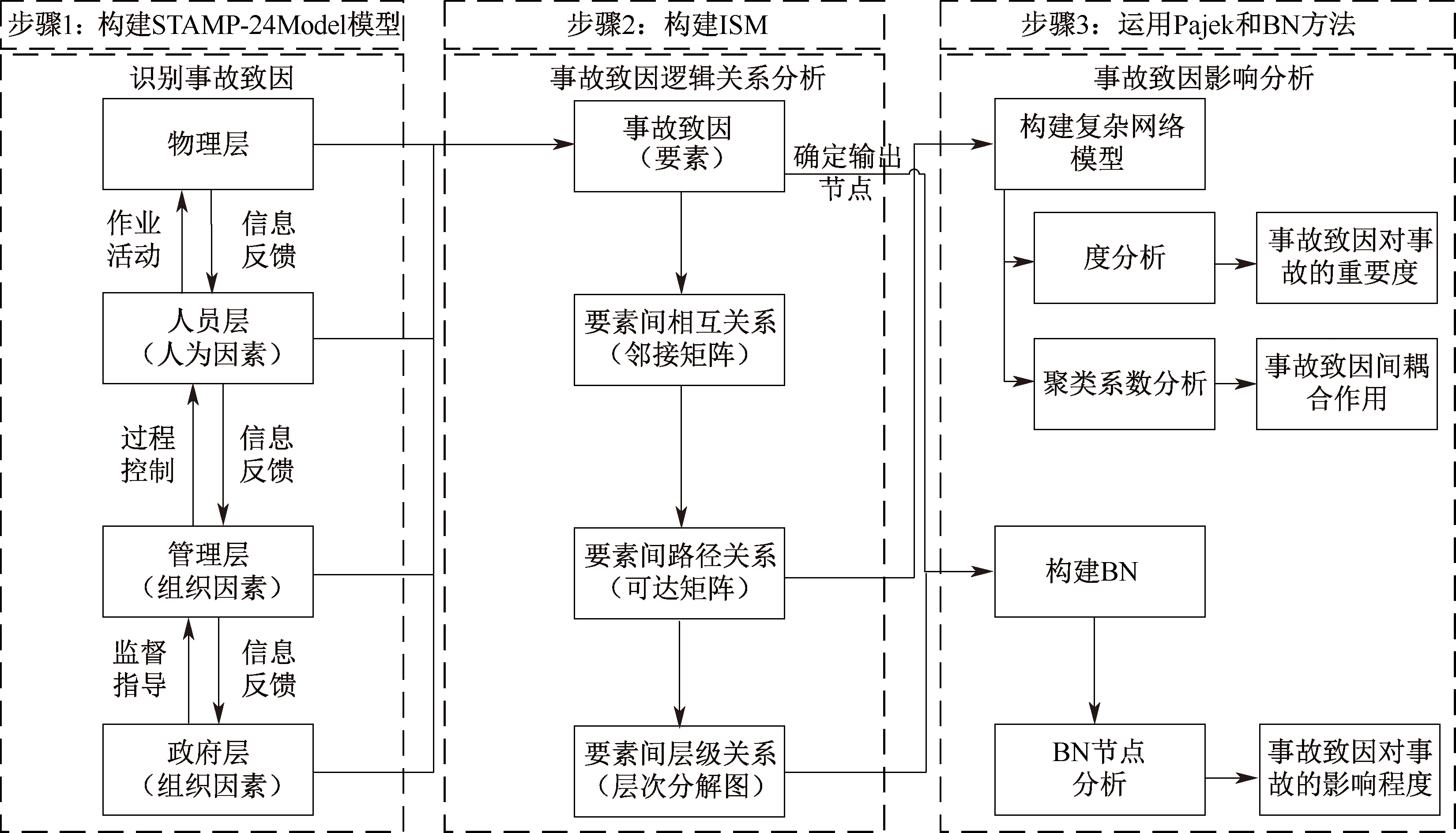
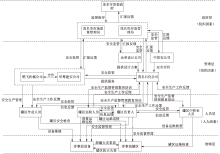
曾明荣, 秦永莹, 刘小航, 等. 采用STAMP-24Model的多组织事故分析[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2024, 24(7): 2741-2750.
|
|
ZENG Mingrong, QIN Yongying, LIU Xiaohang, et al. Analysis of multi-organization accident based on STAMP-24Model[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2024, 24(7): 2741-2750.
|
| [15] |
WARFIELD J N. Binary matrices in system modeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1973, 3(5): 441-449.
|
| [16] |
张玥, 帅斌, 尹德志, 等. 基于STAMP-ISM的铁路危险品运输系统风险-事故分析方法[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2020, 16(9): 147-153.
|
|
ZHANG Yue, SHUAI Bin, YIN Dezhi, et al. Risk-accident analysis method of railway dangerous goods transportation system based on STAMP-ISM[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2020, 16(9): 147-153.
|
| [17] |
BATAGELJ V, MRVAR A. Pajek-program for large network analysis[J]. Connections, 1998, 21(2): 47-57.
|
| [18] |
陈文瑛, 杜艳洋, 张艺凡, 等. 基于复杂网络的地铁运营风险传导规律研究[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2017, 24(3): 170-174.
|
|
CHEN Wenying, DU Yanyang, ZHANG Yifan, et al. Research on metro risk conduction based on complex network theory[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2017, 24(3): 170-174.
|
| [19] |
PEARL J, BACCHUS F, SPIRTES P, et al. Probabilistic Reasoning in intelligent systems: networks of plausible inference[J]. Synthese, 1988, 104(1): 161-176.
|
| [20] |
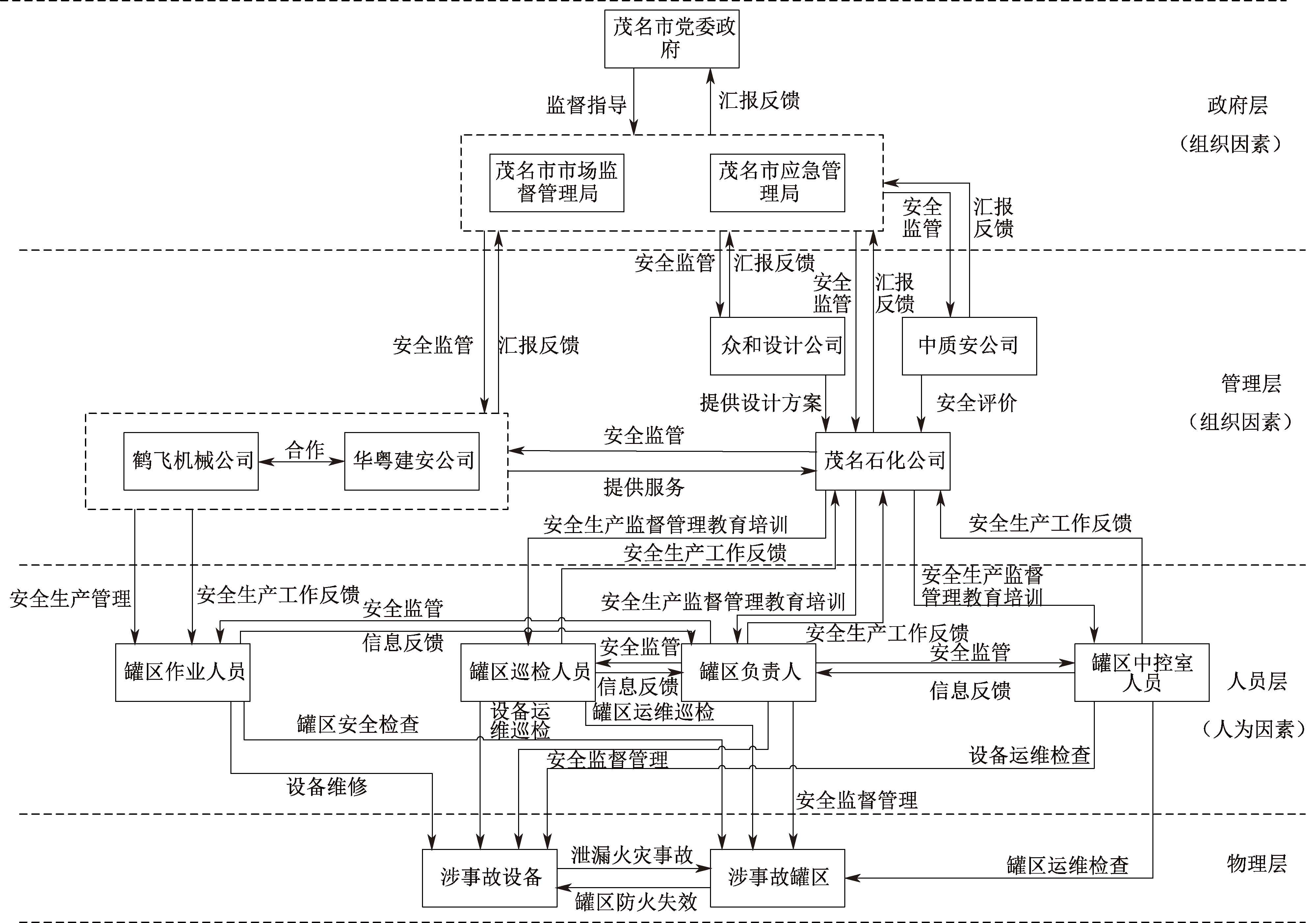
茂名石化“6·8”泄漏起火事故调查报告及处理结果公布[OL]. [2022-06-08]. http://yjgl.gd.gov.cn/.
|