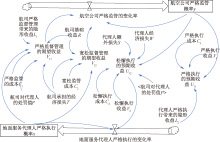
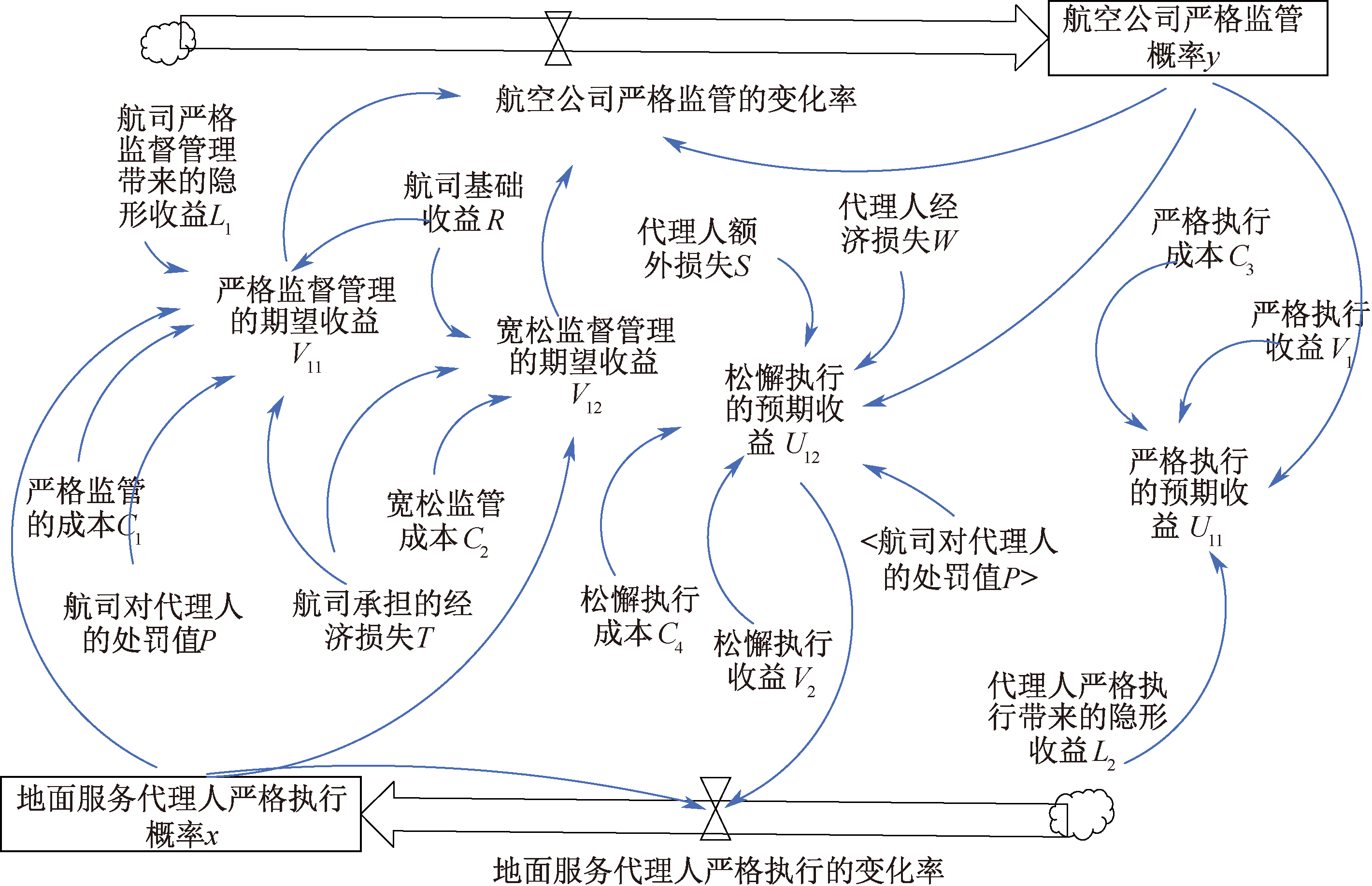
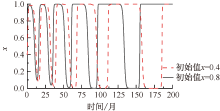
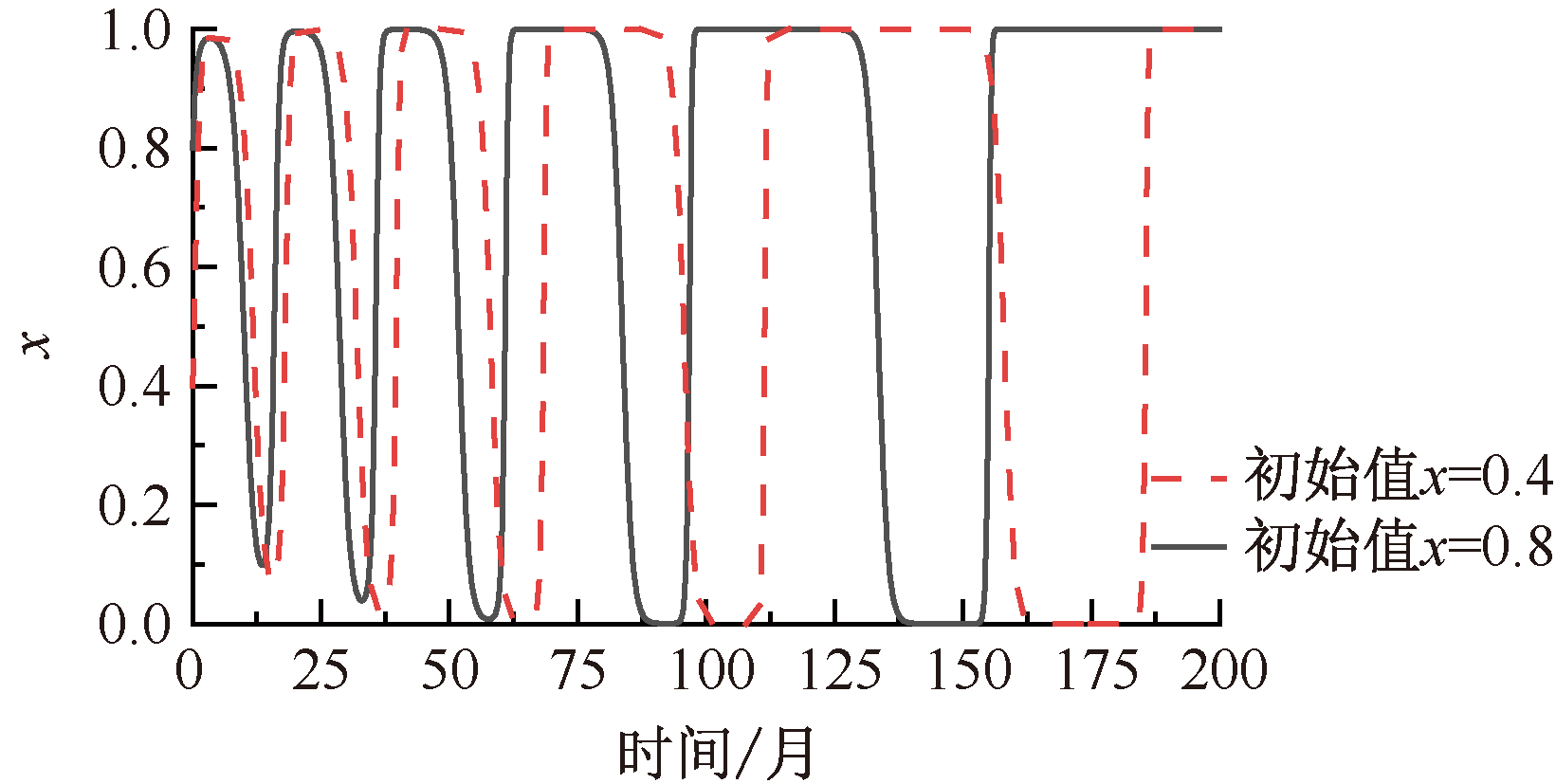
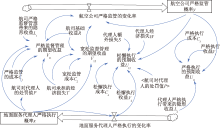
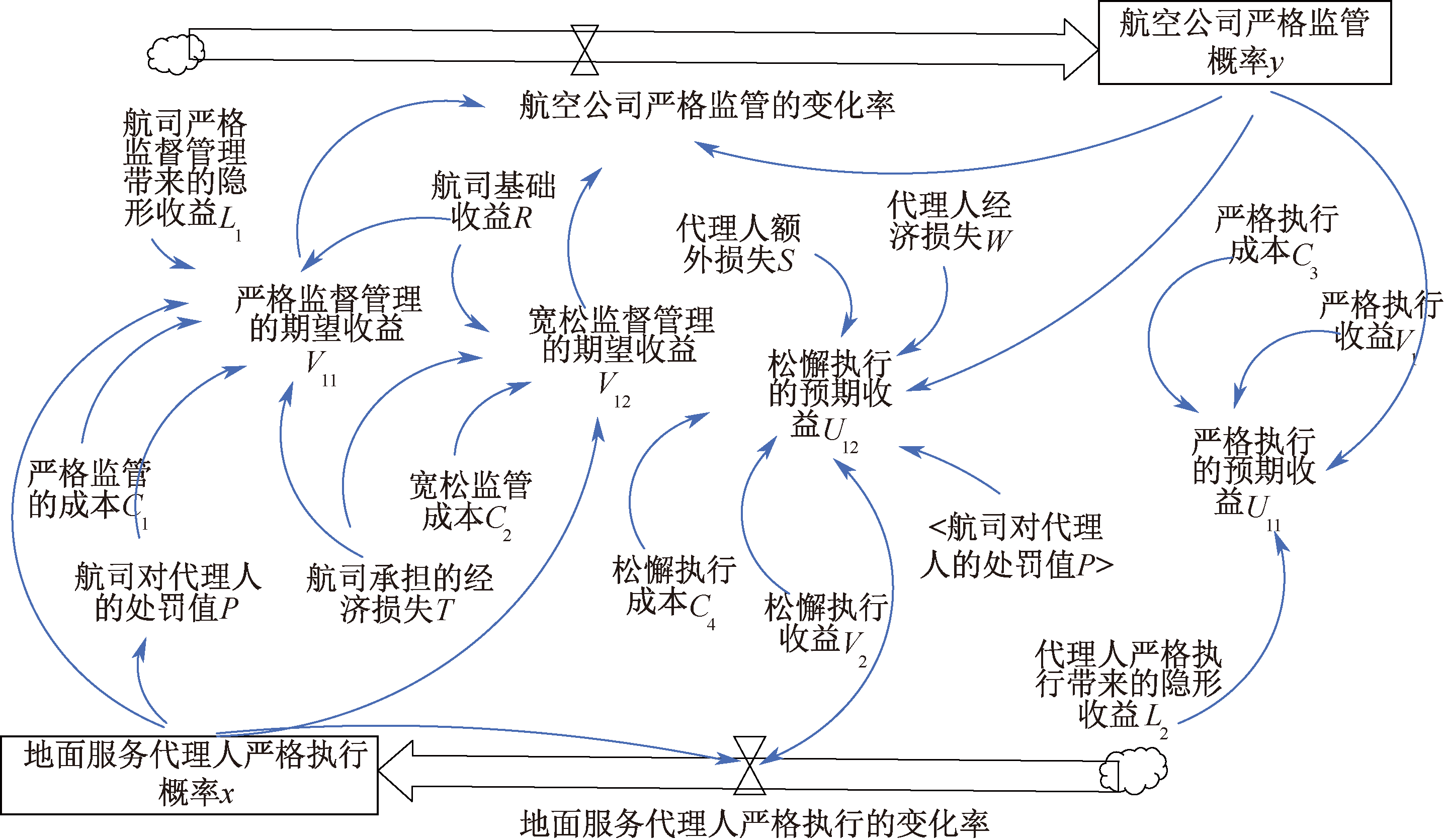
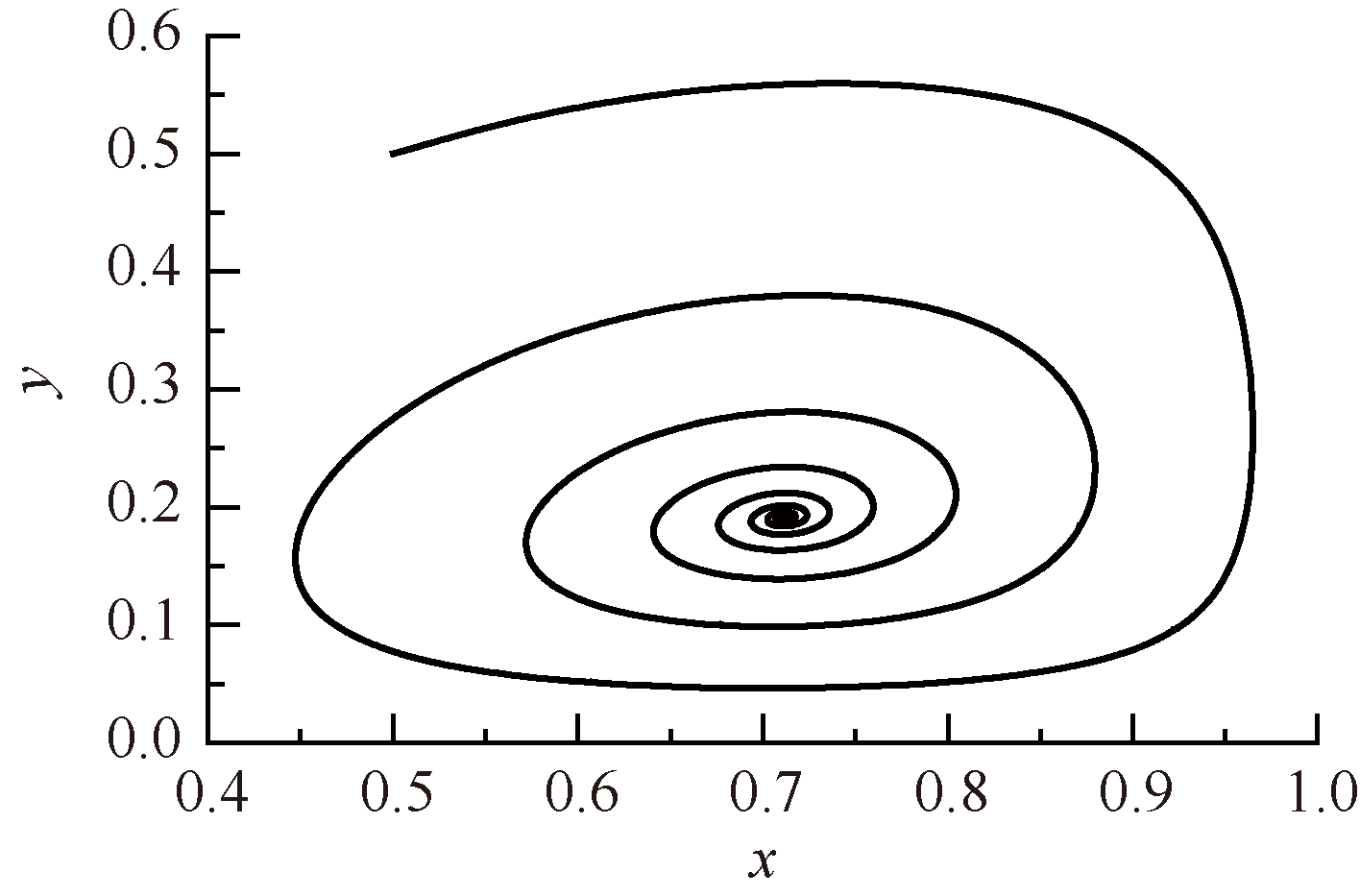
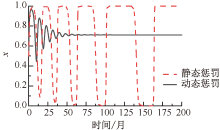
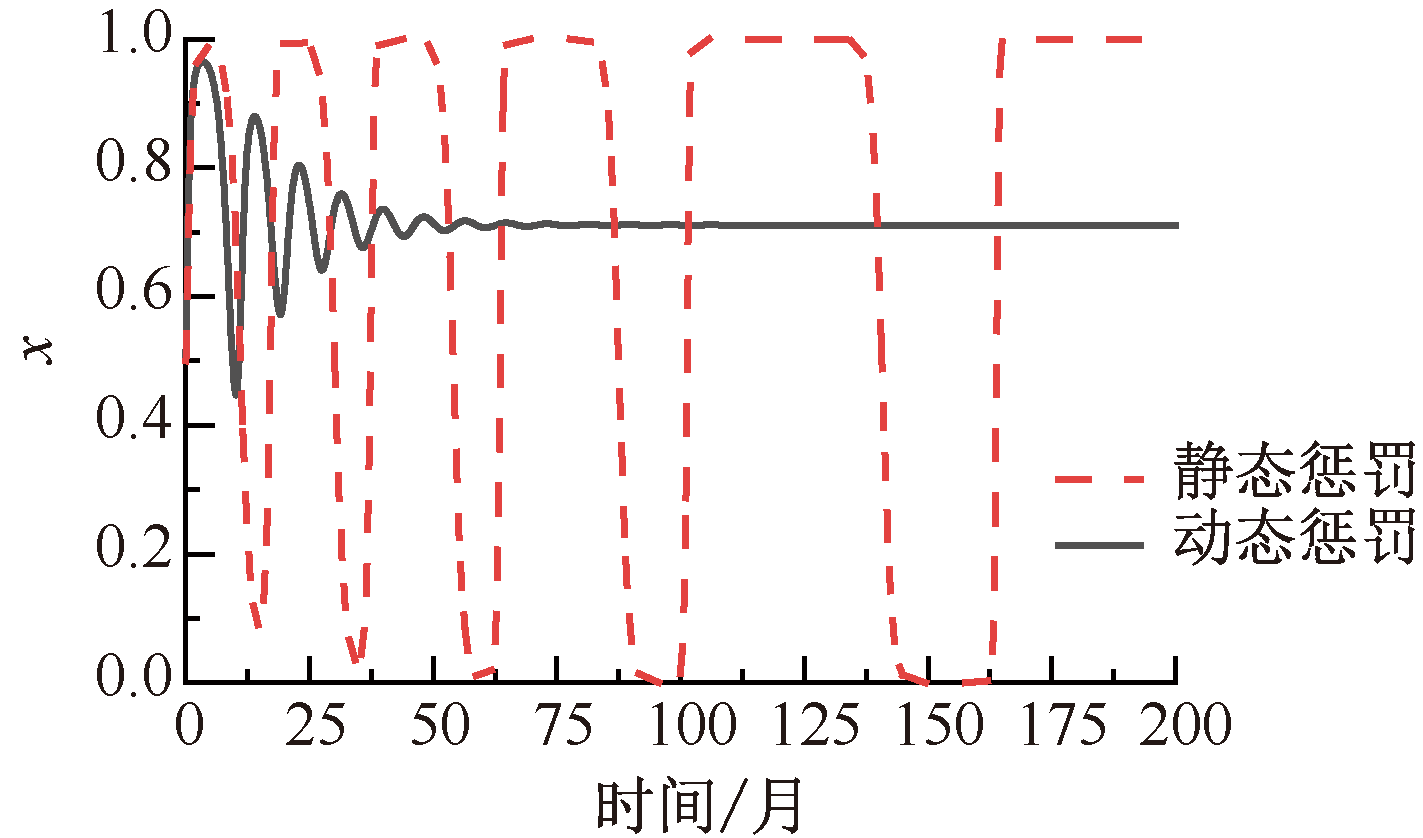
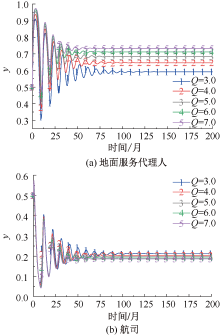
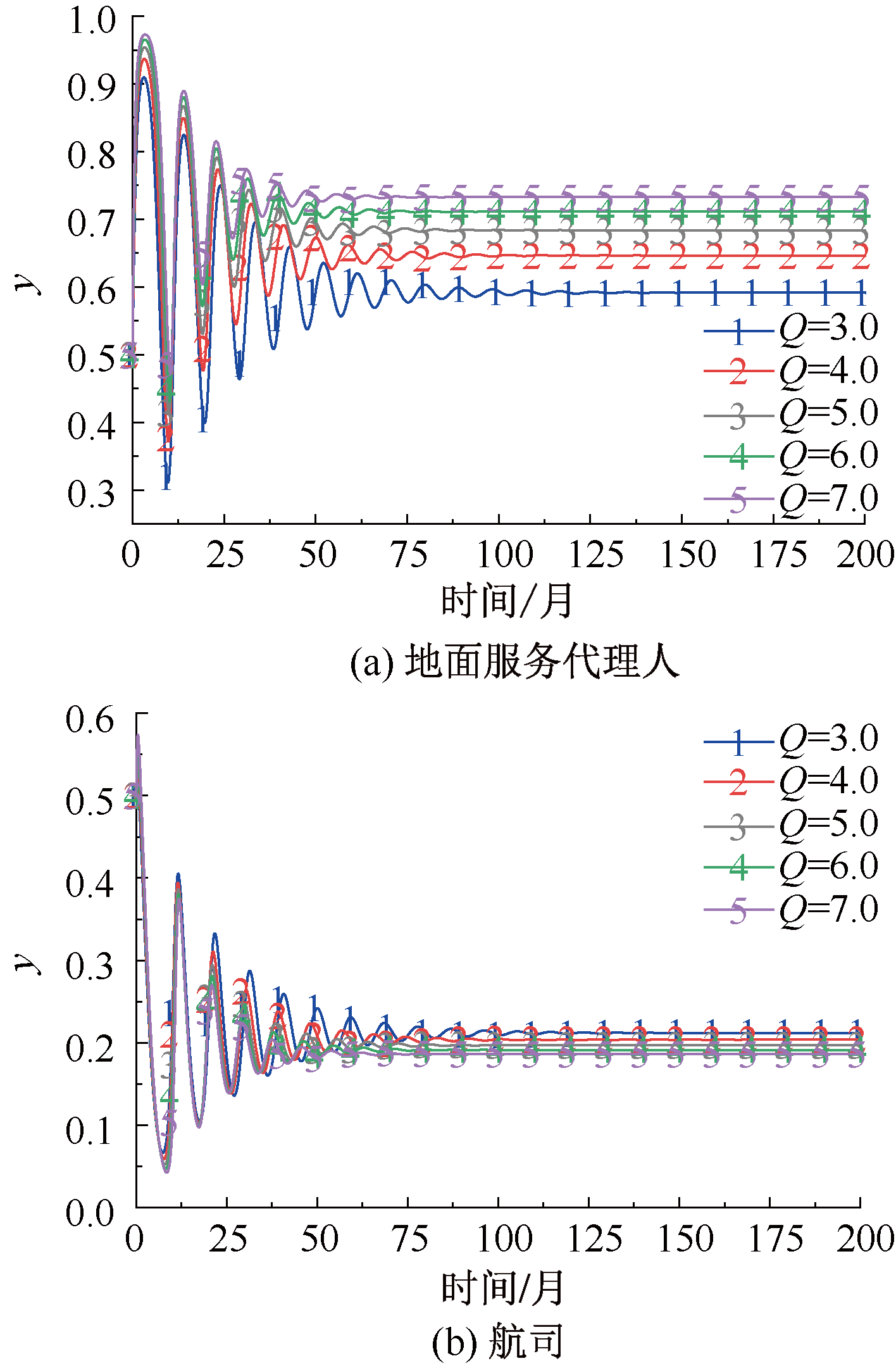
| [1] |
中华人民共和国交通运输部.民用航空危险品运输管理规定[Z].2024-07-01.
|
| [2] |
中国民用航空局.关于2016年危险品航空运输违规行为行政处罚情况的公告[Z].2017-05-17.
|
| [3] |
中国民用航空局.关于2017年危险品航空运输违规行为行政处罚情况的公告[Z].2018-05-09.
|
| [4] |
中国民用航空局.关于2018年危险品航空运输违规行为行政处罚情况的公告[Z].2019-04-30.
|
| [5] |
中国民用航空局.中国民用航空局关于2020年危险品航空运输违规行为行政处罚情况的公告[Z].2021-03-30.
|
| [6] |
杜珺, 何家力. 基于社会网络的危险品航空运输违规行为分析[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2018, 14(7): 73-78.
|
|
DU Jun, HE Jiali. Analysis of dangerous goods air transportation violations based on social network[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2018, 14(7): 73-78.
|
| [7] |
YUAN Liang, TAO Xiaorui, RAMSEY T S, et al. Simulating the principal-agent relationship between enterprise owners and professional managers using evolutionary game theory and system dynamics[J]. Complexity, 2021, 2021: 1-18.
|
| [8] |
宋猛, 刘伯恩. 全民所有自然资源资产所有权委托代理机制探析—基于监管风险管控与规避的视角[J]. 自然资源学报, 2023, 38(11): 2889-2898.
doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20231113
|
|
SONG Meng, LIU Bo'en. Exploring the proxy mechanism of ownership of nationally owned natural resource assets: a perspective based on regulatory risk control and avoidance[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2023, 38(11): 2889-2898.
doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20231113
|
| [9] |
崔琳, 周方伟. 信息搜集与激励视角下的金融监管模式[J]. 金融与经济, 2022(11):3-15.
|
|
CUI Lin, ZHOU Fangwei. A model of financial regulation under the perspective of information collection and incentives[J]. Finance and Economy, 2022(11):3-15.
|
| [10] |
朱庆华, 王一雷, 田一辉. 基于系统动力学的地方政府与制造企业碳减排演化博弈分析[J]. 运筹与管理, 2014, 23(3): 71-82.
|
|
ZHU Qinghua, WANG Yilei, TIAN Yihui. Game analysis of carbon emission reduction evolution between local governments and manufacturing enterprises based on system dynamics[J]. Operations Research and Management, 2014, 23(3): 71-82.
|
| [11] |
罗宏森, 王传生, 石夫磊. 基于系统动力学的动态惩罚机制下食品安全生产监管博弈[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2022, 22(5): 2660-2667.
|
|
LUO Hongsen, WANG Chuansheng, SHI Fulei. A system dynamics-based game of food safety production regulation under dynamic penalty mechanism[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2022, 22(5): 2660-2667.
|
| [12] |
韩震, 王菡, 孟好. 基于系统动力学的港口危险品管理演化博弈分析[J]. 大连海事大学学报, 2019, 45(2): 28-35.
|
|
HAN Zhen, WANG Han, MENG Hao. Evolutionary game analysis of port dangerous goods management based on system dynamics[J]. Journal of Dalian Maritime University, 2019, 45(2): 28-35.
|
| [13] |
GAO Honghu, CAO Guangmei, XING Daning. Evolutionary dynamics of the port hazardous chemical logistics enterprises' security behavior under dynamic punishment[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2019, 94(S1): 437-442.
|
| [14] |
FENG Fenling, LIU Chengguang, ZHANG Jiaqi. China's railway transportation safety regulation system based on evolutionary game theory and system dynamics[J]. Risk Analysis: An Official Publication of the Society for Risk Analysis, 2020, 40(10): 1944-1966.
|
| [15] |
王先甲, 全吉, 刘伟兵. 有限理性下的演化博弈与合作机制研究[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2011, 31(增1):82-93.
|
|
WANG Xianjia, QUAN Ji, LIU Weibing. Research on evolutionary games and cooperative mechanisms under limited rationality[J]. Systems Engineering Theory and Practice, 2011, 31(S1):82-93.
|
| [16] |
李利华, 王瑶, 邓亚军, 等. 碳税政策下绿色物流发展的三方演化博弈[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2023, 20(10):3715-3726.
|
|
LI Lihua, WANG Yao, DENG Yajun, et al. Three-party evolutionary game of green logistics development under carbon tax policy[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2023, 20(10):3715-3726.
|
| [17] |
张明, 武文琪, 黄孟, 等. 环保社会组织参与下的企业漂绿行为治理:演化博弈及仿真分析[J]. 环境经济研究, 2023, 8(4):121-140.
|
|
ZHANG Ming, WU Wenqi, HUANG Meng, et al. Governance of corporate greenwash behavior with the participation of environmental social organizations: evolutionary game and simulation analysis[J]. Environmental Economics Research, 2023, 8(4):121-140.
|
| [18] |
ALEXANDER J M K. Evolutionary game theory[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press,2023:17-21.
|