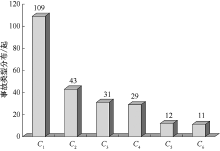
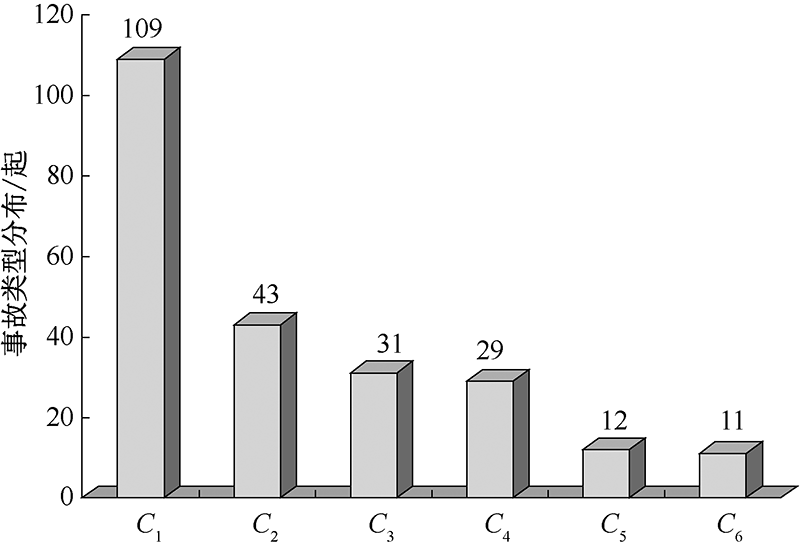
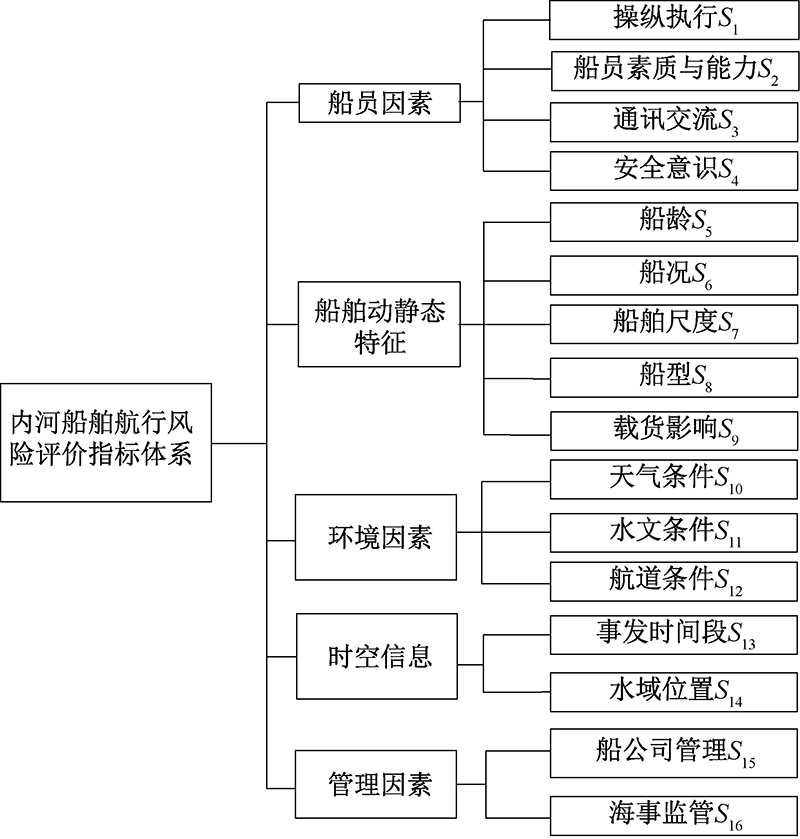
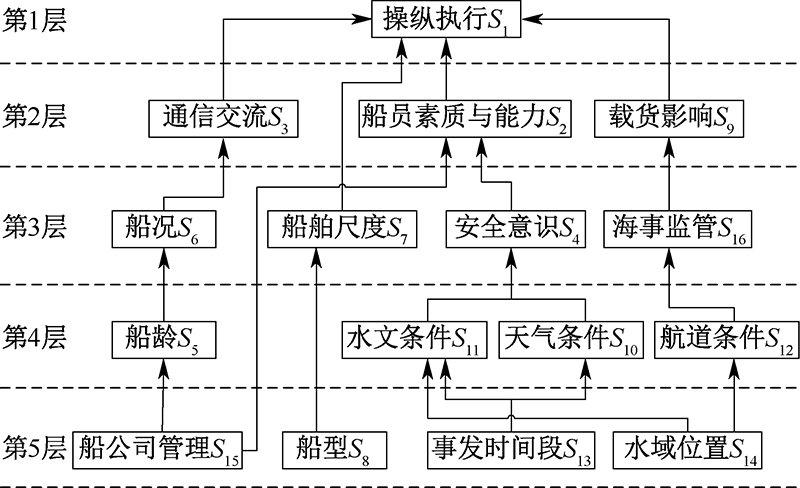
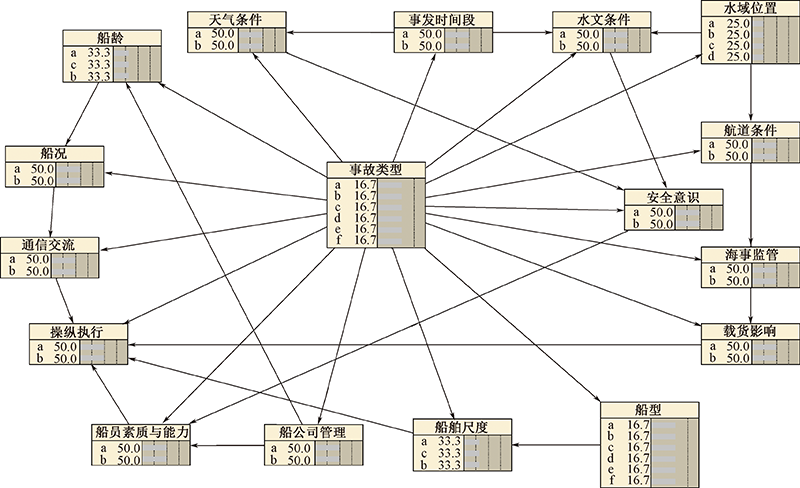
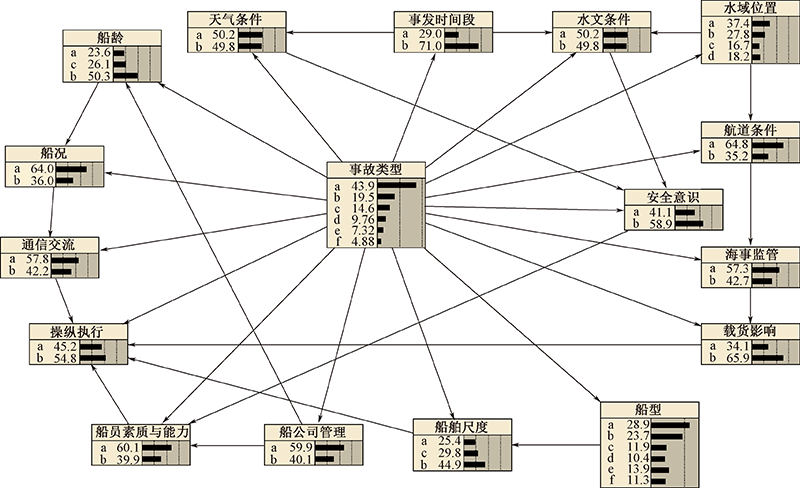
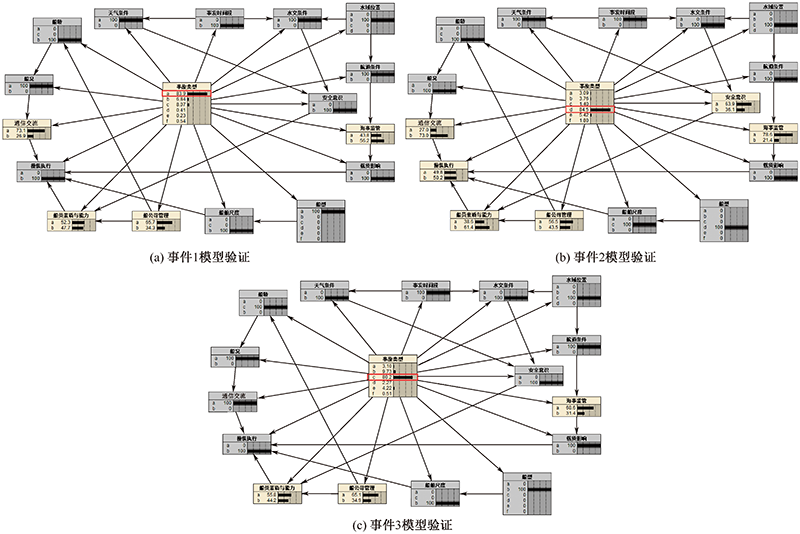
| [1] |
ZHANG Liye, WANG Hua, MENG Qiang, et al. Ship accident consequences and contributing factors analyses using ship accident investigation reports[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part O: Journal of Risk and Reliability, 2019, 233(1):35-47.
|
| [2] |
ROLF J, ASBJORN L. Maritime navigation accidents and risk indicators: an exploratory statistical analysis using AIS data and accident reports[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2018, 176:174-186.
doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2018.03.033
|
| [3] |
韩天园, 田顺, 吕凯光, 等. 基于文本挖掘的重特大交通事故成因网络分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(9):1-7.
|
|
HAN Tianyuan, TIAN Shun, LYU Kaiguang, et al. Network analysis on causes for serious traffic accidents based on text mining[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(9):150-156.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2021.09.021
|
| [4] |
吴伋, 江福才, 姚厚杰, 等. 基于文本挖掘的内河船舶碰撞事故致因因素分析与风险预测[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2018, 36(3):8-18.
|
|
WU Ji, JIANG Fucai, YAO Houjie, et al. An analysis and risk forecasting of inland ship collision based on text mining[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2018, 36(3):8-18.
|
| [5] |
李文杰, 张浩游, 张文, 等. 基于模糊贝叶斯网络的长江上游航道整治筑物技术状况评价研究[J]. 重庆交通大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 39(9):112-118.
|
|
LI Wenjie, ZHANG Haoyou, ZHANG Wen, et al. Technical status evaluation of regulation buildings in upper reaches of Yangtze River channel based on fuzzy Bayesian network[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University:Natural Science, 2020, 39(9):112-118.
|
| [6] |
ZHANG Di, YAN Xinping, YANG Zaili, et al. Incorporation of formal safety assessment and Bayesian network in navigational risk estimation of the Yangtze River[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2013, 118: 93-105.
doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2013.04.006
|
| [7] |
FAN Shiqi, EDUARDO B, YANG Zaili, et al. Incorporation of human factors into maritime accident analysis using a data-driven Bayesian network[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2020, 203: DOI: 10.1016/j.ress.2020.107070.
doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2020.107070
|
| [8] |
李壮, 付姗姗, 高郭平, 等. 海冰影响下船舶北极水域航行风险评估方法[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2020, 38(3):92-98.
|
|
LI Zhuang, FU Shanshan, GAO Guoping, et al. A risk assessment method of ship navigation in the arctic waters under influences of sea ice[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2020, 38(3):92-98.
|
| [9] |
司东森, 张英俊, 郎坤. 基于改进BN的集装箱船舶碰撞事故致因分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(10):31-37.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.10.006
|
|
SI Dongsen, ZHANG Yingjun, LANG Kun. Causation analysis of container ship collision accidents based on improved BN[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2019, 29(10):31-37.
doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2019.10.006
|
| [10] |
徐东星, 尹勇, 张秀凤, 等. 长江干线水上交通事故的灰色分析与预测[J]. 中国航海, 2019, 42(2):59-65.
|
|
XU Dongxing, YIN Yong, ZHANG Xiufeng, et al. Grey analysis and prediction of maritime traffic accidents on the trunk line of Yangze River[J]. Navigation of China, 2019, 42(2):59-65.
|
| [11] |
CENK S, BURAK K, ALI C et al. Analysing the effects of liquefaction on capsizing through integrating interpretive structural modelling (ISM) and fuzzy Bayesian networks (FBN)[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 215: DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107917.
doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107917
|